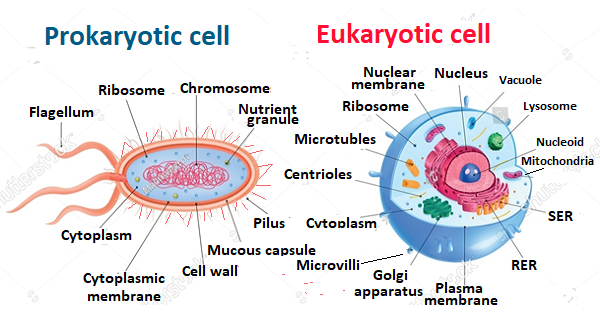
What is the difference between Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells?
The prokaryotic cell is the oldest cell on the way of evolution on the earth, prokaryotic cell is a unicellular cell, it is an undeveloped cell in which some of the cell organelles are absent. The eukaryotic cell is the advanced cell that is modified from the prokaryotic cell, the eukaryotic cell contains all the membrane-bound cell organelles, all the multicellular organisms are made of the eukaryotic cell, the example of prokaryotic cells are germs, blue-green algae, etc .the examples of eukaryotic cells are amoeba, paramecium, euglena, and multicellular organisms.
Table of content
- Prokaryotic Cell Vs Eukaryotic Cell
- The difference between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic Cell Vs Eukaryotic Cell
A prokaryotic Cell is an undeveloped cell that has no true nucleus and membrane-bound cell organelles. Prokaryote is derived from the Greek word ‘Pro’ (meaning: old) and ‘Karyone’ (meaning: nut), its meaning is before nuclei.The eukaryotic Cell is a developed cell that has a true nucleus and membrane-bound cell organelles. A eukaryote is derived from the Greek word ‘Eu’ (meaning: well defined) and ‘Karyone’ (meaning: nut), its meaning is a well-defined nucleus. Prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms, these are the most ancient group of living organisms on the earth which are explored by scientists by observing the many samples of fossils dating back to 3.5 billion years. Prokaryotic cells are simpler than the eukaryotic cell. A prokaryotic cell is smaller in size as compared to a eukaryotic cell. A prokaryotic cell has an absence of membrane-bound cell organelles like ER, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, etc. Unicellular organisms like germs,archae are made of prokaryotic cells while all protozoal organisms like amoeba, paramecium, euglena, etc, and multicellular organisms are made of the eukaryotic cell. The cell division in prokaryotic organisms takes place through binary fission while cell division in multicellular organisms takes place through the process of mitosis.
The difference between Prokaryotic CProkaryoticell and Eukaryotic Cell?
Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
| It has an undefined nucleus called a nucleoid | It has a defined nucleus |
| The nuclear membrane is absent | A nuclear membrane is present |
| It is always found in unicellular organisms | It is found in a unicellular and multicellular organism |
| Cell organelles are not bounded by the membrane | All cell organelles are bounded by the membranes |
| All of the reactions take place inside the cytosol | All of the reactions take place inside the cytoplasm and individually inside the cell organelles |
| It is smaller in size | It is larger than a prokaryotic cell |
| Mitochondria, Lysosome, and centrosome are absent | Mitochondria, Lysosome and centrosome are present |
| Endoplasmic reticulums are absent | Endoplasmic reticulums are present |
| Only cytosol is present | Cytoplasm is present |
| Cell division takes place through binary fission | In unicellular organisms like amoeba Cell division takes place through binary fission but in a multicellular organism, the cell division takes place through mitosis |
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
See the video
Class 9 Biology Important Notes
Function and structure of Mitochondria
Difference between Animal cell and Plant Cell
Difference between Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Class 9 Science Chapterwise NCERT Solutions and Important notes of Science
Structure and Function of Cell : Cell Biology
What are Chromosomes, DNA and Genes?
Types of plant tissues : Class 9 CBSE Notes
Animal Tissues : Class 9 Science CBSE
What is the green house effect?
Class 10 Important Biology Notes
Hormones System of our Body : Endocrine System
Male and Female Reproductive System: Complete Anatomy for Grade 10 Students
The structure and anatomy of the Heart
Human digestive system structure and function
What is the difference between the homologous and analogous structure of organs
Modes of reproduction used by single organisms-Asexual reproductions
Anatomy of the Human brain-Class 10 CBSE
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted.
Food chain and food web in an ecosystem
Class 9 Physics Important Notes
Average Speed and Average velocity
Momentum: Definitions,units,formula and Uses in real life:Class 9 CBSE
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
Archimedes Principle: Complete detail
CBSE IX Class Science Sample Papers
Class 9 Chemistry Important Notes
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat
How does the water kept in an earthen pot become cold during summer?
What are the factors affecting evaporation?,
What is the difference between solution,colloid and suspension?
What is the difference between element and the compound?
What is the difference between Atom and Molecule?
Determining Valency, Net Charge and Molecular Formula
Molar mass,molecular mass and mole concept
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?