Difference between Solution, Colloid, and Suspension
The solution is a homogeneous mixture in which two components solute and solvent are dissolved to each other completely for example water and salt. A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture that looks like a homogeneous mixture because of the moderate size of its particles as for example milk, its two components are the dispersed phase(cream) and dispersing medium(water), the dispersed phase and dispersing mediums are the counterparts of solute and solvent of the solution respectively. Suspension is an unstable heterogeneous mixture, the size of its particles is large enough to be seen by the naked eyes due to the gravity its particles settle down at the bottom immediately after its formation.
Point of content
- Features of a solution
- Features of a suspension
- Feature of a colloid
- Difference between Solution, Colloid and Suspension
- FAQ.s on Solution, Colloid, and Suspension
Features of a Solution
A solution is a true solution in which solute particles are completely dissolved in a solvent.
- The particle size of the solute in a solution is small to such an extent that can not be seen even with a powerful microscope.
- A solution is a homogenous mixture.
- The solution is stable and its solute particle do not settle down on keeping undisturbed.
- The particles of solute in a solution can not be separated by filter paper.
- The solution is transparent.
- The size of solute particles in a solution is less than 10-9 m
- The substance in smaller quantity dissolved in other substance is called the solute and other which is in larger quantity is called the solvent.
Features of a Suspension
Suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which solute particles remain suspended in the solvent.
- A suspension is unstable
- Particles of solute settle down keeping it undisturbed for some time.
- A suspension is opaque.
- The particle of solute of a suspension can not pass through the pores of the filter paper.
- The size of solute particles in a suspension is more than 10-6 m.
- Particles in a suspension can be seen by the naked eye or a simple microscope.
Features of a colloidal solution
A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture in which particle size is relatively bigger than the particle size of the solution. In the colloid dispersed phase(i.e solute) is moderately dissolved to the dispersing phase(i.e solvent).
- A colloid solution is a heterogeneous mixture.
- A colloid solution is stable and its particles do not settle down on keeping it undisturbed.
- A colloid solution is translucent (i.e it allows a portion of the light through it).
- Particles of a dispersed phase in a colloid solution can not be seen by the naked eyes but can be seen by a powerful microscope.
- The particles of a colloidal solution can not be separated by ordinary filter paper.
- The size of particles of dispersed phase lie between (1 to 100 nm) i.e 10-9 m to 10-7 m.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Difference between Solution, Colloid, and Suspension
| Solution | Colloid | Suspension |
| The solution is a homogenous mixture. | The colloid is a mixture that looks like a homogenous mixture but actually a heterogeneous mixture. | Suspension is a heterogeneous mixture. |
| The components of solutions are solute and solvent. | The components of Colloid are dispersing medium and dispersed phase. | The component of suspension are suspended particles and the liquid. |
| The size of the particles of the solution is the least. | The size of particles of colloid is moderate. | The size of particles of Suspension is the largest |
| Both of the components are dissolved in each other completely. | Both of the components are dissolved in each other moderately. | Both of the components are not dissolved in each other. |
| The size of the particles is less than 10-9 m | The size of the particles is 10-6 m – 10-9m | The size of the particles is more than 10-9m |
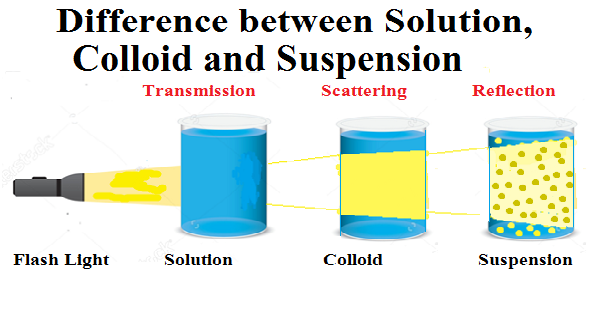
| The solution doesn’t show the Tyndal effect because its particles are very small therefore when a beam of light is allowed to pass through the solution, the light is transmitted through it without scattering and reflection of the light by its particles, therefore light can’t be seen through the solution. | The colloid shows the Tyndal effect because the size of its particles is more than that of the solution, due to which its particles scatter light resultantly a strip of light is seen through the colloid when a beam of light is allowed to pass through it. The colour of the light strip depends on the size of the particles. | Suspension shows the Tyndal effect, because of the excess size of its particles, its particles can be seen by the naked eyes, when a beam of light is allowed to pass through it. resultantly a strip of light is seen through the suspension due to the reflection of the light by its particles. |
NCERT Solutions and CBSE notes for classes 9,10,11 and 12 of Maths and Science
NCERT Solutions and CBSE notes for Class 9,10,11 and 12 of Maths and Science
Download:Direct and Indirect Narration rules Tenses wise and Sentences wise
You can also study
Active Voice to Passive Voice Rules
Learn Tenses in English and translate Hindi sentences into English language
Download PDF-Learn Tenses in English and translate Hindi sentences into the English language
Download: PDFActive Voice to Passive Voice rules,tenses wise and sentences wise
You can also study
Percentage questions for competitive entrance exams with Solutions
NCERT Questions on mensuration helpful for competive entrance exams
Tips to get success in competitive exams
The best books for cracking the competitive entrance exams of CPO,NDA, IAS, CDS and Bank PO
Government jobs after 10 or 12 th pass : Qualify Entrance exams of SSC MTS and SSC CHSL
Science Notes
What is the difference between virtual and real images?
Image formation by Convex and Concave Lenses
Image formation by Convex and Concave Mirrors
Difference between Convex and Concave lenses
What are the factors affecting evaporation?
How does the water kept in an earthen pot become cold during summer ?
Functioning of Soda-Acid Fire Extinguisher
Structure and Function of Cell : Cell Biology
Archimedes Principle: Complete detail
Average Speed and Average velocity
The universal law of gravitational force
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat
Important salts class 10 CBSE sceience notes
Reflection, Refraction, Dispersion, and Scattering
Determining Valency, Net Charge and Molecular Formula
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted.
Human Eye – Structure and functions
Myopia, Hypermetropia, and Presbyopia
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
Complete detail of electrical resistance and conductance
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board 2020-21
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Important maths notes
Tricks – How to write linear equations
Tricks- How to solve question from algebraic equations
Three ways of solving quadratic equation
Solutions- Specific questions of mensuration
Finding the roots of the polynomial by Complete square method
Technics – Achieving 100% marks in Maths
You can compensate us
Paytm number 9891436286
The money collected by us will be used for the education of poor students who leaves their study because of a lack of money.
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper and Question Papers for Term-1 and Term 2 2021-22 CBSE Board
Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper Term-1 2021-22 CBSE Board
Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 2 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22 with Solution
Solutions of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard Examination (First) 2021 -22 Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Sample paper of Science 2020
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution