NCERT Solutions of class 10 science chapter 5- Periodic Classification of Elements
The class 10 science NCERT solutions of chapter 5 periodic classification of elements presented to you for clearing your basic concept of chemistry. The importance of NCERT solutions of chapter 5 class 10 science is enabling you to analyze and understand the properties of elements and their compound since all the elements are arranged in periodic table systematically and orderly. The NCERT solutions of chapter 5 class 10 are not only beneficial for the academic exam but also useful for all kinds of entrance exams.
Chapter 5- The periodic classification of elements of class 10 Science is one of the chapters of the chemistry portion of the class 10 science textbook.Futurestudypoint.com is an internet coaching organization in India gives you Free PDF download of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 – Periodic Classification of elements, unraveled by Expert Teachers according to CBSE Board rules. Every question of back exercise and within the pages of ‘Periodic classification of elements’ are presented here with solutions to assist you with revising the total Syllabus and Score excellent marks. Register for our free online course class with the best science mentor in India. Download Future Study Point NCERT Book Solutions or study it in our published posts of each chapter.
NCERT Solutions of class 10 science chapter 5- Periodic Classification of Elements
You can also download the PDF-NCERT Solutions of class 10 science chapter 5- Periodic Classification of Elements
PDF-NCERT Solutions of class 10 science chapter 5
Page No: 81
Q1. Did Dobereiner’s triads also exist in the columns of Newlands’ Octaves? Compare and find out.
Ans. Yes, Dobereiner’s triads also exist in the columns of Newlands’ Octaves. One such column is Li, K, Na.
Q2. What were the limitations of Dobereiner’s classification?
Ans.Limitation of Dobereiner’s classification: All known elements could not be classified into groups of triads on the basis of their properties.
Q3. What were the limitations of Newlands’ Law of Octaves?
Ans.Limitations of Newlands’ law of octaves:
- It was not applicable throughout the arrangements. It was applicable up to calcium only. The properties of the elements listed after calcium showed no resemblance to the properties of the elements above them.
- Those elements that were discovered after Newlands’ octaves did not follow the law of octaves.
- The position of cobalt and nickel in the group of the elements (F, Cl) of different properties could not be explained.
- Placing of iron far away from cobalt and nickel, which have similar properties as iron, could also not be explained.
Page No: 85
Q1. Use Mendeleev’s Periodic Table to predict the formulae for the oxides of the following elements:
K, C, Al, Si, Ba.
Ans. K is in group 1. Therefore, the oxide will be K2O.
C is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be CO2.
Al is in group 3. Therefore, the oxide will be Al2O3.
Si is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be SiO2.
Ba is in group 2. Therefore, the oxide will be BaO.
Q2. Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendeleev in his Periodic Table? (any two)
Ans.Scandium and germanium.
Q3. What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table?
Ans. Mendeleev used atomic mass of the elements as the unique criteria of the elements. He proposed that the chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic masses. And thus, he arranged the elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses.
Q4. Why do you think the noble gases are placed in a separate group?
Ans. Noble gases are inert elements. Their properties are different from all other elements. Therefore, the noble gases are placed in a separate group.
Page No: 90
Q1. How could the Modern Periodic Table remove various anomalies of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table?
Ans. Various anomalies of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table removed as follows in the Modern Periodic Table:
- Elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number in the Modern Periodic Table, thus there was no need for keeping more than one element in one slot.
- In the Modern Periodic Table, there was no problem of the place of isotopes, as isotopes have the same atomic mass with different atomic numbers.
- Elements having the same valence electron are kept in same group.
- Elements having same number of shells were put under the same period.
- Position of hydrogen became clarified in as it is kept in the group with the elements of the same valence electrons.
Q2. Name two elements you would expect to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium. What is the basis for your choice?
Ans. Calcium (Ca) and strontium (Sr) are expected to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium (Mg). This is because the number of valence electrons (2) is same in all these three elements and since chemical properties are due to valence electrons, they show the same chemical reactions.
Q3. Name (a) three elements that have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(b) two elements that have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) three elements with filled outermost shells.
Ans.(a) Lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K) have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) Neon (Ne), argon (Ar), and xenon (Xe) have filled outermost shells.
Q4. (a) Lithium, sodium, potassium are all metals that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas. Is there any similarity in the atoms of these elements?
(b) Helium is an unreactive gas and neon is a gas of extremely low reactivity. What, if anything, do their atoms have in common?
Ans.(a) Yes. The atoms of all the three elements lithium, sodium, and potassium have one electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Both helium (He) and neon (Ne) have filled outermost shells. Helium has a duplet in its K shell, while neon has an octet in its L shell.
5. In the Modern Periodic Table, which are the metals among the first ten elements?
Ans. Among the first ten elements, lithium (Li) and beryllium (Be) are metals.
6. By considering their position in the Periodic Table, which one of the following elements would you expect to have maximum metallic characteristics?
Ans. Since Be, lies to the extreme left-hand side of the periodic table, Be is the most metallic among the given elements.
Page No: 91
Excercise
Q1. Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of periodic Table.
(a) The elements become less metallic in nature.
(b) The number of valence electrons increases.
(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily.
(d) The oxides become more acidic.
Ans.(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily.
Q2. Element X forms a chloride with the formula XCl2, which is solid with a high melting point. X would most likely be in the same group of the Periodic Table as
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) Al
(d) Si
Ans. (b) Mg
Q3. Which element has
(a) two shells, both of which are completely filled with electrons?
(b) the electronic configuration 2, 8, 2?
(c) a total of three shells, with four electrons in its valence shell?
(d) a total of two shells, with three electrons in its valence shell?
(e) twice as many electrons in its second shell as in its first shell?
Ans.
(a) Neon
(b) Magnesium
(c) Silicon
(d) Boron
(e) Carbon
Q4. (a) What property do all elements in the same column of the Periodic Table as boron have in common?
(b) What property do all elements in the same column of the Periodic Table as fluorine have in common?
Ans.
(a) Valency equal to 3.
(b) Valency equal to 1.
Q5. An atom has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7.
(a) What is the atomic number of this element?
(b) To which of the following elements would it be chemically similar? (Atomic numbers are given in parentheses.)
N(7) F(9) P(15) Ar(18)
Ans.
(a) The atomic number of this element is 17.
(b) It would be chemically similar to F(9) with configuration as 2, 7.
Page No: 92
Q6. The position of three elements A, B and C in the Periodic Table are shown below –

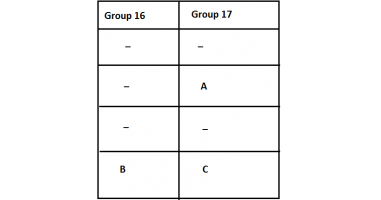
(a) State whether A is a metal or non-metal.
(b) State whether C is more reactive or less reactive than A.
(c) Will C be larger or smaller in size than B?
(d) Which type of ion, cation or anion, will be formed by element A?
Ans.
(a) A is a non-metal.
(b) C is less reactive than A, as reactivity decreases down the group in halogens.
(c) C will be smaller in size than B as moving across a period, the nuclear charge increases and therefore, electrons come closer to the nucleus.
(d) A will form an anion as it accepts an electron to complete its octet.
Q7. Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong to group 15 of the Periodic Table. Write the electronic configuration of these two elements. Which of these will be more electronegative? Why?
Ans.
Nitrogen (7): 2, 5
Phosphorus (15): 2, 8, 5
Since electronegativity decreases with moving from top to bottom in a group, thus Nitrogen will be more electronegative.
Q8. How does the electronic configuration of an atom relate to its position in the Modern Periodic Table?
Ans.
In the modern periodic table, atoms with similar electronic configurations are placed in the same column. In a group, the number of valence electrons remains the same.
Elements across a period show an increase in the number of valence electrons.
Q9. In the Modern Periodic Table, calcium (atomic number 20) is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 12, 19, 21, and 38. Which of these have physical and chemical properties resembling calcium?
Ans.
The element with atomic number 12 has same chemical properties as that of calcium. This is because both of them have the same number of valence electrons (2).
Q10. Compare and contrast the arrangement of elements in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table and the Modern Periodic Table.
Ans.
| Mendeleev’s Periodic Table | Modern Periodic Table |
| Elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic masses | Elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic number |
| There are 8 groups | There are 18 groups |
| Each group is divided in subgroups (a) and (b) | Groups are not divided in subgroups |
| Group for noble gas is not present as noble gases were not discovered by that time | A separate group is meant foe noble gases |
| There was no place for isotopes | Rectified as slots are determined according to the atomic number. |
You can compensate us
Paytm number 9891436286
The money collected by us will be used for the education of poor students who leaves their study because of a lack of money.
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution





