Solutions of Class 10 Science Question Paper for Term 1 Preboard Examination (First) 2021 -22 Class 10 Science
Solutions of Class 10 Science Question Paper for Term 1 Preboard Examination (First) 2021 -22 Class 10 Science are created by an experienced science teacher of CBSE board .All questions in the preboard science question paper for Term 1 are of MCQ’s types .The total questions in the preboard science question paper for Term 1 are 60,the students have to answer 50 questions. All questions in preboard science question paper for Term 1 carry equal marks i.e 0.80 marks for each question, There is no negative marking. The solutions of preboard science question paper 2021 is a practice question paper for Term-1 exam science paper.
Solutions of Class 10 Science Question Paper for Term 1 Preboard Examination (First) 2021 -22 Class 10 Science
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Q1. In the given chemical equation ‘A ’ stands for:
Zn + A → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu
A. H2SO4 B. HNO3 C. HCl D.CUSO4
Ans. D.CUSO4
Explanation: The reaction is a displacement reaction in which Zn being more reactive than Cu displaces copper in CuSO4 and forms ZnSO4
Q2.Identify the change in the colour of the lime water during this experiment.
A.transparent to milky (white) B. yellow to milky(white) C. bluish to milky(white) D.reddish to milky(white)
Ans.A.transparent to milky (white)
Explanation: Lime water is colourless or we can say transparent,when CO2 enters in it,it forms Calcium Carbonate which is milky(white) in colour and precipitated at the bottom of the container
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3↓(s) + H2O(l)
Q3. is only for Visually impaired Candidates
The chemical formula of lime water is
A. CaO B. CaCO3 C. Ca(OH) 2 D. CaCl2
Ans. C. Ca(OH) 2
Q4. Metal + Dilute acid → Salt + Hydrogen
The above chemical reaction not occur with
A. H2SO4 B. HCl C. HNO3 D. Both A and B
Ans. C. HNO3
Explanation: The reaction, Metal + Dilute acid → Salt + Hydrogen, doesn’t occur if dilute acid is HNO3 because HNO3 releases more oxygen ions in an aqueous state so it is a strong oxidising agent when HNO3 reacts with metal H2 gas released but instantly it is oxidized to H2O.
Q5. Which of the following correctly represents a balanced chemical equation?
A. Na + O2 → Na2O B.2Na + O2 → 2 Na2O C. 4Na + O2 → 2Na2O D.Na +2O2 →2Na2O
Ans. C. 4Na + O2 → 2Na2O
Explanation: In LHS and RHS,there are same number of Na and O atoms
Q6.pH of a compound A is indicated on pH scale. Which statement is not true about this compound.
A.it has more H+(aq) than OH-(aq) B.it is sour in taste C.it is basic in nature D.it is acidic in nature
Ans. C.it is basic in nature
Explanation: Compound A has pH value less than 7 indicated that it has more H+ions than OH- ions so it is acidic nature and we know every acid is sour in taste
Q7.pH of compound A indicated on a pH scale is 5. Which statement is not true about this compound.
A. it has more H +(aq) than OH -(aq) B. it is sour in taste C.it is basic in nature D.it is acidic in nature
Ans. A. it has more H +(aq) than OH –
Explanation: Since the pH value of the compound A is 5 which is less than 7,so it will have more H+ ion than OH-,so the compound A is acidic in nature
Q8. When 1 g copper powder is heated in a china dish,it becomes coated with black copper oxide beacause:
A.copper is reduced B.copper is oxidised C.copper is first reduced and then oxidised D.copper is first oxidised and then reduced
Ans.B.copper is oxidised.
Explanation: When copper is heated, copper oxide is formed which is black in colour
2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
Since there is a gain of oxygen atom when Cu is transformed into CuO,therefore Cu is oxidised
Q9.A reaction between magnesium (s) and copper sulphate solution is categorized as:
A.Combination reaction B.Decomposition reaction C.Double displacement reaction D.Displacement reaction
Ans. D.Displacement reaction
In the reaction between magnesium and copper supphate solution magnesium being more reactive displaces Cu in copper sulphate solution,so it is an example of displacement reaction
Mg + CuSO4 → MgSO4 + Cu
Q10.Neutral salts are formed by the reaction between a
A. weak acid and strong base B.weak base and strong acid C,strong acid and strong base D.both A and B
Ans.C, strong acid and strong base
If weak acid reacts with strong base then salts formed is alkaline in nature.If weak base reacts with strong acid then salts formed is acidic in nature and when strong acid reacts with strong base then salts formed is neutral in nature.
Q11. Turmeric paper indicator turns red in
A.Acidic medium B. Basic mmedium C. Both (A) and (B) D.Neutral medium
Ans.B. Basic medium
Turmeric is acidic in nature, so when it is added to acid reaction doesn’t take place and its colour remains yellow but when it is added to base its colour turns yellow to red because of a neutralization reaction.
Q12.Balanced chemical equation :
A.justifies the law of conservation of mass B.justifies the law of conservation of energy
C.have different mass of reactants and product D.both (A) and (C)
Ans..justifies the law of conservation of mass
According to the law of conservation mass, the mass of reactants is always equal to the mass of reactants during chemical reactions or in other words, no new atoms are formed during chemical reactions hence the number of atoms in reactants is equal to the number of atoms in products, therefore we are needed to balance chemical reactions in order to follow the conservation of mass.
Q13.Which are the products formed during aerobic respiration inside the cell:
A. CO2 +H2O +Energy B. CO2 +H2O C.H2O +Energy D.CO2 +Energy
Ans.A. CO2 +H2O +Energy
Aerobic respiration occures in presence of oxygen,in this reaction the molecule of glucose break down into CO2 ,water and energy is stored in the form of ATP
Q14.Where is nephron located in the given picture of excretory organ system?
A. i B. ii C. iii D. Both i and iii
Ans.C. iii
The kidney is shown by iii in the figure made of the special type of cells called nephrons,kidney is capable to filter all toxicity in the blood like extra urea through the nephrons.The extra urea is stored in the urinary bladder which is passed through the urethra as shown by i in the figure.
Question no 15 is only for Visually impaired Candidates
Q15. Where are nephrons located in human excretory organ system.
A.Kidney B. uretor C. urinary bladder D.both A and B
Ans. A.Kidney
Q16. Identify X,Y and Z in the following equation of photosynthesis.
A. X= water Y = chlorophyll Z = oxygen
B. X=chlorophyll Y = water Z = oxygen
C. X=water Y = oxygen Z = chlorophyll
B. X=water Y = nitrogen Z = chlorophyll
Ans.A. X= water Y = chlorophyll Z = oxygen
Photosynthesis occurs in presence of chlorophyll and sunlight,in this process carbon dioxide reacts with water and starch and oxygen molecules are formed,therefore Y is chlorophyll,X is water and Z is oxygen.
Q17.During breathing:
A. air is inhaled and carbon dioxide is exhaled.
B.oxygen is inhaled and oxygen is exhaled.
C.air rich in oxygen is inhaled and air rich in carbon dioxide is exhaled.
D.air rich in carbon dioxide is inhaled and air rich in oxygen is exhaled.
Ans.C.air rich in oxygen is inhaled and air rich in carbon dioxide is exhaled.
Explanation: The inhaled air by us contains the gases available in our atmosphere nitrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide and the gases nitrogen and carbon dioxide are exhaled by us, therefore air rich in oxygen is inhaled and air rich in carbon dioxide is exhaled.
Q18.Study the given diagram and select the option which gives correct identification and main function.
A. X = stomach produces bile
B. Y = small intestine absorbs digested nutrients
C. Z = liver store HCl
D. X =pancreas produces pancreatic juice
Ans.B. Y = small intestine absorbs digested nutrients
The complete digestion of the food and absorption takes place in small intenstine, for this intestinal wall contains a figure-like structure known as villi increase the surface area of the intestinal walls compatible for absorption of nutrients.
Q19 is only for Visually impaired Candidates
Q19.Select the correct organ and its main function in human digestive system.
A. liver – produces bile
B. small intestine – release enzyme that help in digestion of cellulose
C.stomach -produces pancreatic juice
D.pancreas – releases HCl
Ans.A. liver – produces bile
The function of the liver is to produce biles which emulsifies the fat available in the food takn by us.
Q20. Which fuction is not performed by bile juice during digestion.
A. emulsification of fat B. make the food alkaline
C. help in digestion of cellulose D. none of the above
Ans.C. help in digestion of cellulose
The function of bile juice is to break down larger fat globule into smaller globule so that pancreatic juice lipase act on it to digest fats completely, biles also make the food alkaline so that pancreatic juices act on it to break down the food completely.
Q21.Which of the following mirror is used for wider view in shopping mall ?
A. big plane mirror B.big convex mirror C.big concave mirror D. any spherical mirror
Ans. B.big convex mirror
Explanation: The convex mirror is a diverging mirror, the images formed by it are virtual , errected and small that’s we can see the wider view in shopping malls by using it.
Q22.Which is not a characteristic of the image formed by a concave mirror.
A. always erect B.usually inverted and of different size
C.real D. Both (A) and (C)
Ans.A. always erect
Explanation: A concave mirror usually shows real and inverted images of different sizes when the object is kept in different positions, the exceptional case is when the object is located between the focal point and pole in which the image is formed by it is virtual and erect.
Q23. Identify the type of mirror X and Y in the given figure.
A. X = converging mirror , Y = diverging mirror
B.X = diverging mirror , Y = converging mirror
C.X = plane mirror , Y = concave mirror
D.X = concave mirror Y = plane mirror
Ans.A. X = converging mirror , Y = diverging mirror
Explanation: In a concave mirror the reflecting surface is bent and the curved surface is polished, when the parallel light rays incidents on it, it converges them on the focal point located on the principal axis, it is that’s why the concave mirror is known as a converging mirror.
In a convex mirror, the reflecting surface is bulged and the bent surface is polished, when the parallel light rays incidents on it,it diverges them when these rays extend towards the backside of the mirror then they meet on a focal point located in the principal axis, it is that’s why the concave mirror is known as a diverging mirror.
Q24. The radius of curvature of a converging mirror is 20 cm. Its focal length will be
A. 20 cm B. -10 cm C. +10 cm D. -20 cm
Ans. B. -10 cm
Explanation: The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror or lens is twice the focal length of the mirror or lens, since the given mirror is a converging mirror(concave mirror),so the sign of the focal length must be negative according to sign convention.
-f = R /2= 20/2 ⇒f = -10 cm
Q25 is only for Visually impaired Candidates
Q25. What will be the focal length of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 30 cm?
A. 40 cm B. 15 cm C. 30 cm D. 20 cm
Ans.B. 15 cm
Explanation: Refer to Q24.
Q26.The phenomenon of twinkling of stars is observed due to:
A. atmospheric refraction B dispersion of light
C.scattering of light D. both (A) and (B)
Ans.A. atmospheric refraction
Explanation: The atmosphere of the Earth is made of different layers, when light ray from the star enter it , it refracts continuously through different layers of the earth atmosphere and reaches to our eye, since the earth atmosphere changes from time to time, so the position of the images of stars changes accordingly,it gives the twinkling effect of the stars.
Q27. Relationship between SI unit of power of a lens and SI unit of focal length is :
A. 1D = 1 m B. 1D = 1m²
C.1D = 1/m D. 1D = 1/m²
Ans.C.1D = 1/m
Explanation: The relationship between power(P) of a lens and its focal length(f) is
P = 1/f
Where power is measuered in dioptor(D) and focal length is measured in meter
When P = 1D,then 1D = 1/1m = 1/m
Q28.Power of a concave lense is
A.Positive B. negative
C.can be positive or negative D. never be negative
Ans.B. negative
Explanation: The relationship between focal length and power of a lens is
P(D) = 1/f(m)
Since the focal length of the concave lens is negative, therefore power is also negative.
Q29. In the given diagram the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism is shown correctly-
Ans. B
Q30 is only for Visually impaired Candidates
Q30.When beam of white light fall on one face of a prism, a spectrum is formed on the screen. In this spectrum which colour bends the most and which the least.
A. red and violet B.violet and red C. blue and red D. violet and yellow
Ans.D. violet and yellow
Explanation: When a light ray passes through the prism,it dispersed the light ray into seven colours, the pattern of the colour is seen below to upper VIBGYOR, which is an increasing order of the wavelengths. Violet colour has the least wavelength, so it bends or deviates the most while red colour has the largest wavelength, so it bends or deviates least.
SECTION B
Q31. Identify X and Y in the given equation.
A. X= sunlight,Y =Cl2 B. X = heat, Y = Cl
C. X= current D. X= water,Y= Na
Ans.A. X= sunlight,Y =Cl2
Explanation: Silver chloride decomposes into silver and chlorine gas in presence of sunlight,it is an example photodecomposition reaction
Q32.Some amount of HCl is added to the solution of MgO for which a given graph is drawn. As per the graph what will be the nature of the solution after adding 5 drops of HCl in it.
A. acidic B.basic C.neutral D. none of the above
Ans.C.neutral
Explanation: MgO is a basic oxide, when HCl is add to it,MgO neutralizes it
MgO + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O
Magnesium oxide and Hydrochloride forms salt (MgCl2) and water
Q33 is only for Visually impaired Candidates
Q33. When some amount of an acid and a base of some strength and quantity are mixed together, what will be the pH and nature of the resulting mixture.
A. 5; neutral B.6; basic C. 7; neutral D.acidic
Ans.C. 7; neutral
Explanation: The same strength of the base and acid neutralizes each other and the pH value of the resulting solution is 7.
Q34. Those metallic oxide which can dissolve in water are called:
A. alkali B. amphoteric oxide C. acidic oxide D.neutral oxide
AnsA. alkali
The metallic oxide which can dissolve in water are called alkali because these metallic oxide reacts with water and forms base,as an example
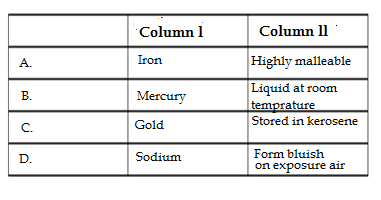
Q35.Which is correctly matched in column l with the items in column ll
Ans. B. Mercury : Liquid at room temperature
Q36. Chemical formula of bleaching powder is:
A. CaOCl2 B.CaCl2 C.Na2CO3.10H2O D.CaSO4.2H2O
Ans.A. CaOCl2
Explanation: Bleaching powder is formed when chlorine gas is passed through the dry slaked lime ,Ca(OH)2
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Q37. The best way to prevent tooth decay is to use toothpaste regularly,because it is:
A. Acidic in nature B.Basic in nature C.Neutral in nature D.Corrosive in nature
Ans. B.Basic in nature
Explanation: The food particles stucked between the teeth generates bacteria,these bacteria breakdown the food , in this reaction certain amount of acid is also released which causes small halls on the surface of tooth .Therefore we are required to brush our teeth by applying tooth paste because it is basic in nature that neutralizes the acid formed by the bacteria preventing the formation of the cavities on the tooth.
Question No.38 to 42 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R).Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true and R is false.
(D)A is false and R is true.
Q38. Assertion: Plaster of Paris is used by doctors for setting fractured bones.
Reason: When Plaster of Paris is mixed with water it sets into hard mass.
Ans.(A) Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A
Explanation: When gypsum is heated upto 120° and smashed into fined powder then this powder is known as plaster of paris,it is mostly found in Paris the capital of France
When plaster of paris is mixed with water it is again converted to Gypsum which is a hard mass.When doctor apply the plaster of paris after mixing it with water in the fractured area of the body,it changes into Gypsum,that supports the fractured bones and sets it into the place.
Q39.Assertion: The burning of a candle also shows the physical change.
Reason: In physical change new substance is formed.
Ans.(C) A is true and R is false.
Explanation: Burning of candle has two changes physical change because as per the time its size decreases and it melts (solid to liquid) and chemical change occurs because of the formation of CO2 and H2O.
Q40.Assertion: Xylem and phloem are the vascular tissue in the plant.
Reason: Xylem and phloem do not help in transportation of water,minerals and food in the plant.
Ans.(C) A is true and R is false.
Explanation: Xylem and phloem are called vascular tissue because these tissues are responsible for the transportation of food , water and minerals. Xylem tissues transports water and minerals from root to the leaves and after photosynthesys the resulting food is transported by the phloem tissues to all other parts of the plants.
Q41. Assertion: The sun appears white at noon.
Reason: Only a little of the blue and violet colour of light is scattered.
Ans.(C) A is true and R is false.
Explanation: The sun appears white at noon because all types of colours scattered equally because at that time sun is nearest to us,therefore all the colours reaches to our eyes which resulted sun appears white at noon.
Q42.Assertion: When zinc is added to iron sulphate solution no change observed.
Reason: Zinc is more reactive than iron.
Ans.Zinc is more reactive than Fe in reactivity series,so when zinc is added to FeSO4 solution,Zn displaces Fe and forms ZnSO4.FeSo4 is of light green colour , when Zn is added the colour of solutions turns colourless due to the formation of ZnSO4.
Q43.Which part of the blood helps in clottig of blood ?
A.Plasma B.RBC’s C.Platelets D.WBC’s
Ans.C.Platelets
Fibrozen is a type of protein in the plasma which is converted into threadlike protein fibrin on contact with sticky surface caused by the injured blood vessel.Fibrin trap platelets to form blood clot which known as blood coagulation or clotting of the blood.
Q44……..helps in translocation of food in plants.
A. Xylem B.Phloem C.Mesophyll cells D.Root hairs
Ans. B.Phloem
Explanation: After the process of photosynthesis the food is distributed to all parts of plants from the leaves of the plant body above the leaves and bellow the leaves.The food is transported from one phloem cell to another phloem cell by the process of osmosis,the process of transfering food from one part of plant to another part is known as translocation of food.
Q45.Which is the correct order option among i,ii and iii in the given diagra of human heart ?
(i) Aorta-supply oxygenated blood to body
(ii) left ventricle – have oxygennated blood
(iii) left atrium -collect dxyeogenated blood from body
A. i and ii B. ii and iii C.i and iii D. i,ii and iii
Ans. i and ii
Explanation: The oxygenated blood in the heart is recieved by left atrium through pulmonary veins when left atrium contracts, this oxygenated blood enters dilated left ventricle and then left ventricle conntracts and blood is supplied to all body parts through aorta. On the same time dioxygenated blood recieved by right atrium from all body parts through upper vena cava and lower vena cava,when right atrium is dilated,when it contracts then right ventricle dilates and receives dioxygenated blood ,when right ventricle dilates ,the dioxygenated blood send to lungs through the pulmonary altery.
Q46. is only for Visually impaired Candidates
Q46. Between i,ii and iii pair of parts of human heart and its functions are correctly matched.
i. Aorta – supply oxygenated blood to body
ii. left ventricle -have oxygenated blood
iii.left atrium – collect deoxygenated blood from body
A. i and ii B. ii and iii C. i and iii D. i,ii and iii
A. i and ii
Refer to the explanation for Q45
Q47.When light passes from denser to rare medium then,which of the following statement is true-
A. angle i > angle r B. angle i < angle r C.angle i = angle r D. refraction will not takes place
Ans.B. angle i < angle r
Explanation: When light passes from denser medium to rare medium,light ray bent away from the normal,so the angle of refraction is > angle of incident.
Q48.An object is placed at 20 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm,the image of the obeject is formed at
A. at C B. between C and F C. behind the mirror D. P and F.
Ans. The position of the object, u = -20 cm, focal length,f = -10 cm, the position of image,v = ?
Applying the mirror formula
1/f = 1/v +1/u
1/(-10) = 1/v +1/(-20)
-1/10 + 1/20 = 1/v
(-2 +1)/20 = 1/v
-1/20 = 1/v
v = -20
The image is located at the distance 20 cm in front of the mirror =2×10 = 2f,means at C ,the centre of curvature of the mirror
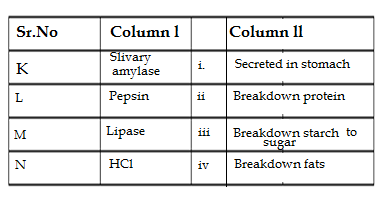
Q49. Match the words of column l with that of column ll
A. K = i,L = ii,M=iii, N= iv B. K = iv,L = iii,M=ii, N= i
C. K = iii,L = ii,M=i, N= iv D. K = iii,L = ii,M=iv, N= i
Ans. D. K = iii,L = ii,M=iv, N= i
Explanation: Slivary amylase is secreted by slivary gland located at the root of the tongue and initiates the digestion of food inside the mouth by converting the carbohydrate(starch) into sugar.In the stomach pepsin is secreted which help to digest protein partially,HCl is also secreted by the stomach which helps to maintain pH value of stomach and in killing the bacteria.When partially digested food from the stomach reaches to intenstine ,lipase secreted by the pancreas breakdown the fats .
Q50. During respiration,Yeast converts glucose into:
A.ethenol B. lactic acid C.carbon dioxide D.both (A) and (C)
Ans. A.ethenol
Explanation: In the Yeast anaerobic respiration takes place ,in this condition alcohol is produced as a waste product as the carbon dioxide is produced in aerobic respiration.
Q51. If the angle between incident ray and reflected ray is 60°. Then the angle of incidence is:
A. 60° B. 30° C.15° D. 90°
Ans. Since ∠i = ∠r
We are given that the angle between incident ray and reflected ray = 60°
∠i + ∠r = 60°
∠i + ∠i = 60°
2∠i = 60°
∠i = 30°
Q52. While looking at the diagram ,a student concluded the following:
(i) the image of the object will be a virtual one
(ii) the reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in opposite direction.
(iii) the image of the object will be inverted.
(iv) this is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative.
Which of the above statements is /are correct :
A. (i) and (ii) B. (i) and (iii) C. (ii),(iii) and (iv) D. (i),(ii) and (iv)
You can compensate us by donating any amount of money for our survival
Our Paytm No 9891436286
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions of class 9 maths
| Chapter 1- Number System | Chapter 9-Areas of parallelogram and triangles |
| Chapter 2-Polynomial | Chapter 10-Circles |
| Chapter 3- Coordinate Geometry | Chapter 11-Construction |
| Chapter 4- Linear equations in two variables | Chapter 12-Heron’s Formula |
| Chapter 5- Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry | Chapter 13-Surface Areas and Volumes |
| Chapter 6-Lines and Angles | Chapter 14-Statistics |
| Chapter 7-Triangles | Chapter 15-Probability |
| Chapter 8- Quadrilateral |
NCERT Solutions of class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions of class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT solutions of class 10 science
Solutions of class 10 last years Science question papers
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Latest sample paper of science
NCERT solutions of class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions of class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |