Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions of Chapter 13 exercise 13.1
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of chapter 13-Surace areas and volumes are presented here for helping the class 10 students in their preparation of maths paper in forthcoming assessments and CBSE board exam 2020-21. The NCERTquestions of the chapter 13-Surface areas and volume will help the students of 10 class in complete comprehension of the areas and volumes of three-dimensional figures like 3D shapes, cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, spheres and three-dimensional composite shapes made of at least two or more than two figures.All questions of the chapter 13 exercise 13.1 are solved by a specialist of maths subject according to the CBSE standards. The NCERT solutions published here by Future Study Point will benifit all categories of students in light of the fact that each question is explained by step by step strategy so every students could comprehend the concept unmistakably with no assistance of teacher or tutor.
You can also study
Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions of Chapter 13 exercise 13.1
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Q1. 2 cubes each of volume 64 cm3 are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboid.
Ans.
The volume of cubes = Side³ = 64
Side = 4 cm
Length of resulting cuboid = 4 + 4 = 8 cm
Breadth of cuboid = 4 cm
Height of resulting cuboid = 4 cm
Surface area of resulting cuboid = 2 ( lb + bh + hl)
l = 8 cm, b = 4 cm, h = 4 cm
Surface area of resulting cuboid = 2 ( 8 ×4 + 4×4 + 4×8) = 2(32 + 16 + 32) = 2× 80 = 160
Hence the required surface area of resulting cuboid = 160 cm²
Q2. A vessel is in the form of a hollow hemisphere mounted by a hollow cylinder. The diameter of the hemisphere is 14 cm and the total height of the vessel is 13 cm. Find the inner surface area of the vessel.
Solution:
Ans.Height of vessel is=13cm
Diameter of hemisphere = 14 cm, radius of hemishere = 14/2 = 7 cm
Height of cylinder = 13 – 7 = 6 cm
The inner surface area of the vessel = CSA of hemisphere + CSA of cylinder
CSA of hemisphere = 2πr²
The curved surface area of the hemisphere is = 308 cm²
CSA of cylinder = 2πrh
The curved surface area of cylinder = 264 cm²
Hence surface area of the vessel = 308 + 264 = 572 cm²
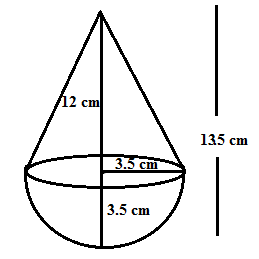
Q3.A toy is in the form of a cone of radius 3.5 cm mounted on a hemisphere of the same radius. The total height of the toy is 15.5 cm. Find the total surface area of the toy.
Ans.
Height of cone = 13.5 – 3.5= 12 cm, radius of hemishere = 3.5 cm
The total surface area of the toy = CSA of hemisphere + CSA of cone
CSA of hemisphere = 2πr²
CSA of cone = πrl, where l is slant height
CSA of cone
The total surface area of the toy = 77 + 137.5 = 214.5
Hence the total surface area of the toy is 214.5 sq.cm
Q4.A cubical block of side 7 cm is surmounted by a hemisphere. What is the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have? Find the surface area of the solid.
Ans. The greatest diameter of the hemisphere surmounted on a cube will be side of cube i.e 7 cm
The surface area of so formed solid = Total surface area of cube + curved surface area of the hemisphere – area of the base of the hemisphere
Total surface area of cube = 6×side² = 6 × 7 × 7 = 294
The total surface area of cube = 294 sq.cm
The curved surface area of hemisphere = 2πr²
Area of base (i.e circle) = πr²
Surface area of given solid = 294 + 77 – 38.5 = 332.5 sq.cm
Hence the surface area of the solid is 332.5 sq.cm
Q5.A hemispherical depression is cut out from one face of a cubical wooden block such that the diameter d of the hemisphere is equal to the edge of the cube. Determine the surface area of the remaining solid.
Solution:
Ans. Let the side of the cubical wooden block is = a unit
Diameter d of the hemisphere = a unit
The radius of hemisphere depression = a/2
The remaining surface area of the solid = Total surface area of cube + curved surface area of the hemisphere – area of the base of the hemisphere
The total surface area of cube = 6a²
The curved surface area of the hemisphere = 2πr²
Area of the circular base of hemisphere =πr²
The remaining surface area of the solid
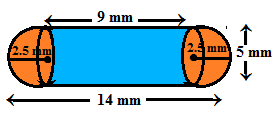
Q6.A medicine capsule is in the shape of a cylinder with two hemispheres stuck to each of its ends. The length of the entire capsule is 14 mm and the diameter of the capsule is 5 mm. Find its surface area.
Ans. The length of the capsule = 14 mm, length of the cylindrical portion of capsule = Length of the capsule – 2×2.5 = 14 – 5 = 9 mm
The surface area of the capsule = CSA of the cylindrical portion of the capsule + CSA of two hemispheres
CSA of the cylindrical portion of the capsule = 2πrh
CSA of two hemispheres = 2× 2πr² = 4πr²
r = 2.5 mm
CSA of two hemispheres
The surface area of the capsule
The surface area of the capsule is =220 mm²
Q7.A tent is in the shape of a cylinder surmounted by a conical top. If the height and diameter of the cylindrical part are 2.1 m and 4 m respectively, and the slant height of the top is 2.8 m, find the area of the canvas used for making the tent. Also, find the cost of the canvas of the tent at the rate of Rs 500 per m2. (Note that the base of the tent will not be covered with canvas.)
Ans.
Area of the canvas used for making the tent = Curved surface area of the cylindrical part of tent + Curved surface area of the conical part of the tent
The curved surface area of the cylindrical part of tent = 2πrh
Radius r of the cylindrical shape = 4/2 = 2 m
Height h of the cylindrical part = 2.1 m
The curved surface area of the cylindrical part of the tent
The curved surface area of cylindrical shape = 26.4 m²
The curved surface area of the conical part of the tent = πrl
Radius r of the conical shape = 4/2 = 2 m
Slant height l of the conical part = 2.8 m
The curved surface area of the conical part of the tent
The curved surface area of conical shape = 17.6 m²
Area of the canvas used for making the tent = 26.4 + 17.6 = 44 m²
The rate of canvas = Rs 500 per m²
∴The cost of the canvas = 500 × 44 = Rs 22000
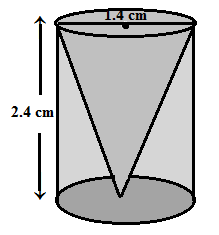
Q8.From a solid cylinder whose height is 2.4 cm and diameter 1.4 cm, a conical cavity of the same height and same diameter is hollowed out. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest cm2.
Ans. Height of the given cylinder = 2.4 cm
The diameter of the given cylinder = 1.4 cm
Radius of the given cylinder = 1.4/2 = 0.7 cm
The height of the hollowed-out conical cavity = 2.4 cm
The remaining surface area of the cylinder = Curved surface area of cylinder + area of the circular base of cylinder + Curved surface area of the conical cavity
= 2πrh + πr² + πrl
= πr( 2h + r + l)
Therefore the remaining surface area of the cylinder = 17.6 ≈ 18 cm²
Q9.A wooden article was made by scooping out a hemisphere from each end of a solid cylinder, as shown in the figure. If the height of the cylinder is 10 cm, and its base is of radius 3.5 cm, find the total surface area of the article.
Ans.
The total surface area of the article = Curved surface area of the cylinder + Curved surface area of scooped out hemispheres
The radius of cylinder and hemispheres = 3.5 cm
Height of the cylinder = 10 cm
The curved surface area of the cylinder = 2πrh
The curved surface area of scooped out hemispheres = 2× 2πr² = 4πr²
The total surface area of the article = 220 + 154 = 374 cm²
You can compensate us by donating any amount of money for our survival
Our Paytm NO 9891436286
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions of class 9 maths
| Chapter 1- Number System | Chapter 9-Areas of parallelogram and triangles |
| Chapter 2-Polynomial | Chapter 10-Circles |
| Chapter 3- Coordinate Geometry | Chapter 11-Construction |
| Chapter 4- Linear equations in two variables | Chapter 12-Heron’s Formula |
| Chapter 5- Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry | Chapter 13-Surface Areas and Volumes |
| Chapter 6-Lines and Angles | Chapter 14-Statistics |
| Chapter 7-Triangles | Chapter 15-Probability |
| Chapter 8- Quadrilateral |
CBSE Maths Class IX solutions of important questions of last years question papers
CBSE Class 9 maths assignment for SA-1
CBSE class 9 Notes on Lines, angles, and triangles
Addition, subtraction, and division of polynomials
Solutions of maths specific questions of mensuration
NCERT Solutions of class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions of class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT solutions of class 10 science
Solutions of class 10 last years Science question papers
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Latest sample paper of science
NCERT solutions of class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions of class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |