Class 10 Maths MCQ’S with Answers -Coordinate Geometry for CBSE Board 2021 Term 1

Class 10 Maths MCQ’S with Answers -Coordinate Geometry for CBSE Board 2021 Term 1 are created here in view of helping the students in the preparation of the Term-1 CBSE Board exam 2021 ,in which questions are based on MCQ’s .MCQ’s are going to be asked are simple but students has to do 40 questions in 90 minutes so students are required to practice the additional MCQ-based questions within time slots. Here we have created and collected a few MCQs with their solutions to boost the preparations of the exam Term-1 CBSE Board 2021 for class 10 students.
Class 10 Maths Sample Paper (Basic) with Solutions for Term 1 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22
Class 10 Maths Trigonometry MCQ’s With Solutions for Term-1 CBSE Board Exam 2021
Class 10 MCQ’s questions with solutions-Polynomial
Class 10 Maths Sample Paper(Standard) for 2021 CBSE Board Exam -Term 1 with Solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
Class 10 Maths MCQ’S with Answers -Coordinate Geometry for CBSE Board 2021 Term 1
Q1. The distance of the point (-3,5) from the x -axis
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 1 (d) 5
Ans. (d) 5
The given point is (-3,5)
First number,3 in the point (-3,5) is known as abscissa i.e distance from y-axis and second number, 5 is ordinate i.e distance from x -axis
Q2. The points (2,1), (-3,2),(k,4) are collinear if the value of k is
Ans. Area of triangle formed by joining the given points must be zero because points given to us are collinear
Area of triangle =1/2[x1(y2-y3) +x2(y3-y1) + x3(y1-y2) ]
x1=2,y1=1,x2=-3,y2=2,y3=4,x3=k,
1/2[x1(y2-y3) +x2(y3-y1) + x3(y1-y2) ] = 0
x1(y2-y3) +x2(y3-y1) + x3(y1-y2) = 0
2(2-4) -3(4-1) + k(1-2) = 0
2×-2 -3×3 + k×-1 =0
-4 -9 -k =0
-13 -k = 0
k = -13
Q3. The distance of the point (α, β) from the origin is
(a) α + β (b) α² + β² (c) √(α² +β²)
Ans. The coordinates of origin are (0,0)
The distance between (0,0) and (α, β) = √[(α -0)²+(β -0)²] =√(α²+β²)
Q4.The area of the triangle whose vertices are P(1,2), Q(-2,3) and R(-3,-4) is
(a) 22 (b) 33 (c) 41 (d) 11
Ans.(d) 11
Area of triangle =1/2[x1(y2-y3) +x2(y3-y1) + x3(y1-y2) ]
x1=1,y1=2,x2=-2,y2=3,y3=-4,x3=-3
Area of triangle =1/2[1(3+4) -2(-4-2) -3(2-3) ]
= 1/2(1×7 -2×-6-3×-1) = 1/2(7 +12 +3) = 1/2(22) = 11 sq.unit
Q5. The distance between the points (p +q,p-q) and (p-q,-p-q) is
Ans. The distance(d) between two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is
d = √[(x2-x1)²+ (y2-y1)²] = √[(p-q-p-q)²+ (-p-q-p+q)²] =√[(-2q)² +(-2p)²] =√(4q² +4p²) =2√(p²+q²)
Q6.If (k/4,5) is the mid point of the line segment joining the points (-3,10) and (-9,6),then value of k is
Ans. The mid point of the line segment joining the points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is given as
[(x1+x2)/2,(y1+y2)/2] = [(-3-9)/2,(10+6)/2] = (-12/2, 16/2) = (-6,8)
Q7.The points (1,1),(-2,7) and (3,-3) are
(a) collinear (b) vertices of equilateral triangle (c) vertices of isoscles triangle (d) None of these
Ans.(a) collinear
The given points are (1,1),(-2,7) and (3,-3)
Area of triangle formed by joining the given points must be zero because points given to us are collinear
Area of triangle =1/2[x1(y2-y3) +x2(y3-y1) + x3(y1-y2) ]
x1=1,y1=1,x2=-2,y2=7,y3=-3,x3=3
1/2[x1(y2-y3) +x2(y3-y1) + x3(y1-y2) ] = 0
1(7+3) -2(-3-1) + 3(1-7) = 0
10 – 2×-4 + 3×-6 = 10 + 8 – 18 = 18 -18 =0
Therefore the given points are collinear
Q8.The coordinates of centroid of the triangle whose vertices are (0,6),(8,12) and (8,0) is
(a) (4,6) (b) (16,6) (c) (8,6) (d) (16/3,6)
Ans.(d) (16/3,6)
The coordinates of the centroid of a triangle with vertices (x1,y1),(x2,y2),(x3,y3) are given as
[(x1+x2+x3)/3,(y1+y2+y3)/3]
Therefore centroid of the triangle with vertices (0,6),(8,12) and (8,0) is
[(0+8+8)/3, (6 + 12 + 0)/3] = (16/3,18/3) = (16/3,6)
Q9. Two vertices of the triangle are (3,-5) and (-7,4).If its centroid is (2,-1),then the third vertex is
(a)(10,2) (b) (-10,2) (c) (10,-2) (d) (-10,-2)
Ans.(c) (10,-2)
Let the third vertex of the triangle is (x,y)
The coordinates of the centroid of a triangle with vertices (x1,y1),(x2,y2),(x3,y3) are given as
[(x1+x2+x3)/3,(y1+y2+y3)/3]
(3 -7 +x)/3,(-5 +4 +y)/3 = (2,-1)
(-4 +x)/3 = 2 and (-1+y)/3 = -1
-4 + x = 6 and -1 + y = -3
x = 6 + 4=10 and y = -3 +1 = -2
Therefore third vertex of the given triangle is (10,-2)
Q10.If the points A(1,2),B(0,0) and C (a,b) are collinear then
(a) a = -b (b) 2a = b (c) a = 2b (d) a = b
Ans.(b) 2a = b
The given points are A(1,2),B(0,0) and C(a,b)
Area of triangle formed by joining the given points must be zero because points given to us are collinear
Area of triangle =1/2[x1(y2-y3) +x2(y3-y1) + x3(y1-y2) ]
x1=1,y1=2,x2=0,y2=0,y3=b,x3=a
1/2[1(0-b) +0(b-2) + a(2-0) ] = 0
-b +2a = 0
b = 2a
Q11.If the distance between the points (2,-2) and (-1,x) is 5,one of the value of x is
(a) -2 (b) 2 (c) -1 (d) 1
Ans. (b) 2
The given points are (2,-2) and (-1,x) and distance(d) between them is 5
The distance(d) between two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is
d = √[(x2-x1)²+ (y2-y1)²]
x1=2,y1=-2,x2=-1,y2=x
√[(-1-2)²+ (x+2)²] = 5
Squaring both sides
(-3)²+ (x+2)²=25
9 + x² +4 +4x = 25
x²+4x + 13 -25 =0
x²+4x -12 = 0
x² +6x -2x -12 =0
x(x +6) -2(x +6) =0
(x +6) (x -2) =0
x = -6 and x = 2
Hence one of the zeros is 2
Subscribe our U tube channel
Q12. ABCD is a rectangle whose three vertices are A(0,3), B(0,0) and C(5,0), the length of its diagonal is
(a) 5 (b) 3 (c) √34 (d) 4
Ans. (c) √34
Vertices of the rectangle given to us are A(0,3), B(0,0) and C(5,0)
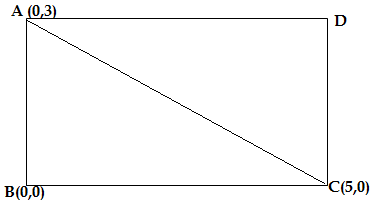
The length of the diagonal AC is evaluated by applying the distance formula
The distance(d) between two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is
d = √[(x2-x1)²+ (y2-y1)²]
x1=0,y1=3,x2=5,y2=0
d = √[(5-0)²+ (0-3)²] =√[5² +(-3)²] =√(25 +9) =√34
Q13.A circle drawn with origin as a centre passes through the point (13/2,0), the point which doesn’t lie in the interior of the circle is
(a) (-3/4,1) (b) (2,7/3) (c) (5,-1/2) (d) (-6,5/2)
Ans. (d) (-6,5/2)
Centre of the circle is the origin (0,0) and passes through the point (13/2,0)
The distance between (0,0) and (13/2,0) i.e (6.5,0) is the radius of the circle
r = √[(6.5-0)²+(0-0)²]=√6.5² = 6.5 unit
The distance between (-3/4,1) and (0,0) < 6.5
The distance between (2,7/3) and (0,0) <6.5
The distance between (5,-1/2) and (0,0) <6.5
The distance between (-6,5/2) and (0,0) > 6.5
Therefore (-6,5/2) lies in the exterior of the given circle
Q14.The point which divides the line segment joining the points (7,-6) and (3,4) in the ratio 1 : 2 internally lies in the
(a) I quadrant (b) II quadrant (c) III quadrant (d) IV quadrant
Ans.(d) IV quadrant
The given points are (7,-6) and (3,4)
Let the point is (x,y) which divides the line segment joining the given points in the ratio of 1 : 2
If a line segment joining the given points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is divided by a point (x,y) internally in the ratio of m : n then coordinates (x,y) are determined by the section formula as following
x = (mx2+nx1)/(m+n) and y = (my2+ny1)/(m+n)
x1=7,y1=-6,x2=3,y2=4, m =1 and n = 2
x = (1×3+2×7)/(1+2) and y = (1×4+2×-6)/(1+2)
x = (3+14)/3 and y = (4 -12)/3
x = 17/3 and y = -8/3
The required point is (17/3,-8/3) which lies in (iv) quadrant
Q15.One of the two points of trisection of the line segment joining the points A(7,-2) and B(1,-5) which divides the line segment in the ratio 1 : 2 are
(a) (5,-3) (b) (5,3) (c) (-5,-3) (d) (13,0)
Ans.(a) (5,-3)
The end points of the line segment AB given to us are A(7,-2) and B(1,-5), let it is trisected by the points C and D

The point C(x,y) divides the line segment AB into the ratio of 1 : 2
Applying the section formula
x = (mx2+nx1)/(m+n) and y = (my2+ny1)/(m+n)
x1=7,y1=-2,x2=1,y2=-5, m =1 and n = 2
x = (1×1+2×7)/(1+2) and y = (1×-5+2×-2)/(1+2)
x = (1+14)/3 and y = (-5 -4)/3
x = 15/3 and y = -9/3
x = 5 and y = -3
Q16.A line intersects y axis and x axis at the point P and Q,respectively .If (2,-5) is the mid point of PQ ,then coordinates of P and Q are,respectively
(a) (0,-5) and (2,0) (b) (0,10) and (-4,0) (c) (0,4) and (-10,0) (d) (0,-10) and (4,0)
Ans.(d) (0,-10) and (4,0)
Let the line intersects x axis and y axis at P(x,0) and Q(0,y) respectively
The mid point of the line segment joining the points P(x,0) and Q(o,y) given to us is (2,-5)
[(x+0)/2, (0+ y)2] = [2, -5]
(x/2, y/2) = (2.-5)
x/2 = 2 and y/2 = -5
x =4 and y = -10
The coordinates of P(x,0) =(4,0) and the coordinates of Q(0,y) =(0,-10)
Hence coordinates of P and Q are (4,0) ,(0,-10) respectively
Q17.The ratio in which the point Q(3/4,5/12) divides the line segment joining the points A(1/2,3/2) and B(2,-5) is
(a) 1 : 5 (b) 5 : 1 (c) 3 : 1 (d) 1 : 3
Ans.(a) 1 : 5
Let the given point Q(3/4,5/12) divides the line segment joining the points A(1/2,3/2) and B(2,-5) into m : n
Applying the section formula
x = (mx2+nx1)/(m+n) and y = (my2+ny1)/(m+n)
x1=1/2,y1=3/2,x2=2,y2=-5, x =3/4 and y = 5/12
3/4 = (m×2+n×1/2)/(m+n) and 5/12 = (m×-5+n×3/2)/(m+n)
3m + 3n = 8m +2n and 5m +5n = -60m +18n
-5m = -n and 65m = 13n
m/n =1/5 and m/n = 13/65 = 1/5
Q18.The coordinates of a point P,where PQ is the diameter of a circle whose centre is (2,-3) and Q is (1,4) is
(a) (3,-10) (b) (-3,10) (c) (2,-10) (d) (-2,10)
Ans.(a) (3,-10)
Let the coordinates of the point P of the given diameter PQ are (x,y)
Coordinates of Q given to us are (1,4)
The given centre of the circle is (2,-3) is the mid point of the diameter PQ
The mid point of the line segment joining the points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is given as
[(x1+x2)/2,(y1+y2)/2]
(x + 1)/2, (y + 4)/2 = (2,-3)
(x + 1)/2 = 2 and (y + 4)/2 = -3
x + 1 = 4 and y + 4 = -6
x = 3 and y = -10
Q19.The area of rhombus if its vertices are (3,0),(4,5),(-1,4) and (-2,-1) taken in order is
(a) 12 sq.unit (b) 24 sq.unit (c) 30 sq.unit (d) 32 sq.unit
Ans.(b) 24 sq.unit
The given vertices of the rhombus are (3,0),(4,5),(-1,4) and (-2,-1)

Area of the rhombus = (Product of the diagonals )/2
The length of the diagonal AD is = √[(3+1)²+(0-4)²] =√[4²+(-4)²] =√(16 +16) =4√2 unit
The length of the diagonal BC is = √[(4+2)²+(5+1)²] =√[6²+6²] =√(36 +36) =6√2 unit
Area of the rhombus = (4√2 ×6√2)/2 = 24 sq.unit
Q20.If the points A(6,1),B(8,2),C(9,4) and D(p,3) are the vertices of a parallelogram,taken in order,then the value of p is
(a) 4 (b) -6 (c) 7 (d) -2
Ans. (c) 7
The given vertices of the parallelogram are A(6,1),B(8,2),C(9,4) and D(p,3)

Since diagonal of the parallelogram bisects each other, therefore centre O is the mid point of BD as well as of AC
The mid point of the line segment joining the points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is given as
[(x1+x2)/2,(y1+y2)/2]
(6+9)/2,(4+1)/2 =(p+ 8)/2,(3+2)/2
15/2, 5/2 = (p+8)/2, 5/2
(p + 8)/2 = 15/2
p+ 8 = 15
p = 15 -8 = 7
The importance of the MCQ questions and their solutions
The incoming CBSE board exam term-1 is totally based on MCQ’s, therefore a proper understanding of the chapter is needed to every student.The questions in the exams would be simple but the time boundation is also there, you have to do 40 MCQ’s in just 90 minutes. Therefore the practice of solving MCQ questions in the time slots is required for every student for achieving excellent marks.
You can compensate us by donating any amount of money for our survival
Our Paytm No 9891436286
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions of class 9 maths
| Chapter 1- Number System | Chapter 9-Areas of parallelogram and triangles |
| Chapter 2-Polynomial | Chapter 10-Circles |
| Chapter 3- Coordinate Geometry | Chapter 11-Construction |
| Chapter 4- Linear equations in two variables | Chapter 12-Heron’s Formula |
| Chapter 5- Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry | Chapter 13-Surface Areas and Volumes |
| Chapter 6-Lines and Angles | Chapter 14-Statistics |
| Chapter 7-Triangles | Chapter 15-Probability |
| Chapter 8- Quadrilateral |
NCERT Solutions of class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions of class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT solutions of class 10 science
Solutions of class 10 last years Science question papers
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Latest sample paper of science
NCERT solutions of class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions of class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |



