Solutions of Class 10 Maths Practice Paper for Current CBSE Board Exam

Solutions of Class 10 Maths Practice Paper for Current CBSE Board Exam for the students is presented here for rectifying the maths skill of students so that they could contribute their talent to the Nation’s interest. The practice maths paper of class 10 launched by the Directorate of Education NCT (National Capital Territory of Delhi) is the initiation of the Delhi government to boost the talent of the students. Maths is a subject that can contribute to increasing your aggregate percentage in the exam, therefore students have required a little more attention in maths because little negligence in practising maths may lead to a decrease in your aggregate percentage. Every student should study its marking scheme, NCERT solutions, solutions of the latest CBSE sample paper, and solutions of last year’s question papers.
Solutions of Class 10 Maths Practice Paper for Current CBSE Board Exam
Max Marks: 40 Duration: 2 hours
General Instruction:
1. The question paper consists of 14 questions divided into 3 sections A,B, and C.
2. Section A has total 6 questions of 2 marks each.
3. Section B has total 4 questions of 3 marks each.
4. Section C has total 4 questions of 3 marks each.
5. There is no overall choice. However internal choices are provided in 2 questions of 2 marks,1-1 questions of 3 marks and 4 marks each. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all such questions.
6. There is no negative marking.
7. Use of calculators is not permitted.
Solutions of Class 10 Maths Practice Paper for Current CBSE Board Exam
Section-A
Q1.The curved surface area of a cylinder is 264 m² and its volume is 924 m³.Find the ratio of its height to its diameter.
Ans. The curved surface area of the cylinder is 264 m²
The curved surface area of the cylinder = 2πrh = 2r (πh) =dπh(d is diameter and h is the height of the cylinder)
dπh = 264……(i)
The volume of the cylinder is 924 m³
The volume of the cylinder =πr²h =π(d/2)²h =πd²h /4
πd²h /4 = 924….(ii)
Dividing equation (ii) by equation (ii)
d/4 = 924/264 =3.5
d =4×3.5 = 14 cm
Putting this value of d in equation (i)
14×22h/7 = 264
h = (264×7)/(14×22) =1848/308=6 cm
Hence the ratio of its height to its diameter =6/14 =3/7
The ratio of its height to its diameter is 3 : 7
OR
A 20 m deep well with a radius 7 m is dug and the earth from digging is evenly spread out to form a platform 22 m× 14 m. Find the height of the platform.
Ans. Let the height of the platform is H
The volume of the platform = (22 × 14 ×H)m³
The depth of well,h = 20 m
The radius of the well,r = 7 m
The earth is taken out from the well = Volume of the well = Volume of the platform
The volume of the well = πr²h (where r is the radius of the well and h is the depth of the well)
The earth is taken out from the well = πr²h =(π ×7×7×20)m³
22 × 14 ×H = π ×7×7×20=(22/7)×7×7×20 =(22×7×20) =3080
H = (3080/(22×14) =3080/308 = 10 m
Q2.Find the value of k for which the equation x² + k(2x +k-1) +2 = 0 has no real roots.
Ans. If the quadratic equation ax² +bx +c = 0 has equal roots then we should have
b² -4ac <0
Rearranging the quadratic equation into the standard form
x² + 2kx +k²-k +2 < 0
a =1,b =2k and c=k²-k +2
(2k)² -4×1(k²-k +2) <0
4k² -4k² +4k-8 <0
4k -8 <0
4k <8
k < 2
Hence for all the values of k <2 ,the roots of the given equation have no real roots
Q3.In the figure, PQ and RS are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB with the point of contact C intersecting PQ at A and RS at B . Prove that AB =AD +BE.

GIVEN: PQ and RS tangents to the circles with centre O such that PQ ∥ RS
AB is another tangent with the point of contact C intersecting PQ at A and RS at B
TO PROVE:AB =AD +BE
PROOF: AC = AD……(i)[tangents drawn to the circle from an external point are equal]
BC = BE……(ii)[tangents drawn to the circle from an external point are equal]
Adding both equations (i) and (ii)
AC + BC=AD + BE
AB=AD + BE ,Hence proved
Q4. In the given figure, find the value of l.

Ans.sin 60° = 5/l [since sin θ = perpendicular/hypotenuse]
We know sin 60° =√3/2
∴ 5/l =√3/2
l = 10/√3
Rationalizing the denominator
l = (10×√3)/(√3×√3) = 10√3/3 m
Q5.Find the mean of children per family from the data given below.
| Number of Children | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Number of Family | 5 | 11 | 25 | 12 | 5 | 2 |
Ans.
| Number of Children(x) | Number of Family(f) | fx |
| 1 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 11 | 22 |
| 3 | 25 | 75 |
| 4 | 12 | 48 |
| 5 | 5 | 25 |
| 6
|
2
∑f =60 |
12
∑fx =187 |
Hence mean of the children per family is 3.12
OR
Find the class interval having classmark 18 and class-size 10.
Ans. Let L1 and L2 are the lower and the upper limit of the class interval
Since Classmark =(L1 + L2)/2
(L1 + L2)/2 =18
L1 + L2 = 36….(i)
Also given class size 10
Class size =10
Class size =L2 – L1
L2 – L1 = 10……(ii)
Adding both equations (i) and equation (ii)
2L2 = 46
L2 = 23
Putting L2 =23 in equation (ii)
23- L1 = 10
L1 = 23 -10 = 13
Hence required class interval is 13 – 23
Alternative method
Lower limit of the C.I =Class mark -Class size/2 = 18 -10/2 =18-5 =13
Upper limit of the C.I =Class mark +Class size/2 = 18 +10/2 =18+5 =23
Required C.I is 13 -23
Q6.If the equation (m² +n²)x² -2(mp +nq)x +p² +q² =0 has equal roots ,then show that mq =pn.
Ans. We know if roots of a quadratic equation ax² +bx +c =0 then
b² -4ac =0
The given equation is
(m² +n²)x² -2(mp +nq)x +p² +q² =0
Where a =m² +n²,b =-2(mp +nq) and c =p² +q²
[-2(mp +nq)]² -4×(m² +n²)(p² +q²) =0
4(mp +nq)² -4(m² +n²)(p² +q²) =0
(mp +nq)² -(m² +n²)(p² +q²) =0
m²p² +n²q² +2mpnq -m²p² -m²q²-n²p²-n²q²=0
-m²q²-n²p²+2mpnq =0
m²q²+n²p²-2mpnq =0
(mq -np)² = 0
mq -np =0
mq =pn,Hence proved
Solutions of Class 10 Maths Practice Paper for Current CBSE Board Exam
Section- B
Q7. Find the 7thterm from the end of the AP 17,21,25,…..93.
Ans. nth term of an AP is given by
an= a +(n -1)d
The given AP is 17,21,25,…..93
Where an= 93,d =21-17 =4,a =17
But we have to find 7thterm from the end of the AP
Therefore putting an= a=93,d =17-21=-4 =4,a7=?
a7 = 93 +(7 -1)×-4 =93 -24 =69
Therefore 7thterm from the end of the given AP is 69
Q8.The median weight(in kg) of the employees in an office is found to be 82.Find the missing frequency z.
| Weight(in kg) | 45-55 | 55-65 | 65-75 | 75-85 | 85-95 | 95-105 | 105-115 |
| No.of employees | 7 | 12 | 17 | z | 32 | 6 | 10 |
Ans.
| Weight in kg(class interval) | No. of employees(f) | CF |
| 45 -55 | 7 | 7 |
| 55-65 | 12 | 19 |
| 65-75 | 17 | 36(CF) |
| 75-85 | z(f) | 36+z |
| 85-95 | 32(F) | 68+z |
| 95-105 | 6 | 74+z |
| 105-115 | 10 | 84+z |
N/2 =(84+z)/2 =42 +z/2[where N is the no.of total employees)
Therefore median class interval is 75-85
The median(M) of data is given as
Where l1=75,CF =36,h =85-75=10 and N/2 =42 +z/2,F=z
(6+z/2)10/z = 82 -75 =7
10(6 +z/2) =7z
60 +5z =7z
7z -5z =60
2z =60
z = 60/2 =30
Hence the missing frequency(z) is 30
Q9.Draw a line segment of length 7.6 cm and divide it internally in the ratio 3: 2. Measure the two parts.
Ans.
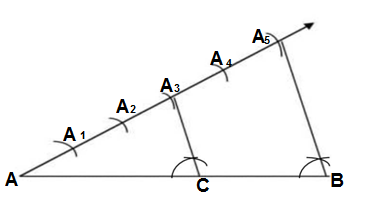
(i) Draw a line segment of length, AB=7.6 cm
(ii) Draw an acute angle from point A.
(iii) Taking equal arcs of AA1=A1A2=A2A3=A3A4=A4A5
(iv) Join B to A5
(iv) Drawing A3C ∥ A5B
The required ratio AC : CB = 3:2
Q10.From a point P which is at a distance of 13 cm from the centre O of a circle of radius 5 cm,the pair of tangents PQ and PR to the circle are drawn . Find the area of the quadrilateral PROQ.
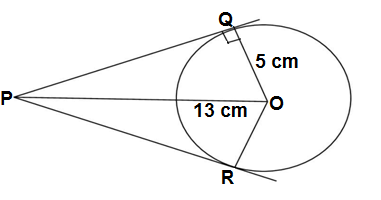
Ans. In ΔPOQ and ΔPOR
∠PQO = ∠PRO =90°(the radius and tangents are perpendicular to each other)
OR =OQ (radii of the circle)
OP =OP (common)
ΔPQO ≅ ΔPRO (RHS rule of congruency)
∴area of ΔPQO =area of ΔPRO
area of PROQ = 2× area of ΔPQO
Area of ΔPQO =1/2(PQ × OQ) = 1/2(PQ × OQ) [PQ =√(13²-5²) =12]
Area of ΔPQO =1/2(12 × 5 )=30 cm²
Area of PROQ = 2× 30 =60 cm²
Solutions of Class 10 Maths Practice Paper for Current CBSE Board Exam
Section- C
Q11.Draw two tangents to a circle of radius 6 cm inclined at an angle of 80°.
Ans. The sum of the angle between two radii joining contact points of the circle and tangent and the angle between tangents of the circle drawn to the circle from an external point is 180°
(i) Draw a circle of the radius 6 cm.
(ii) Draw two radii OA and OB subtended by an angle 180° -80°=100°.
(iii)Draw two rays AC and BC such that ∠OAC=90°and ∠OBC=90° which intersects at C.
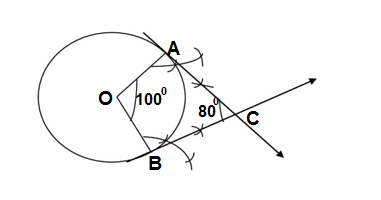
The required tangents are AC and BC.
Q12.From the top of a vertical tower, the angles of depression of two cars, in the same straight line with the base of the tower, at an instant are found to be 30° and 45°. If the cars are 83 m apart and on the same side of the tower, find the height of the tower.
Ans. Let the height of the tower is AB and D are C are the points where both cars are located

tan 45° = AB/BD
1 = AB/BD
BD = AB
tan 30° = AB/BC
BC =BD + DC =BD +83
tan 30° = AB/(AB+83)
1/√3 =AB/(AB+83)
AB+83 = AB√3
AB√3 -AB=83
AB(√3 -1) = 83
AB = 83/(√3 -1)
AB =83(√3 +1)/(√3 -1)(√3 -1
AB = 83(√3 +1)/(√3² -1²)
AB =83(√3 +1)/(3-1) =83(√3 +1)/2 =41.5(√3 +1)
Hence the height of the tower is 41.5(√3 +1) m
OR
The angle of elevation of the top and the angle of the depression of the bottom of a lighthouse is found to be 30° and 60° from a 60 m high tower . Find the distance between the lighthouse and the tower . Also, find the height of the lighthouse.
Ans. Let the height of the lighthouse is AB and the height of the tower is DC
Joining D to E such that DE ∥ BC

EDCB is a rectangle
BE = DC =60 m
tan 60° = BE/DE=60/DE
√3 =60/DE
DE = 60/√3 =60√3/√3² =60√3/3 =20√3 m
tan 30° =AE/DE =(AB -BE)/DE=(AB -60)/20√3
1/√3 =(AB -60)/20√3
AB -60 = 20
AB = 60 +20 = 80 m
Hence height of the tower is 80 m
OR
The angle of elevation of the top and the angle of depression of the bottom of a lighthouse is found to be 30° and 60° respectively from a 60 m high tower. Find the distance between the lighthouse and the tower. Also, find the height of the light-house.
Ans. Let the AB is the height of the lighthouse and DC is the height of the Tower
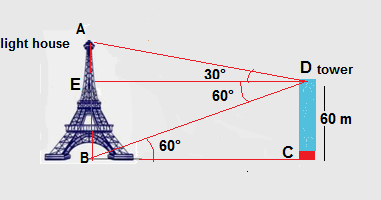
tan 60° = DC/BC,where BC is the distance between the lighthouse and the tower
√3 = 60/BC
BC = 60/√3 =60√3/√3² =60√3/3 =20√3 m
DC = BE =60 m
tan 30° =AE/DE ,where DE =BC =20√3 m
1/√3 =AE/20√3
AE = 20 m
Hence the height of the tower = AE +BE =20 + 60 =80 m
Q13.A school charges a fee of Rs 1500 monthly if paid till 10th of the respective month.From 11th day they put a penalty of Rs 105 per day. Rama was not able to pay the fees on the 10th of February,2020.
(i) Rama paid a total of 2445(in rupees) fees for the month of February. On which date of February did Rama pay the fees?
Ans. Let Rama paid the fee after x days onwards 10th of February
A penalty is given of Rs 105 per day
∴ The penalty of x days is =Rs 105x
The fee of Rama is Rs 1500 monthly
Since Rama paid a total of Rs 2445
∴1500 + 105x = 2445
105x = 2445 – 1500= 945
x = 945/105 =9
Rama paid the fee on the (10 +9=19) th of February
(ii) If Rama pays the fees on 1st of march 2020 for February and March both then how much amount will she has to pay?
Ans. The no.of days dues in the month of February =28-10 =18 days
The no. of days dues in the month of the march of February fee =1 day
Total no. of days which are dues of February fee =19 days
Fee of the February including penalty =Rs 1500 + 19×105 =Rs(1500 +1995)=Rs 3495
Fee of the March =Rs 1500
Hence Rama will pay the fee Rs(3495+1500=4995)of February and March on 1st of march 2020
Q14.Selvi’s house has an overhead tank in the shape of a cylinder. This is filled by pumping water from a sump (an ground tank) which is in the shape of a cupboard. The sump has a dimension of 1.57 m×1.44m×95cm. The overhead tank has a radius of 60 cm and a height 95 cm. One day while pumping the water into the tank, the power shut down and the tank is filled up to a height of 70 cm only.
(i) Find the remaining water in the sump.
Ans. The volume of the water(V) in the tank =πr²h, where h =70 cm
V = (22/7)×60×60 ×70=22×60×60×10 =792000 cm³
The volume of the water(V’) in the sump =Length×Breadth×Height
V’ =1.57 m×1.44m×95cm
V’ = 157 cm×144cm×95cm= 2147760 cm³
Remaining water in the sump =V’ -V = 2147760 cm³ – 792000 cm³=2128560 cm³ =2128.560 litre
(ii) How many times the cylindrical tank can be filled by the completely filled sump?
Ans. The number of times the cylindrical tank can be filled by the completely filled sump
=Volume of sump/Volume of tank
=2147760 cm³/[( (22/7)×60×60 ×95] cm³
=[15034320/(22×60×60 ×95)]cm³
=15034320/7524000
=1.998≈2
Hence the cylindrical tank can be filled 2 times by the completely filled sump
You can compensate us by donating any amount of money for our survival15034320/7524000
Our Paytm No 9891436286
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions of class 9 maths
| Chapter 1- Number System | Chapter 9-Areas of parallelogram and triangles |
| Chapter 2-Polynomial | Chapter 10-Circles |
| Chapter 3- Coordinate Geometry | Chapter 11-Construction |
| Chapter 4- Linear equations in two variables | Chapter 12-Heron’s Formula |
| Chapter 5- Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry | Chapter 13-Surface Areas and Volumes |
| Chapter 6-Lines and Angles | Chapter 14-Statistics |
| Chapter 7-Triangles | Chapter 15-Probability |
| Chapter 8- Quadrilateral |
NCERT Solutions of class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions of class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions for Term 2 CBSE Board Exam with Marking Scheme
Solutions-Class 10 Maths(Basic) sample paper Term 2 published by CBSE-2022 Board
Solutions-Class 10 Maths(Standard) sample paper Term 2 published by CBSE-2022 Board
NCERT solutions of class 10 science
Solutions of class 10 last years Science question papers
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Latest sample paper of science
NCERT solutions of class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions of class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |



