Solutions of class 9 NCERT maths chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
Solutions of class 9 NCERT maths chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry are created for class 9 CBSE students to help them in doing homework and in preparation for the forthcoming exam. Solutions of class 9 NCERT maths chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry will clear the basic concept of coordinate geometry since chapter 3 of class 9 maths is based on the introduction of the coordinate geometry which is required to solve the questions of coordinate geometry in higher classes. Solutions of class 9 NCERT maths chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry are explained here beautifully with the help of proper diagrams.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
Solutions of class 9 NCERT maths chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
Exercise 3.1
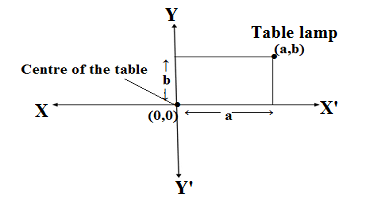
Q1.How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person?
Ans. Let the table is in the shape of a rectangle.
Drawing two line of symmetry perpendicular to each other such that both the lines intersect at the centre of the table.
The horizontal line is supposed as XX’ and vertical line as YY’
The position of the table lamp is ‘a’ unit distance from YY’ and ‘b’ unit distance from XX’,the position of the table is represented by (a,b) with respect to the position of the centre of the table (0,0)
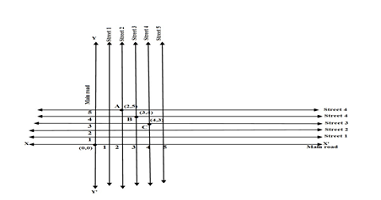
Q2.Street plan: A city has two main roads which cross each other at the centre of the city . These two roads are along the north-south direction and east-west direction. All other streets of the city-run parallel to these roads and are 200 m apart. There are 5 streets in each direction.Using 1 cm = 200m.Draw a modal of the city on your notebook. Represent the roads/streets by single lines.
There are many cross streets in your modal. A particular cross street is made by two streets, one running in the north-south direction and another in an east-west direction. Each cross street is referred to in the following manner. If the second street running in the north-south direction and 5 th in the east-west direction meet at some crossing, then we will call this cross street. Using this convention, find
(i) How many cross streets can be referred to as (4,3)
(ii) How many cross streets can be referred to as (3,4)
Ans. Drawing one horizontal line XX’ and Vertical line YY’ as main roads crossing each other at the centre (0,0), thereafter drawing 5 lines parallel to XX’ and YY’ showing the 5 streets crossing each other.
(i) There is only one cross streets can be represented by the unique point A(4,3)
(ii) There is only one cross streets can be represented by the unique point B(3,4)
Solutions of class 9 NCERT maths chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
Exercise 3.2
Q1. Write the answer to each of the following questions.
(i) What is the name of the horizontal and the vertical line is drawn to determine the position of any point in the cartesian plane?
(ii) What is the name of each part of the plane formed by these two lines?
(iii) Write the name of the point where these two lines intersect.
Ans. (i) The name of the horizontal line is X-axis and the name of the vertical line is Y-axis
(ii) Each part of the plane formed by the horizontal line X-axis and the vertical line Y-axis are known as quadrants.
(iii) The name of the point where these two lines intersect is the origin
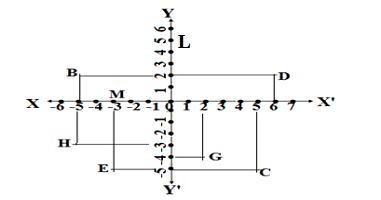
Q2.See the given figure and write the following:
(i) The coordinates of B
(ii) The coordinates of C
(iii)The point identified by the coordinates (-3,-5)
(iv)The point identified by the coordinates (2,-4)
(v) The abscissa of point D
(vi) The ordinate of point H
(vii) The ordinate of point L
(viii) The ordinate of point M
Ans. (i) The coordinates of B is (-5,2)
(ii) The coordinates of C is (5,-5)
(iii)The point identified by the coordinates (-3,-5) is E
(iv)The point identified by the coordinates (2,-4) is G
(v) The abscissa of point D is 6
(vi) The ordinate of point H is -3
(vii) The coordinates of point L is (5,0)
(viii) The coordinates of point M is (-3,0)
Solutions of class 9 NCERT maths chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
Exercise 3.3
Q1.In which quadrant or on which axis do each of the points (-2,4),(3,-1),(-1,0),(1,2) and (-3,-5) lie? Verify your answer by locating them on the cartesian plane.
Ans.(-2,4) lies on second quadrant
(3,-1) lies on the fourth quadrant
(-1,0) lies on X-axis
(1,2) lies on the first quadrant
(-3,-5) lies on third quadrant
Q2.Plot the points (x,y) given in the following table on the plane,choosing suitable units of distance on the axis.
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y | 8 | 7 | -1.25 | 3 | -1 |
Ans. We are given the coordinates (-2,8),(-1,7),(0,-1.25), (1,3),(2,-1)
Drawing XX’ and YY’ lines perpendicular to each other and intersect at the point O known as origin.
Taking 1 unit = 1 big square
Locating the points as following
(-2,8) : lies at the distance of 2 units from the left of the origin and 8 unit above the X-axis
(-1,7): lies at the distance of 1 unit from the left of the origin and 7 unit above the X-axis
(0,-1.25): lies at the distance of 1.25 unit below the origin on the Y-axis
(1,3): lies at the distance of 1 unit left of the origin and 3 units above the X-axis
(2,-1) lies at the distance of 2 unit right of the origin and 1 un
it below the X-axis
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions of class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
Solutions of class 10 last years Science question papers
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -sample paper of science
NCERT solutions of class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions of class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |