How to determine Valency,net charge of an ion and Molecular formula of a substance.

Study science notes
Archimedes Principle: Complete detail
Average Speed and Average velocity
The universal law of gravitational force
Click bellow Class 9,10 and 11 NCERT solutions and notes of science and maths
Science and Maths NCERT solutions for Class 9 ,10 and 11 classes
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Valency: Valency of an element is the holding capacity of an atom of a substance, as we know atom is neutral then how is this capable to react with other atoms of a substance? The reaction of an atom of an element with other atoms is decided by the electrons available in its outermost orbital called valence electrons of an atom. Every atom of a substance has a tendency to have 8 electrons in its outermost orbits, so an atom of a substance can either loss or gains the electrons. When an atom of an element comes in contact with another particular atom, both of them excited to exchange or share the electrons and form molecules. As an example the formation of sodium chloride.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
The electronic configuration of Na(11) is= 2,8,1 and of chlorine (17) is =2,8,7
When Na atom comes in contact with Cl atom both of them excited and form ions, the charged particles. It is clear from the electronic configuration of both the atoms that Na losses 1 electron to make an octet in its outermost orbit and Cl atom gains 1 electron to make octet in its outermost orbit.therefore after losing 1e Na forms ion and After a gain of 1e Chlorine forms
ion.
As we know opposite charges attracted each other and so both and
attracted and stuck together and forms a molecule of sodium chloride and such type of bonds between two ions is known as ionic bond.
In the formation of carbon dioxide molecule when carbon atom and oxygen comes in contact with each other in a particular circumstance, they share electrons with each other because carbon can not form ions since it is requiring large amount of energy in exchanging its 4 outermost electrons.
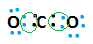
Here, in this case, carbon atoms and oxygen molecules share electrons in fulfilling their outermost orbit. Sharing means, now electrons of carbon and oxygen atoms can enter into each other’s orbits and such type of chemical bond is known as Covalent bond.
Net Charge of an ion
Ions are of two kinds on the basis of the number of atoms (a) Mono-atomic ions (b) Polyatomic ions. Monoatomic ions are made of a single atom and Polyatomic ions are made of more than one atoms, when whole of the molecule of a substance ionized then polyatomic ions are formed.These polyatomic ions are also called radicals. The atoms in these polyatomic ions are bonded with covalent bonds and have net charge.
The net charge of polyatomic ions is the sum of charges(or valency) of individual atoms in it, as an example
.
The charge in a sulphur atom is +6 because it shares its 6 electrons to 4 oxygen atoms charge in 4 oxygen atoms = -2×4=-8, so the net charge of sulphate ion is =-8 + 6= -2.
The molecular formula of a substance:
The molecular formula of a substance shows the proportions of all elements in a substance,as an example from the formula of water we can get the volumes and masses wise ratio of hydrogen and oxygen in the water.
The mass of two hydrogen atoms in water is = 1×2= 2u and of one oxygen atom is =16
The ratio of hydrogen and oxygen in water is = 1: 8
Volume-wise ratio = number of hydrogen atoms: number of oxygen atoms=2: 1
The chemical or molecular formula of a substance is determined by the valency or charges of atoms and ions. Let the valency of a substance X is 2 and of Y substance is 3 then the chemical formula of the substance formed by them is X3Y2.
As an example calcium hydroxide
Valency of Ca is = 2 and the net charge of Hydroxide ion is =-1
Then the number of atoms involved in the formation of a molecule depends on the charges on another atom or radical, as example net charge of hydroxide ion (-1) compels one atom of Ca to combine in it, and charge 2 of Ca compel one ion of OH to combine in it.
Therefore the chemical formula for calcium hydroxide is
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution



