Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations
Study of these important NCERT solutions of important questions from class 10 maths NCERT book Chapter 3 Linear Equations in two variables lead the full preparation of the CBSE board exams concerning to the questions of class 10 maths chapter 3 Linear equations in two variables in the maths question paper of CBSE board exams. The selection of Class 10 Maths NCERT solutions of unique and important questions of chapter 3 pair of linear equations is based on the previous year’s question papers, these questions or similar type of questions are repeatedly asked by the CBSE in every year.
Chapter 3 of the maths NCERT textbook of class 10 CBSE is the key to solving two unknown variables in maths. In this chapter 3 pair of linear equations of class 10 maths NCERT textbook, you will learn two ways of solving the linear equations in two variables, one is a graphical method of solving a pair of linear equations and another is the algebraic way of solving a pair of linear equations. Here we have solved unique questions of the chapter 3 pair of linear equations with proper explanations so that you could do all questions of the chapter 3 pair of linear equations would be asked in maths paper of CBSE board because this set of questions accommodate all type of question in class 10 maths NCERT textbook.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Linear Equations in Two Variables
Exercise 3.1 -Linear Equations in Two Variables
Exercise 3.2 -Linear Equations in Two Variables
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations
Exercise 3.7 – Linear Equations in Two Variables
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
This set of NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations contains following features.
(1) The number of questions in the set are 28
(2) Type of solutions are two (a) Graphical Method (b) Algebraical Method
(b) Algebraical Methods are of three types
(i) Substituition Method (ii) Elimination Method (iii) Cross multiplication method
NCERT Solutions of class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations
See the video how to solve the questions of linear pair of equations in two variable by the graphical method
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations
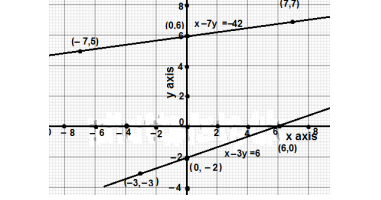
Q1. Aftab tells his daughter, “seven years ago I was seven times as old as you were then, also 3 years from now, I shall be three times as old as you will be”(Isn’t this interesting), Represent this situation algebraically and graphically.
Ans. Let the present age of Aftab is = x and the present age of his daughter = y
The age of Aftab 7 years ago = x – 7 and his daughter’s age 7 years ago = y– 7
Three years from now Aftab’s age = x + 3 and 3 years from now his daughter’s age = y + 3
According to the first condition
7 years ago Aftab’s age = 3 × 7 years ago his daughter’s age
x – 7 = 7 (y– 7)
⇒ x – 7y = –42……..(i)
According to the second condition
3 years from now Aftab’s age = 3× 3 years from now his daughter’s age
x + 3 = 3 (y + 3)⇒x –3 y = 6….(ii)
Solutions of equation (i) x – 7y = –42
| x | 0 | 7 | –7 |
| y | 6 | 7 | 5 |
Solution of equation (ii) x –3 y = 6
| x | 0 | –3 | 6 |
| y | –2 | –3 | 0 |
Plotting the graphs of both equations as follows
Q2. 10 students of class X took part in a mathematics quiz. If the number of girls is 4 more than the number of boys, find the number of boys and girls who took part in the quiz.
Ans. (i) Let the number of boys participated in the quiz = x and the number of girls participated = y
Total number of students is = 10
∴ x + y = 10…………(i)
We are given, the number of girls = number of boys + 4
y = x + 4 ………….(ii)
Solutions of eq.(i) x + y = 10
| x | 6 | 4 | 2 |
| y | 4 | 6 | 8 |
Solutions of eq. (ii) y = x + 4
| x | 0 | 2 | –2 |
| y | 4 | 6 | 2 |
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations
See the video of solutions of the pair of linear equations by the Graphical method and Algebraical methods like Substitution, Elimination, and Cross Multiplication method.
Q3 5 pencils and 7 pens together cost Rs 50 whereas 7 pencils and 5 pens together cost Rs 46, find the cost of one pencil and that of one pen.
Ans. Let the cost of one pen = x and of one pencil = y
Cost of 7 pen = 7x and cost of 5 pencils = 5y
According to first condition
7x + 5y = 50……….(i)
Cost of pen = 5x and cost of 7 pencils = 7y
According to the second condition
5x + 7y = 46………(ii)
Draw the graph of both equations as in the previous question
Q4. On comparing the ratios find out whether the lines representing the following pair of the linear equations intersect at a point, are parallel or coincident.
(i) 5x – 4y + 8 = 0
7x +6y – 9 = 0
(ii) 9x +3y +12 = 0
18x + 6y +24 = 0
Ans.(i) We are given the pair of equations 5x – 4y + 8 = 0, 7x +6y – 9 = 0
Comparing both equations with the standard pair of linear equations we have
On comparing, we get
Therefore, the given pair of linear equation intersect each other at the point and the coordinates of that point is the unique solutions of the given equations.
(ii) We are given the pair of the linear equations 9x +3y +12 = 0,18x + 6y +24 = 0, comparing both equations on the same way as in (i)
On comparing, we get
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations are coincident and has infinite solutions.
(iii) The given pair of linear equations is 2x – 3y = 8, 4x – 6y = 9, comparing it on the same way as above, we have
Therefore, the given pair of linear equations are parallel to each other and has no solution.
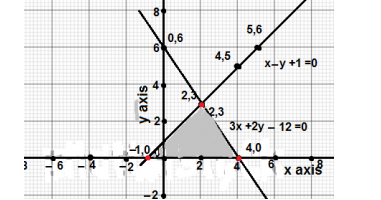
Q5. Draw the graph of the equations x – y +1 = 0 and 3x + 2y – 12 = 0. Determine the coordinates of the vertices of the triangles formed by these lines and the x-axis, and shade the triangular region.
Ans. The given pair of the equations is
Solutions of the equations x – y +1 = 0
| x | 4 | 2 | 5 |
| y | 5 | 3 | 6 |
Solutions of the equations 3x + 2y – 12 = 0
| x | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| y | 3 | 0 | 6 |
Drawing the graph of both equations as follows
It is clear from the figure that the pair of lines and x-axis intersect each other at (– 1,0),(2,3), and (4,0), therefore the vertices of the triangle are (– 1,0),(2,3) and (4,0).
Q6. Solve the following pair of linear equations by the substitution method.
(i) s – t = 3
(ii) 0.2x + 0.3y =1.3
0.4x + 0.5y = 2.3
Ans.(i) We are given the pair of the linear equation
s – t = 3 ………(i)
…..(ii)
The (i) equation is s – t = 3 , solving it for the value of s, we have s = t+3
Substituting s = t+3 in equation (ii)
5t = 30
t = 6
Putting the value of t =6 in equation no (i)
We have s – 6 = 3⇒s = 9
Therefore the required solutions of both equations are, s =9 and t = 6
(iii)3x-y=3
9x-3y=9
(iv) We are given the pair of the equations
0.2x+0.3y=1.3………(i)
0.4x+0.5y=2.3…….(ii)
From eq.(i) 0.2x+0.3y=1.3,we have
Substituting the value of x in eq.(ii)
2.6 – 0.6y +0.5y = 2.3
–0.1y = 2.3 – 2.6 = –0.3
y = 3
Putting this value in eq.(i), we have
Therefore the required solutions of the equation are x = 2 and y = 3
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations
Q7. Solve 2x + 3y = 11 and 2x – 4y = –24 and hence find the value of’ ‘m’ for which y = mx + 3.
Ans. The pair of equation is given ,2x + 3y = 11 …….(i) and 2x – 4y = –24………(ii)
From (i) we have 2x + 3y = 11
Putting the value of x in (ii)
11 – 3y – 4y = – 24
–7y = –35
y = 5
Putting the value of y in eq.(i)
2x + 3× 5 = 11
2x = –4
x = – 2
Putting the value of x and y in the given expression
y = mx + 3
5 = –2 m +3
m = –1
Therefore the value of m=–1
Q8. The larger of two supplementary angles exceeds the smaller by 18º. Find them.
Ans. Let x is the larger and y is smaller in a pair of supplementary angle
As we know the sum of supplementary angle is = 180º
∴ x + y = 180º……..(i)
It is given that larger angle = smaller angle +18º
x = y + 18º………..(ii)
Putting the value of x from eq.(ii) to in eq.(i)
y + 18º + y = 180º
2y = 162
y = 81
Putting the value of y in eq.(i), we get
x + 81 = 180º
x = 99
Hence both of the supplementary angles are 81º and 99º
Q9. The taxi charges in a city consist of fixed charges together with the charge for the distance covered. For a distance of 10 km, the charge paid is Rs 105 and for a journey of 15 km, the charge paid is Rs 155. What are the fixed charges and charges per km? How much does a person have to pay for traveling a distance of 25 km?
(ii) Let the charges per km is = x and fix charges = y
For covering the distance of 10 km, total charge = fixed charge + distance × per km charge
y + 10x = 105………(i)
For covering the journey of 15 km, total charges = fixed charge + distance × per km charge
y + 15x = 155………(ii)
From (i) Substituting y = 105 – 10 x in eq.(ii)
105 – 10 x + 15x = 155
x = 10
Putting this value in eq.(i), we have
y + 10× 10 = 105
y = 5
Hence the fixed charge of the taxi is Rs 5 and charges per km is Rs 10
Therefore in traveling 25 km the net charge of taxi = fix charge + distance × per km charge = 5 + 25× 10 = Rs 255
Q10.5 years hence the age of Jacob will be three times as that of his son. Five years ago Jacob’s age was 7 times that of his son. What are their present ages?
Ans.(iii) Let the present age of Jacob = x and of his son’s present age = y
After 5 years the ages of Jacob = x + 5 and of his son’s age = y +5
According to the first condition
x + 5 = 3(y +5)
x – 3y =10……….(i)
5 years ago Jacob’s age = x – 5 and of his son’s age = y – 5
x – 5 = 7(y – 5)
x – 7y = –30……(ii)
From eq.(i), we have x = 10 + 3y, substituting this value of x in (ii)
10 + 3y – 7y = –30
– 4y = – 40
y = 10
Putting the value of y = 10, in eq.(i)
x – 3×10 =10
x = 40
Therefore the present age of Jacob is 40 years and of his son’s present age is 10 years
Q11.Solve the following pair of linear equations by the elimination method.
x + y = 5, 2x – 3y = 4
Ans. The given pair of linear equation is
x + y = 5 ………(i)
2x – 3y = 4……(ii)
Multiplying the eq.(i) by 2 for equalizing the coefficient of x in both equations
2x + 2y = 10…..(iii)
Subtracting (iii) from (ii)
Putting the value of y in eq.(i)
Hence the solutions of both equations are x = 6/5 and y = 19/5
Q12.If we add 1 to the numerator and subtract 1 from the denominator, a fraction reduces to 1. It becomes 1/2 if we only add 1 to the denominator. What is the denominator?
Ans. Let the numerator = x and the denominator = y
According to the first condition that numerator becomes = x +1 and denominator become =y – 1
x +1 = y – 1
x – y = – 2………(i)
According to the second condition the denominator = y +1
2x = y +1
2x – y = 1…….(ii)
Multiplying eq.(i) by 2
2x –2 y = – 4……(iii)
Subtracting (iii) from (ii), we have
y = 5
Putting the value of y in eq.(i)
x – 5 = – 2
x = 3
Therefore the numerator is 3 and denominator is 5
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations
Q13.Five years ago, Nuri was thrice as old as Sonu. Ten years later, Nuri will be twice as old Sonu. How old are Nuri and Sonu?
Ans. Let the age of Sonu is = x and Nuri’s age is = y
5 years ago the age of Sonu = x – 5 and of Nuri’s age = y– 5
According to the first condition
y – 5 = 3( x – 5)
y – 3x = – 10………..(i)
10 years later Sonu’s age = x + 10 and of Nuri’s age = y + 10
According to the second condition
y + 10 = 2 (x + 10)
y – 2x = 10………..(ii)
Subtracting (ii) from (i), we get
– x = – 20
x = 20
Putting the value of x in eq.(i)
y – 3 ×20 = – 10
y = 50
Hence the age of Sonu is 20 years and the age of Nuri is 50 years.
Q14. The sum of the digits of a two-digit number is 9. Also nine times this number is twice the number obtained by reversing the order of the digits. Find the number.
Ans. Let the unit digit of the two-digit number is = x and of tense digit is = y
Since sum of both digits is given 9
x + y = 9……..(i)
The given number is = 10y + x
After reversing the digits the number will become = 10x +y
According to the second condition
9 (10y + x) = 2(10x + y)
90y + 9x = 20x + 2y
88y – 11x = 0……..(ii)
Multiplying the eq.(i) by 11, we get
11x + 11y = 99…….(iii)
Adding both eq.(i) and (ii), we get
99 y = 99
y = 1
Putting the value of y in eq.(i)
x +1 = 9
x = 8
Therefore the tense digit is 1 and the unit digit of the number is 8 implies that the required two-digit number is 18
Q15. Meena went to a bank to withdraw Rs 2000. She asked the cashier to give her Rs 50 and Rs 100 notes only. Meena got 25 notes in all. Find how many notes of Rs 50 and Rs 100 she received.
Ans. Let the number of Rs 50 notes = x and of Rs 100 notes = y
The total number of notes are given = 25
So, x + y = 25………..(i)
Total money = Rs 2000
Therefore
50x + 100y = 2000
x + 2y = 40………..(ii)
Subtracting eq.(ii) from (i)
– y = – 15
y = 15
Putting this value of y in eq.(i)
x + 15 = 25
x = 10
Therefore the number of Rs 50 notes are 10 and of Rs, 100 notes are 15
See the video for the solutions of Q14 and Q15
Q16.A lending library has a fixed charge for the first three days and an additional charge for each day, thereafter, Saritha paid Rs 27 for a book kept for seven days, while Susy paid Rs 21 for the book she kept for five days. Find the fixed charge and charge for each extra day.
Ans. Let the fixed charge of the library = x and additional charge each day = y
According to the first condition, Saritha kept the book for seven days
So, total charges paid by Saritha = fixed charge for 3 days + per day charges for 4 days
∴ x + 4y= 27………(i)
According to second condition, the book kept for 5 days
∴ x + 2y = 21…….(ii)
Subtracting eq.(ii) from eq.(i)
2y = 6
y = 3
Putting the value of y in eq.(i)
x + 4×3 = 27
x = 15
Therefore fixed charges of the library are Rs 15 and additional per day charges are Rs 3
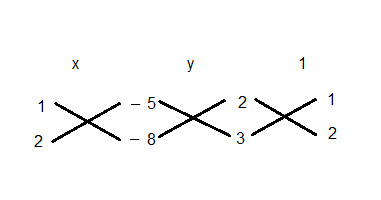
Q17. Which of the following pair of linear equations has unique solutions, no solutions, or infinitely many solutions? In case there are unique solutions, find it by cross multiplication method.
(i)x-3y-3=0
3x-9y-2=0
(ii)2x+y=5
3x+2y=8
Ans. (i) We are given the pair of linear equation,
x-3y-3=0………(i)
3x-3y-2=0…….(ii)
Comparing the pair of equations with standard pair of linear equations
On comparing, we get
Therefore both of the equations are parallel to each other and have no solutions.
(ii) The given pair of the equations is
2x+y=5
3x+2y=8
Rearranging the equations
2x + y –5 = 0………(i)
3x+2y – 8 = 0……..(ii)
Arranging the coefficients in a matrix as follows
x = 1, y= 1
Therefore the solutions of the above equations is x = 1 and y =1
Q18.For which value of a,b does the following pair of linear equations have an infinite number of solutions?
2x + 3y = 7, (a – b)x + (a + b) y = 3a + b – 2
Ans. The pair of linear equations is given
2x + 3y = 7, (a – b)x + (a + b) y = 3a + b – 2
Arranging the pair of equations as follows
2x + 3y – 7 = 0……..(i)
(a – b)x + (a + b) y – 3a – b + 2 = 0……….(ii)
The condition of a pair of linear equations have infinite solutions
2a + 2b = 3a– 3b
–a + 5b = 0………..(iii)
–9a – 3b + 6 = –7a – 7b
–2a + 4b = – 6……(iv)
Multiplying the eq.(iii) by 2, we get
– 2a + 10b = 0……..(v)
Subtracting eq.(v) from eq.(iv), we get
– 6b = –6
b = 1
Putting the value of b in eq.(iii)
–a + 5× 1 = 0.
a = 5
Hence for a= 5 and b= 1, the given pair of the linear equation has infinite solutions
Q19. For which value of k will the following pair of linear equations have no solution?
3x + y = 1. (2k – 1)x + (k– 1)y = 2k +1
Ans. Arranging both equations as follows
3x + y –1 = 0………(i) , (2k – 1)x + (k– 1)y– 2k– 1 = 0……(ii)
The condition of a pair of linear equations have no solutions
3k – 3 = 2k – 1
k = 2
Hence for k =2 the given pair of linear equations has no solution
Q20.Yash scored 40 marks in a test, getting 3 marks for each right answer and losing 1 marks for each wrong answer. Had 4 marks been awarded for each correct answer and 2 marks been deducted for each incorrect answer, then Yash would have scored 50 marks. How many questions were there in the test?
Ans. Let correct answers of Yash in the exam are = x and wrong answers = y
According to the first condition
3 × x + y× –1 = 40
3x – y = 40………(i)
According to the second conditions
4 × x + y × – 2 = 50
4x – 2y = 50
2x – y = 25……..(ii)
Subtracting eq.(ii) from (i)
x = 15
Putting this value in (i)
3 × 15 – y = 40
y = 5
Therefore number of right answers = 15 and wrong answers = 5
Hence total questions asked in the test are = x +y = 15 +5 = 20
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations
Q21. Places A and B are 100 km apart on a high way. One car starts from A and another car from B at the same time. If the car travels in the same direction at a different speed, they meet in 5 hours. If they travel towards each other, they meet in 1 hour. What are the speeds of the two cars?
Ans. Let the car which moves from A has the speed = x km/h and the car moves from B has the speed = y km/h
According to first condition, the time duration in which both car meets = 5 h
So, total distance covered by the car from A = time × speed = 5 × x = 5x
Total distance covered by the car from B = time × speed = 5 × y = 5y
Therefore 5x – 5y = 100
x – y = 20……….(i)
According to the second condition, both cars meet in a time duration of 1 h when moves in the opposite direction
Distance covered by the car from A = time × speed = 1 × x = x
Distance covered by the car from B = time × speed = 1 × y = y
So, we have
x + y = 100…….(ii)
Adding both eq.(i) and eq.(ii)
2x = 120
x = 60
Putting this value in eq.(i)
y = 40
Hence the speed of the car which starts from A has a speed of 60 km/h and the car which starts from B has a speed of 40 km/h.
Q22.The area of rectangle reduced by 9 square units, if its length is reduced by 5 units and breadth is increased by 3 units. If we increase the length by 3 units and breadth by 2 units, the area increased by 67 square units. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
Ans. Let the length of the rectangle is = x and breadth =y
Area of rectangle = xy
According to the first condition, the length of the rectangle is = x –5 and breadth = y +3 and area reduced by 9 sq.units
∴ ( x –5 )(y +3) = xy – 9
xy + 3x – 5y – 15 = xy – 9
3x – 5y = 6…………..(i)
On the same way, according to second condition, we have
(x +3)(y +2) = xy + 67
xy + 2x + 3y + 6 = xy + 67
2x + 3y = 61………….(ii)
Multiplying eq.(i) by 2 and eq.(ii) by 3, we have
6x – 10y = 12……….(iii)
6x + 9y = 183……….(iv)
Subtracting eq.(iv) from (ii)
–19y = –1 71
y = 9
Putting the value of y in eq.(i)
3x – 5×9 = 6
3x = 6 + 45 = 51
x = 17
Hence the length of the rectangle is 17 units and breadth is 9 units
Q23. Solve the following pair of linear equations.
Ans. The given pair of linear equations
…….(i)
……..(ii)
Let
3a + 2b = 12 ……..(iii)
2a + 3b = 13……..(iv)
Multiplying eq.(iii) by 2 and eq.(iv) by 3, we get
6a + 4b = 24……..(v)
6a + 9b = 39…….(vi)
Subtracting eq.(vi) from eq.(v)
– 5b = –1 5
b = 3
Putting the value of b in eq.(v)
6a + 4 ×3 = 24
a = 2
Class 10 maths NCERT solutions of important questions of chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations
Q24. Solve the following pair of linear equations
Ans. The given pair of equations is
We obtain, the equations
2a + 3b = 2……..(iii) and 4a – 9b = –1……….(iv)
Multiplying eq.(iii) by 2 , we get eq.(v)
4a + 6b = 4………(v)
Subtracting eq.(v) from (iv)
– 15b = –5
b = 1/3
Putting the value of b in eq.(iii)
2a + 3 × 1/3 = 2
a = 1/2
⇒ x = 4 and y = 9
Hence solutions of the given equation is x = 4 and y = 9
Q25. Find the solutions to following linear equations.
Ans. The given pair of the equation is
Substituting these values in (i) and (ii), we get the eq.(iii) and (iv)
4a + 4b =3………(iii)
4a – 4b = – 1…..(iv)
Adding eq.(iii) and eq.(iv), we have
8a = 2
a = 1/4
Putting the value of ‘a’ in eq.(iii)
4 × 1/4 + 4b = 3
b = 1/2
3x +y = 4…….(v) and 3x – y = 2……(vi)
6x = 6
x = 1
Putting the value of x in eq.(v)
3 × 1 + y = 4
y = 1
Hence the required solutions of the given equation is x =1 and y=1.
Q26.Ritu can row downstream 20km in 2hrs, and upstream 4km in 2hrs. Find her speed of rowing in still water and the speed of the current.
Ans. Let the speed of the boat in still water = x km/h and speed of current = y km/h
The distance covered in downstream = 20 km and upstream =4 km
Speed of a boat in downstream = Distance/time = 20/2 =10 km/h
Speed of a boat in upstream = Distance/time = 4/2 = 2km/h
So, according to the first condition
The speed of the boat in downstream = Speed of the boat in still water + Speed of the current
x + y = 10……..(i)
Speed of the boat in upstream = Speed of boat – Speed of the current
x – y = 2……..(ii)
Adding both equations
2x = 12
x = 6
Putting the value of x in eq.(i)
6+ y = 10
y = 4
Hence the speed of the boat in still water = 6 km/h and speed of the current = 4 km/h
Q27. 2 women and 5 men can together finish an embroidery work in 4 days, while 3 women and 6 men can finish it in 3 days. Find the time taken by 1 woman alone to finish the work, and also that time is taken by 1man alone.
Ans. Let the time taken by 1 woman alone to finish the work = x days and the time is taken by 1 man alone to finish the work = y days
Therefore 1 day’s work of woman alone = 1/x and 1 day’s work of man alone = 1/y
Since 2 women and 5 men can together finish an embroidery work in 4 days
In 1 day they will finish the portion of work = 1/4
Therefore according to the first condition
…….(i)
3 women and 6 men can finish the same work in 3 days
In 1 day they will finish the portion of work = 1/3
Therefore according to the second condition
……..(ii)
Substituting these values in (i) and (ii), we get eq.(iii) and eq.(iv)
2a + 5b = 1/4, 3a + 6b = 1/3
8a + 20b = 1……..(iii) 9a + 18b = 1………(iv)
Multiplying the eq.(iii) by 9 and the eq.(iv) by 8
72a + 180 b = 9…….(v)
72a + 144b = 8……..(vi)
Subtracting the eq.(vi) from eq,(v)
36 b = 1
Putting the value of b in eq.(iii)
⇒ x = 18 and y = 36
Therefore 1 woman can alone do the work in 18 days and 1 man alone can do the same in 36 days.
Q28.Roohi travels 300 km to her home partly by train and partly by bus. She takes 4 hours if she travels 60 km by train and the remaining by bus. If she travels 100 km by train and the remaining by bus, she takes 10 minutes longer. Find the speed of the train and bus separately.
Ans. Let the speed of the train = x km/h and of the bus = y km/h
According to the first condition, Ruhi takes 4 h in the journey by train 60 km and by bus = 300– 60 = 240 km
Time is taken by train + Time taken by bus = 4h
According to the second condition, Ruhi takes 4 h in the journey by train 100 km and by bus = 300– 100 = 200 km
Time is taken by train + Time taken by bus = 4h +10 minutes
Substituting these values (i) and (ii), we get the eq.(iii) and (iv)
15a + 60b = 1…….(iii)
4a + 8b = 1/6
24a + 48b = 1…….(iv)
Multiplying the eq.(iii) by 24 and (iv) by 15
360a + 1440 b = 24….(v)
360 a + 720 b = 15……(vi)
720 b = 9
Putting the value of b in eq.(i)
x = 60, y = 80
The speed of train = 60 km/h and the speed of bus = 80 km/h
CBSE maths chapter 3, Pair of linear equations in two variables of class 10 maths NCERT is a very important and unique section for solving unknown variables in the field of mathematics, science, technology, commerce, and economics. Future study point has bought a few unique and important questions from class 10 NCERT maths textbook chapter 3 Pair of linear equations in two variables, questions are selected in order to infuse proper inputs to student’s brains so that they could get thorough knowledge of the chapter. The solution to these unique important questions of the chapter Pair of linear equations will boost your preparation of the exams. Here, maximum questions are taken from chapter 3, Pair of linear equations are of 3-4 marks which are explained by the subject expert teacher as per the CBSE norms. This chapter is. In this site, you can study NCERT solutions, sample papers, previous years’ questions papers, assignments, important questions e-books, articles, and notes of science and maths from class 9 to 12. You can also study here our blog posts on your carrier and carrier in online jobs.
How did you like this post on “Class 10 maths NCERT solution of pair of linear equations: important questions” please comment.
In this lockdown, we have lost our sources of income, so if you are economically strong then you can compensate us. Our Paytm no is 9891436286
Please subscribe to our website for updated information
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution