NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 1-Number Systems
The class 9 NCERT solutions of the chapter 1-Number system are for helping the 9 class students in understanding the type of numbers, their sum, subtraction, division, multiplications, exponents, and number line mentioned in chapter 1-Number systems of class 9 NCERT maths textbook. All the NCERT solutions of chapter 1-Number systems are solved by an expert in maths. The NCERT solutions of the chapter 1-Number system of class 9 the maths NCERT textbook are readily and beautifully explained with the help of proper figures and formulas.
Science and Maths NCERT solutions for Class 9 ,10 and 11 classes
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 1-Number Systems
EXERCISE 1.1
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Q1. Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form of, where p and q are an integer and q ≠0?
Ans. Yes, 0 is a rational no.because we can write it in the form of p/q where p and q are integers and q ≠0, for any value of q, it satisfies all conditions as an example 0/1 = 0,0/2 = 0,0/-3 =0….etc.
Q2. Find 6 rational numbers between 3 and 4?
Ans. Writing 3 and 4 in the form of p/q i.e 3/1, 4/1
Widening the gap between 3 and 4 by multiplying denominator and numerator by 7.
Now, placing the 6 rational number between equivalent fractions of 3 and 4
Q3. Find 5 rational number between
Ans. Since the denominator is same i.e 5 of both the fractions, so multiplying the denominator and numerator of the fractions by (5 +1= 6) hint: We have to insert 5 rational number between the given rational number
Q4.State whether the following statements are true or false? Give reasons for your answers.
• Every natural number is a whole number.
• Every integer is a whole number.
• Every rational number is a whole number
Ans.
- natural no.=1,2,3,4……., whole number =0,1,2,3,4….,so it is true.
- integers =……….-4, -3,-2,-1 ,0, 1, 2, 3……, whole number =0,1,2,3,4….., so it is false.
- rational numbers are always written in the form of p/q where p,q are integers, so rational numbers can not be the whole number.
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 1-Number Systems
Exercise 1.2
1.State whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answers
i) Every irrational number is a real number.
ii) Every point on the number line is of the form of √m, where m is a natural number.
iii) Every real number is an irrational number.
Ans.
i) Irrational numbers are √2, √3, √5, √3 etc, which can be shown in real number line therefore every irrational number is a real number.
ii) All positive numbers as an ex. √1, √2, √3, √4 … can be represented on the number line but
the square root of a negative number, √(–m ) does not exist.so it is false.
iii) The real number is the set of rational numbers as well as of irrational numbers, so it is false.
Q2. Are square roots of all positive integers irrational? If not, give an example of a square root of a
the number that is rational.
Ans. We know the square root of every positive integer cannot give a positive integer such as
√3, √2..etc and some of the numbers which are a complete square number yields a positive integer
as an ex.√1 = 1,√4 = 2, etc. Therefore square roots of all positive integers can’t be irrational.
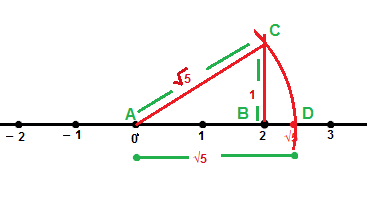
Q3. Show how √5 can be represented on the number line.
Ans. According to the Pythagoras theorem, we can write √5 = √(2²+1²)
Drawing a line segment AB of the length 2 unit
Then draw a line BC ⊥ AB of the length of 1 unit
Joining A to C, then draw an arc of the length AC (√5) on the number line taking A as a center , it intersect at D
Hence the length of AD represents √5 on the number line
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 1-Number Systems
EXERCISE 1.3
1. Write the following in decimal form and say what kind of decimal expansion each has.
(i) Dividing 36 by 100, we get
36 ÷ 100 = 0.36, which is finite decimal
(ii) Dividing 1 by 11, we get
1 ÷ 11 = 0.090909…… = , which is a non-finite recurrent decimal
It is a finite decimal
(iv) Dividing 3 by 11, we get
3 ÷ 11 = , which is a non-finite recurrent decimal
(v) Dividing 2 by 11, we get
2 ÷ 11 = , which is a non-finite recurrent decimal
(vi) On dividing 329 by 400, we get
329 ÷ 400 = 0.8225, which is a finite decimal
Q2. You know that Can you predict what the decimal expansions of
are without actually doing the long division method? If so, how? Hint: Study the reminder while finding the value of
Ans. We can write
Similarly, we can get the value of other fractions
Q3.Express the following in the form of P/q,, where p and q are integers and q≠0
c) 0.001001…..
Ans.
x = 0.66666……(1)
10 x = 6.6666….(2)
Subtracting (1) from (2) we get
9x = 6
x=0.47777…..(1)
Multiplying (i) by 10 because one digit after the decimal is not repeating
10x =4.777…………..(2)
Multiplying eq.(2) by 10 because after decimal only one digit is repeating
100x =47.777…….(3)
Subtracting (2) from (3)
90x =43
An s c) let x =0.001001……..(1)
Multiplying eq.(1) by 1000 because after decimal three digits are repeating(i.e 001)
1000x = 1.001001……………(2)
Subtracting (1) from (2)
We get
999x = 1
See the video , how to insert a number of rational numbers between two rational numbers, and how to write a recurrent decimal number in the form of p/q.
Q4.Express 0.9999….in the form of . Are you surprised by the answer ? Discuss why the answer makes sense with your teacher and classmates.
Ans. Let x = 0.9999…..(1)
Since after decimal only one-digit i.e 9 is repeating so multiplying the equation(i) by 10
10 x = 9.9999………..(2)
Subtracting (1) from (2) , we get
9x =9,
Yes we get surprised to get such an answer but it makes a sense because 0.999999….., expansion never
ends, it can’t be less than 1, so it would be equal to 1.
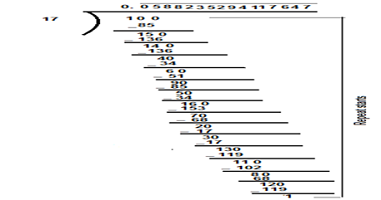
Q5. What can the maximum number of digits be in the recurring block of digits in the expansion of ? Perform the division to check your answer.
Ans. Dividing 1 ÷ 17
We observed that on dividing 1 by 17, the digits start to repeat after a maximum number of 16 digits
Q6.Look at several examples of rational numbers in the form ( q≠0), where p and q are integers with no common factors other than 1 and having terminating decimal representations (expansions). Can you guess what property q must satisfy?
Ans. The examples of rational number which are finite decimal with the condition that there is no common factor between p and q except to 1 are following
It is clear from the above example that the denominator should have the factor 2 or 5 or both for a rational number to be a finite decimal number. Therefore the factor of q must be in the form of
where m and n are whole numbers (0,1,2,3…)
.
Q7.Write 3 numbers whose decimal expansions are non terminating non-recurring.
Ans. All unresolved roots as an example are the numbers whose decimal expansion are non terminating non-recurring.
Q8. Find three different irrational number between
Ans. Converting both numbers into decimal up to two places
9. Classify the following numbers as rational or irrational.
i) √23
ii) √225
iii) 0.3796
iv) 7.478478…
v) 1.1011001000100001…
Ans.
(i) The square root of 23 is not a integer so it is an irrational number
(ii) The square root of 225 is 15, so it is a rational number
So it is a rational number
(iv) 7.478478…, is a non terminating recurrent decimal can be written in the form of p/q, so it is a rational number.
(v) 1.1011001000100001…is a nonterminating non-recurrent decimal so it is an irrational number.
Exercise 1.5
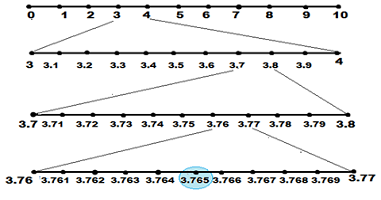
1. Visualize 3.765 on the number line by using successive magnification.
Step 1- Scanning the number line between 3 and 4 and locating 3.7
Step 2- Scanning the number line between 3.7 and 3.8 and locating the number 3.76
Step3- Scanning the number line between 3.76 and 3.77 and locating the number 3.765
2.Visualize on the number line, up to 4 decimal places.
Ans. = 4.262626…
We have to show 4.2626 on the number line
4.2 will be between 4 and 5 s follows
4.26 will be between 4.2 and 4.3 as follows
4.262 will be between 4.26 and 4.27 as follows
4.2626 will be between 4.262 and 4.263 as follows
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 1-Number Systems
EXERCISE 1.5
Q1. Classify the following numbers as rational or irrational
(i) 2 – √5
(ii) π
(v) 2π
Ans.
(i)In 2 – √5, √5 is a non-recurrent infinite decimal number, the difference or the sum of a number with non-recurrent infinite decimal number is always a non-recurrent infinite decimal number, so the number 2 – √5 is an irrational number.
(ii) π is the ratio between circumference and diameter, although for the calculation purpose its approximate rational value 22/7 is taken, basically, the ratio between circumference and diameter always comes non-recurrent infinite decimal, so π is an irrational number.
√2, is a non-recurrent infinite decimal number, the result of the division of a number and a non-recurrent infinite decimal number is always a non-recurrent infinite decimal number, so 1/√2 will be an irrational number.
(v) π, is an irrational number, product of a rational and an irrational number is always an irrational number, so 2π will be an irrational number.
Q2. Simplify each of the following expressions
(i) (3 + √3)(2 + √2)
(ii)(3 + √3)(3 – √3)
(iii) (√5 + √2)²
(iv) (√5 + √2)(√5 – √2)
Ans.
(i) (3 + √3)(2 + √2)= 3(2 + √2)+√3(2 + √2) = 6 + 3√2 + 2√3 +√6
(ii)(3 + √3)(3 – √3) = 3² – √3² 9 – 3 = 6 [ (a +b)(a–b) = a² – b²]
(iii) (√5 + √2)² ,since (a + b)² = a² + b² + 2ab
Therefore, (√5 + √2)² = √5² + √2² + 2√5×√2 = 5 + 2 + 2√10 = 7 + 2√10
(iv) (√5 + √2)(√5 – √2)
= √5² – √2²[ (a +b)(a–b) = a² – b²]
= 5 – 2 = 3
Q3. Recall, π is defined as the ratio of the circumference(c) of a circle to its diameter(d). That is .This seems to contradict the fact that π is an irrational number, How will you resolve this contradiction?
Ans. The circle is such a figure that anyone of both quantity circumference or diameter or diameter and circumference might be irrational because the exact length of any figure can’t be finite, mathematicians have measured this ratio which is observed by them as a non-recurrent infinite decimal. So, there is no doubt that π is an irrational number. We take the approximate value of this ratio 22/7 for the purpose of calculation which is a rational number.
See the video clear the concept,rational numbers,irrational number,surds and π
Q4. Represent √ 9.3 on the number line.
Ans.
• Drawing AB line segment of the length 9.3 units on the number line, extending it by 1 unit, marking the new point C
• Drawing the perpendicular bisection of AC and name the point of intersection by O.
• Draw a semicircle of the radius CO.
• Draw a perpendicular line on AC through B, which intersects the semicircle at C.
• Draw an arc of the radius BC on the number line taking B as a center and mark point D.
• BC =BD =√9.3
So, in the number line B represents 0, C represents 1 and D represents √9.3
Q5.Rationalize the denominator of the following expressions
Ans.
Multiplying the denominator and numerator by √7
Multiplying the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator (√7 +√6)
Multiplying the denominator and numerator by the conjugate of the denominator (√5 –√2)
Multiplying the denominator and numerator of the given fraction by the conjugate of the denominator (√7 + 2)
See the video for Q5
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 1-Number Systems
EXERCISE 1.6
Q1. Find
Ans.
Factorizing,
Factorizing 32=
Q2. Find
Ans.
Q3. Simplify
Ans.
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution