What is a potential difference across an electric field?
Clear your concept what is a potential difference across an electric field? You can understand the potential difference by questioning yourself and visualizing it how does the wind blow from one place to another place. The wind blows from a higher pressure zone to a lower pressure zone, the factors which maintain atmospheric pressure are humidity, dust, pollution etc. The atmospheric pressure is the pressure of air exerted by air all around us to our body. In Rajasthan during summer the sand existing in the Thar desert is heated, the sand mixes with surrounding air particles increase atmospheric pressure. The pressure of other area becomes lesser than this makes the gusty and dusty air flows from Rajasthan to other areas. The water flows from a higher altitude to a lower altitude. The matter flows from high concentration to lower concentration.
As the flow of wind required a pressure difference between two areas, the flow of liquid is needed the difference in altitudes and flow of matter is needed the difference in concentration, in the same way, the flow of charge is also needed an electric potential difference between two points.Now the question is what is the potential difference before we talk about potential difference let’s think what is a work in physics,it is simply defined as the product of force and displacement.
Also, Study our posts
Electric Current and its Heating Effect
Complete Detail of Electric Resistence and Conductance
NCERT solutions of class 10 science chapter 12- Electricity
Human Eye – Structure and functions of each part
Myopia, Hypermetropia and Presbyopia
NEET Sylabus and its preparation
Here, the points are discussed as follows.
- Potential Energy in gravitational and Electrical fields
- Electrical Potential
- Electrical Potential Difference
- The causes of lightning and thunder
What is a potential difference across an electric field?
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
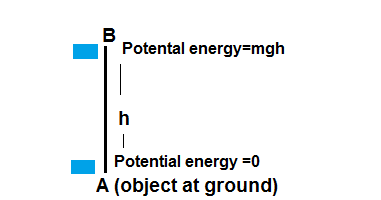
Let an object of mass m is lifted up to the height of h, then the work is done =F.d. Here F = gravitational force applied by the earth on the object= mg, g = gravitational acceleration and d= h
The work is done = mg.h
Now we shall talk about what is energy, energy is defined as the capacity of doing work, or it is simply a transfer of energy from one object to another object. The work done on the given object when lifted to a certain height h is the energy transferred to the object from the person who lifts the object. Initially, when the object was on the ground, its energy was accommodated into the earth, so at the ground, its energy is supposed as zero. In the height of h the energy of object = mgh, the object is stationary so this energy is the potential energy of the object.
Here we can say the potential of point B, is mgh in a gravitational field.
Now we will discuss the electric potential of a point in an electric field, The electric potential of a point in an electric field is the work done on a unit charge while displacing it from infinity to that point. The electric field could be supposed in solids, liquids, gas or anywhere within the universe. For defining the electric potential of a point we need a point of reference, we take that point of reference infinity, the electric potential of the infinity is supposed as zero. The electric potential of two points in an electric field from the same point of reference (i.e infinity) causes the flow of electric current that is known as electric potential difference or simply the potential difference between those points. The electric potential of a point within the electric field is actually the capacity of a charged particle to move within an electric field.
Electric potential difference across a conductor, V = VA – VB
Where VA – VB are the potential of both ends of the conductor
A unit charge is = 1 coulomb charge
The work is done on a 1-coulomb charge = V
The work is done on charge Q in placing it from A to B will be
W = VQ
How does electric potential difference generate between clouds and the earth? The water vapor rises above in the sky because it is hotter than the air in the earth when it loses its energy, the temperature reaches to below freezing temperatures and water vapor changes into tiny crystals of the ice. The frictions between the crystals generated electrons and two kinds of charged particles are formed, the negative charge heavier than positive sink below at the bottom of the cloud. An electric potential difference generated due to opposite charges within the clouds which causes flow of the current inside the cloud, when this voltage is in excess, lightning and thunder is produced.
You can see the video to understand it deeply
Sometimes when some shorts of positive charge is generated on the surface of the earth, a high potential difference developed between clouds and the earth which results in large amount of current flow from cloud to the earth which is capable to glow 100 w of bulb for 100 days, it is known as fall of lightning.
The Importance of Studying this post
The topic Potential difference is useful for clearing the scientific concepts of Electricity which is one of the chapters of every 10-grade student of each type of educational board.To clear the concept on potential difference is necessary for studying higher class ‘Electricity’ a branch of Physics.
We will be carrying on such interesting topics for helping you in your study, so please tell us how did you like this post. Please don’t forget to subscribe to this blog for getting to be updated if you liked it .
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution