Electric Current and its Heating Effect
The heating effect of the electric current means when an electric current flows through a conductor, then it becomes heated, do you know what is the mechanism that the heater glows reddish, irons become heated when you connect those to an electric circuit.
In this post, you will get all the answers to the questions which confuse almost all students.
What is resistance, charge, electric current, the heating effect of current?
Why is the direction of electric current is opposite to the flow of electrons?
When a current flows through a conductor, heat is dissipated through it. This heat energy is nothing but a work done by a flowing charge to overcome the resistance of the conductor.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
You can also study
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Myopia, Hypermetropia and Presbyopia
Human eye structure and its function
Electrical resistance and conductance
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
What is a potential difference across an electric field ?
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
Resistance. It is a characteristic of a substance opposing the flow of electric current.
According to Ohm’s law, there is the following relationship between resistance, potential difference and current
V = IR
Where R is the resistance, V is the potential difference and I is the current
Charge
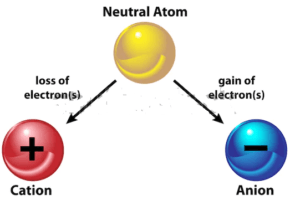
It is one of the properties of the substance when the exchange of electron takes place either the atom loses electrons or gains electrons if it lose electrons then atom transforms into cation and if it gains electrons it forms an anion. In the liquid, the cation drifts towards the negative electrode, and the anion drift towards the positive electrode maintaining the flow of electric current.
Most important questions of science
You can study our important posts
In solids or say metals, the current flow due to the flow of electrons, in metallic atoms, the valance electrons loosen because of the weak force of attraction exerted by the positive charge at the nucleus. These free electrons move freely within the conductor, when a battery is connected in the circuit a potential difference is developed across both of the ends of the conductor that compel the electrons to move from one end to another end generating the current. The emission of charge takes place in a quantized way. The charge emitted in the form of ne, where e= charge in an electron.
Q = ne
e=1.6×10-19C
n = 1C/(1.6×10-19C) = 6.25 ×1018
Therefore the number of electrons in 1C charge
What is current?
The current is the rate of flow of charge.
i = Q/t
Where i is the electric current, Q is the charge and t is the time
Latest Laptops and Desktops on very small EMI:no extra cost
Why is current shown in the direction from positive to negative?
The way in which current flows in the circuit is, the negative terminal emits ne negative charge and at the same time positive terminal emits a positive charge of the amount ne, it is the way how current flows in the circuit. The direction of the current is shown in the direction of a positive charge. Ever since Benjamin Franklin discovered electricity the direction of current conventionally is shown from positive to negative or it may be assumed that as all the types of current flow from high magnitude to lower magnitude as the wind blows from high pressure to lower pressure, water flows from a higher altitude to lower altitude, matter flows from high concentration to lower concentration,on the same way direction of current is logically is shown from positive to negative.
The SI unit of charge is the coulomb, so the unit of current = C/s= ampere
What is electrical energy?
Electric energy is the heat energy dissipated due to the resistance in the circuit.
The relation between work done, voltage and charge is given by the following formula.
V = W/Q
Here W is the work done on charge Q carrying it from one end of the conductor to another end against the resistance of the conductor, this work done is dissipated in the form of heat. this heat increases as per the time the current accessible in the circuit.
As we know V =iR, Q= it
Work = Energy transferred = Heat dissipated
W = H
V = W/Q ⇒ W = VQ
P= W/t = VQ/t = Vit/t = iV…….(i)
Power = Volage × Electric current
From Ohm’s law, we have, V = iR, substituting in eq.(i)
P = i× iR = i² R, Power = current²× Resistance
Since Work = Power/time ⇒Enegy = Power/time (Work↔Energy) ⇒H = P/t
Here energy means the heat dissipated through a current-carrying conductor
H = Pt = Vit from (i)
H = iR.it, From (4)
H = i²Rt
See the video
Henceforth the heating effect created by an electric current, through a conductor of resistance, R for a time period t is given by H = i²Rt. This relation is called Joule’s equation of electrical heating.
Application of heating effect is used in day to day life as an example of electric iron and heater, mostly an alloy nichrome is used made of nickel, chromium, and iron although third component iron could be substituted by other metals.
Nichrome is used in heating effect because it has high resistance, after even an excess of heating it is never oxidized, so it is long-lasting.
This is the study stuff useful for high school students, please write your comment and subscribe to this website if you liked it.
Important Science Notes for Class 9 and 10 grade
Class 10 CBSE Science Notes
Class 10 Biology Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board 2020-21
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Chemistry Practical Based Questions and Answers
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
Chemical properties of Acids and Bases-A note for grade 10 students
What is pH value and its importance in everyday life.
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted.
Difference between soaps and detergents
Why do the star twinkle but planets don’t
Light reflection, refraction, scattering, and dispersion
Extraction of metals as per the activity series
Ionic and covalent compounds and the difference between them
Food chain and food web in an ecosystem
Class 9 CBSE Science Notes
Three Laws of Motion: Class 9 CBSE
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat -Class 9 CBSE notes
What is an atom,molecule and atomicity of a substance?
How to determine Valency,net charge of an ion and Molecular formula of a substance.
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
The Complete Detail of Archimedes Principal
Average Speed and Average Velocity: Differences
How to evaluate recoil velocity of gun
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?
Molar mass,molecular mass and mole concept
What is second law of of motion ?
What is universal law of gravitational force
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution






I found your blog web site on yahoo and examine just a few of your early contents. Proceed to keep up the very good operate. I simply additional up your RSS feed to us RSS Bar News Reader. Searching for forward to reading super from you later on!?I am usually to blogging and i really respect your posts.