Most Important Science Questions For Class 10 for CBSE Board 2022-23
Most Important Science Questions For Class 10 for CBSE Board 2022-23 are created here for helping the class 10 science CBSE student so that they could get an idea about the type of science questions that might be asked in Class 10 CBSE board 2022-23. The CBSE exams might have started in the month of February 2023 and we hope every student would have been preparing well or many of them may be disappointed to their preparation as they had expected, most of the students will be anxious by taking their science and maths paper,so you need not to worry because we have explored the science questions which are most important for CBSE Class 10 Board exam 2022-23.
After having gone through their CBSE textbook many of the students want to go through the most important or extra questions of science and maths to get excellent marks. In these exams of the CBSE board, all students with the preparation of exams they also might be thinking of getting their favorite subject in class 11. The students who want to become engineers, scientists, doctors, professors, science or maths teachers or want to go in the fields where technical skills are required, they would have to study science and maths more deeply for strengthening their base. The most important questions of science published by future study point is very suitable for them. We have explained each question here in this post the most important questions of science technically so that the student could understand the depth of the subject.
Most Important Science Questions For Class 10 for CBSE Board 2022-23
To study the series of the most important questions will definitely enhance your knowledge in the subject and it will clear your concept which you didn’t clear in your daily routine of school classroom and tuition center. The questions in the most important questions of science have been selected by an experienced and subject expert teacher, so if you study it you will get a different flavor in the way of explanation. Here on this website you can download pdf of the most important questions or study these online. At the end of this post don’t forget to write your comment, you can subscribe to our website so that you could get an update of all the important posts published by us.
Most important questions and notes of science and maths class-10
CBSE class 10 science questions bank with answers
Class X important notes the magnetic effect of the current
CBSE Class X science most important questions with answers
Here in this website, you can clear doubts of science and maths
Most Important Science Questions For Class 10 for CBSE Board 2022-23
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Q1. Why do birds fly back to their nest in the evening?
Ans. Birds fly back to their nest in the evening because in their eye at retina only one type of photoreceptor cell cons exists which is responsible to see at day time, the photoreceptor rods which is responsible to see at night is absence in the retina of their eyes.
Q2. Why do you take time to find an object when you enter in the dimly lighted room from outside in the sun?
Ans. The pupil located at the center of iris an opening of the eye controls the amount of light entering it, when our eyes exposed to high intensive light its size decreases and when our eyes exposed to low intensive light its size increases ,when we enter in the dimly lighted room the pupil take time to increase its size to see the things, it is that’s why we take time to find the object.
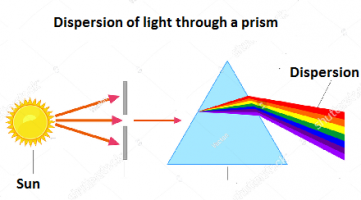
Q3. Why does a ray of light splits when passed from prism?
Ans. The rays of light split when passed through the prism because the light is composed of seven colors of different wavelengths, the colors in the spectrum of light refracted separately due to the difference in their wavelength, red color due to highest wavelength deviated least while on the contrary, the violet color due to least wavelength deviated most.
Q4. Why doesn’t the planet appear to be twinkling?
Ans. The planets are part of our solar system, they are very near to us as compared to the stars. The planets do not look like pinpoints as the star looks. The incoming rays from them is in a bunch which is not refracted to the extent that we could distinguish the change in their virtual images due to the variation in the atmospheric refraction.
Q5. Why we can’t see things very close to our eyes?
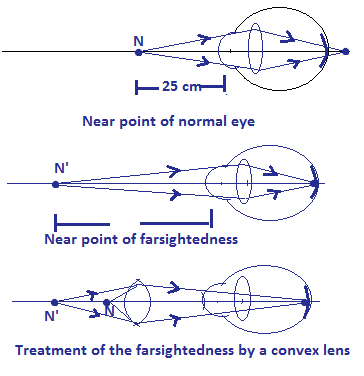
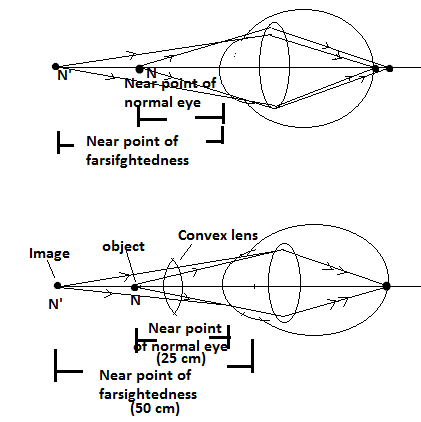
Ans. The crystalline lens of our eyes has the limit of decreasing its focal length to see the objects near to our eye, this limit is known as the near point of the eye, the near point of a normal eye is 25 cm, the things closer to near point looks blurred when seen by the eyes.
Q6. When we see any object through the hot air over the fire, it appears to be wavy, moving slightly. Explain.
Ans. When we see the objects through the hot air over the fire, the objects appear moving slightly, it occurs due to the refraction of the light. In this case, light travels from a denser medium to a rare medium(hot air) and again rare medium to denser medium. The changes in the density of hot air make changes in the path of refractive rays that changes in virtual positions of the object across the fire, it is that’s why it appears wavy or moving slightly.
Q7. Why does the sky appear blue on a clear day?
Ans. The sky appears blue on a clear day because in the clear sky only gas molecules of nitrogen, oxygen and few other gases, water vapor exist and there is the absence of dust, smoke whose particles are of larger size. In the clear sky presence of smaller particles scatter colors of smaller wavelengths, violet, indigo, blue and green, the scattering of the primary color green and blue by the particles due to which sky looks light blue in color.
Q8. What eye defect is hypermetropia? Describe with a ray diagram of how this defect of vision can be corrected by using an appropriate lens.
Ans. The hypermetropia is the defect of the eye due to which we can’t see the nearby object if the eye is unable to see the object located at 25 cm in front of the eye, its meaning is that the eye is suffering from hypermetropia. The distance closer to which we can not see the object known as the near point of farsightedness. The farsightedness occurs because the ciliary muscles of the crystalline lens become unable to constrict and as a result lens couldn’t reduce its focal length to see the nearby objects and image of the object forms far from the eye lens beyond the retina. It is treated by using a proper convex lens of certain power as per the near point of the eye.
Q9. A star sometimes appears brighter and some other times fainter. What is this effect called? State the reason for this effect.
Ans. The star is very far away from the earth, they look like a pinpoints, the light ray from them when entering to the earth it has to pass through the different layers of the earth’s atmosphere, as a result of refraction of light it reaches to our eyes, then we see the virtual image of the star. The density of the atmospheric layers changes due to the variation of temperature in the atmosphere of the earth so the path of refracted rays to our eyes changes, the virtual position of star changes, sometimes the stars appear fainter and sometimes appear brighter that is known as the twinkling effect of the stars.
Q10. A student cannot see a chart hanging on a wall placed at a distance of 3 m from him. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. How can it be corrected? Draw ray diagrams for the (i) defect of vision and also (ii) for its correction .
Q11. Why is the red color selected for danger signal lights?
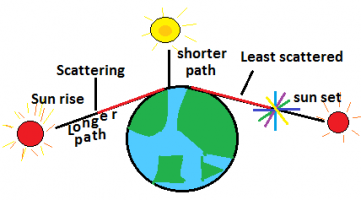
Ans. The red color is of the highest wavelength, which is not scattered by gas molecules present in the atmosphere rests all the colors scattered by the gas molecules, only red color reaches to our eyes from distant away and our eyes can see it even when we are far away from the object.
Q12. (a) A person cannot read a newspaper placed nearer than 50 cm from his eyes. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this defect. List its two possible causes. Draw a ray diagram to show how this defect may be corrected using a lens of appropriate focal length.
(b) We see advertisements for eye donation on television or in newspapers. Write the importance of such an advertisement.
Ans. A person cannot read a newspaper placed nearer than 50 cm from his eye, is suffering from the defect hypermetropia (farsightedness), in this defect, a person is unable to see the nearby object, the person becomes unable to see the object closer to a certain distance. The least distance at which he is capable to see the object is known as the near point of the farsightedness.
Causes.
(i) The efficiency of the ciliary muscles of the eye reduces thereby unable to contract, due to which the radius of curvature of the lens couldn’t decrease and the eye lens becomes thinner.
(ii) Inherited from the parents.
For correcting this defect, a convex lens of the appropriate focal length is required, which is calculated by applying lens formula
The near point of the given hypermetropic eye is 50 cm, which means if we place the object at a distance of 25 cm in front of the eye then the image of the object should be formed at 50 cm in front of the eye after applying the lens.
Therefore V =–50 cm, U = –25 cm, F = ?
F = 50
So, this defect can be corrected by using a convex lens of the 50 cm focal length.
(b) Ans. Death is the bitter truth of life through which everybody has to pass through, so before it, if we donate eye to a blind person then there are no good deeds comparable to this kindly act of humans among all the noble deeds. So, it is meaningful to advertise everywhere so that people could be aware to donate their eyes.
Q13. Explain giving a reason why the sky appears blue to an observer from the surface of the earth? What will the color of the sky be for an astronaut staying in the international space station orbiting the earth? Justify your answer by giving a reason.
Ans. Our atmosphere is made of small particles of the gases like nitrogen and oxygen molecules, water vapor and dust, majority of the particles are of nitrogen and oxygen, the size of these particles is very small, when light ray of sun falls on the atmosphere, the ray is scattered by these particles, as the light spectrum is of seven colors, due to the smaller size of particles, these particles enable the lower wavelength colors like violet, indigo, blue and green to scatter, since the principal colors are green and blue, the combining effect of these colors makes the sky looks light blue.
Q14. (a) List three common refractive defects of vision. Suggest the way of correcting these defects.
Ans. Its answer is in the link mentioned in the table.
(b) About 45 lac people in developing countries are suffering from corneal blindness. About 30 lac children below the age of 12 years suffering from this defect can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. How and why can students of your age involve themselves to create awareness about this fact among people?
Ans. About 45 lac people in developing countries are suffering from corneal blindness. About 30 lac children below the age of 12 years suffering from this defect, it is prevalent in developing countries because of the huge population and their lifestyle. The corneal blindness might occur due to the dust, ash, blow of something in the eye, working in a machine, bacterial infections in the eye, etc. The only way to treat corneal blindness is to transplant the cornea from a donated eye. The 30 lac of children are suffering from corneal blindness, eye donations campaign can save their life. This problem can be treated by increasing public awareness for eye donation. The students can play a crucial role in increasing awareness among the masses because everybody feels children’s emotions, children are altruistic and moreover they are connected to more people means students and their families so it is easier for them to communicate. The students can communicate either by means of a play in the school, through a drawing competition in the school or anywhere sponsored by an organization, speech or awaring the people door to door in their locality.
Q15. With the help of a labeled diagram, explain why the sun appears reddish at the sun-rise and the sunset.
Ans.
During the sunrise and sunset, the sun is at the horizon, these are the longest distances of the sun compared to other positions of the sun with respect to us. The light ray has to pass through a long path, so all the colors of smaller wavelength scattered away by the gas molecules in the atmosphere and the red color being of largest wavelength scattered less so become capable to reach to us, it is that’s why the sun looks reddish at the sun-rise and the sunset.
Q16. (a) What is the dispersion of white light? What is the cause of this dispersion? Draw a diagram to show the dispersion of white light by a glass prism.
Ans. Dispersion of white light- The light ray when passed through a prism it split up into seven colors, violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red, this is known as the dispersion of the light, it occurs because all the colors have their individual wavelengths and hence have different velocities. The light ray travels from one medium to another medium it is refracted by an angle. When light enters the prism these colors deviated in different paths because of the difference in their individual velocities then again the light ray travels from glass to air, again their velocity changes and that is why the colors dispersed through different angles and dispersed separately.
(b) A glass prism is able to produce a spectrum when white light passes through it but a glass slab does not produce any spectrum. Explain why?
Ans. When light ray enters the glass prim, it refracts by a certain angle. Since light travels here from air to glass, the speed of all the colors changes due to the difference in their individual wavelengths, all the colors deviate separately, the light ray further travels from glass to air again the speeds of these color changes and dispersed into seven colors. In case of glass slab when light ray enters the slab, it also dispersed in the first interface but when it again travels from glass to air, these colors recombine due to the fact that ray is transmitted parallel to the incident ray, it happens because both interfaces of the planes are parallel to each other, unlike the prism.
Q17.Give reason for the following:
- Arteries are thick-walled blood vessels.
- Viens are thin-walled blood vessels
- Veins have valves in them.
Ans. Arteries are thick-walled because more blood pressure is needed to pump out the oxygenated blood from the heart to all parts of the body.
Viens are thin-walled blood vessels because veins carry deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body since blood has to transfer from arteries to each cell so veins are needed less pressure so that after the process of respiration blood could be transferred into it.
Veins have valves in them for the prevention of backflow of the blood.
Q18. Why is the energy needs in plants is very less as compared to animals? Explain?
Ans. The plants are autotrophic, the food is prepared by them during photosynthesis is supplied to each part to fulfill cellular requirements only, in their body, there are numbers of dead tissue which are not needed any kind of energy, they don’t have complicated organs like animals which are needed a lot of energy to function, in other words, they don’t move, mate and many other physical activities as the animals do, so they are required less energy for surviving their life.
Q19.Why cesium and gallium melt in our palm?
Ans. The cesium and gallium have lower melting points compared to other substances, it is slightly more than the room temperature, therefore when these are managed to keep on our palm, due to the heat imparted by our palm, these started to melt.
Q20.Why does magnesium ribbon start floating in hot water?
Ans. Magnesium can react with hot water. It forms magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen when the reaction of hot water takes place with it, due to the bubble formation of hydrogen the magnesium ribbon sticks to the surface of the water and starts to float.
If you liked this post then please subscribe to our website and make your comment.
Q21. Explain why a ray of light passing through the center of curvature of concave minor gets reflected along the same path.
Q22. What is the important function of the presence of ozone in the earth’s atmosphere?
Q23. The dark reaction of photosynthesis does not need light. Do plants undergo dark reactions at night? Explain.
Q24. How are we able to see distant and nearby objects clearly? Which part of the eye helps in changing the curvature of the lens? Why no image is formed at the blind spot?
Q25. (a) Which property of carbon leads to the formation of a large number of compounds? Define it.
(b) What is the functional group in the following molecules?
(i) CH3CH2CH2OH
(ii) CH3COOH
Q26. (a) Why magnification is taken negative for real images and positive for virtual images?
(b) Why convex mirror is used in rearview mirrors and not a concave mirror?
Q27. (a) What are ‘magnetic field lines’? How is the direction of a magnetic field at a point determined?
(b) Draw two field lines around a bar magnet along its length on its two sides and mark the field directions on them by arrow marks.
Q28. (a) Mention the pH range within which our body works. Explain how antacids
give relief from acidity. Write the name of one such antacid.
(b) Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How does the pH will change as it turns to curd? Explain your answer.
(c) A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk. Why does this milk take a longer time to set as curd?
(d) Mention the nature of toothpaste. How do they prevent tooth decay?
Q29. Atoms of eight elements A. B. C. D, E, F. G and H have the same number of electronic shells but the different number of electrons in their outermost shell. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound. This compound is added in a small amount to almost all vegetable dishes during cooking. Oxides of elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of D is almost neural. Based on the above information answer the following questions:
(i) To which group or period of the periodic table do the listed elements belong?
(ii) What would be the nature of the compound formed by a combination of elements B and F?
(iii) Which two of these elements could definitely be metals?
(iv) Which one of the eight elements is most likely to be found in the gaseous state at room temperature?
(v) If the number of electrons in the outermost shell of elements C and G are 3 and 7 respectively, write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of C and G.
Q30. Mention the essential material (chemicals) to prepare soap in the laboratory. Describe in brief the test of determining the nature (acidic/alkaline) of the reaction mixture of the saponification reaction.
Q31. Write two precautions to be taken while identifying different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed.
Q32. A student is to conduct an experiment to show CO2 is released during respiration. List two precautions that he/she must take for obtaining correct observation.
Q33.What is the benefit of the residual volume of air in the respiratory process?
Q34.List two different functions of the pancreas in our body.
Q35.Name the plant Mendal used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and F2 generation when he crossed tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in the F2 generation.
Q36.List two differences between acquired traits and inherited traits by giving an example of each.
Q37.Explain the following.
- Sodium chloride is an ionic compound that does not conduct electricity in the solid-state whereas it conducts electricity in the molten state as well as in an aqueous solution.
- Reactivity of aluminum decrease if it is dipped in nitric acid.
- Metals like calcium and magnesium are never found in their free state in nature.
Q38.What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye.
Q39.Draw the structure of neurons and explain its function.
Q40.What are the major parts of the brain? Mention the function of different parts. What constitutes the central and peripheral nervous systems. How are the components of the central nervous system protected?
Q41.Mention one function of each hormone.
- Thyroxine
- Insulin
- Adrenaline
- Growth hormone
- Testosterone
Q42.Name various plant hormones. Also, they give their physiological effects on plant growth and development.
Q43.What is the reflex actions? Give two examples, explain a reflex arc.
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution