Class 11 Chemistry Types of Chemical Bond: Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Cause of Chemical Bonding: Two atoms form a chemical bond in order to achieve an octet or noble gas configuration,for achieving an octet atoms gain, loss or share electrons. According to modern theory, chemical bonds are formed by atoms or molecules because these particles tend to lower their potential energy for gaining a stabilized state.
The kind of force between two atoms or molecules is known as chemical bonding,
There are two types of chemical bonding,
(i)Interatomic Chemical Bond: Chemical bond between atoms, interatomic chemical bonds are strong, these are of 3 types
(ii)Intermolecular Chemical Bond: Chemical bond between molecules, intermolecular chemical bonds are weak
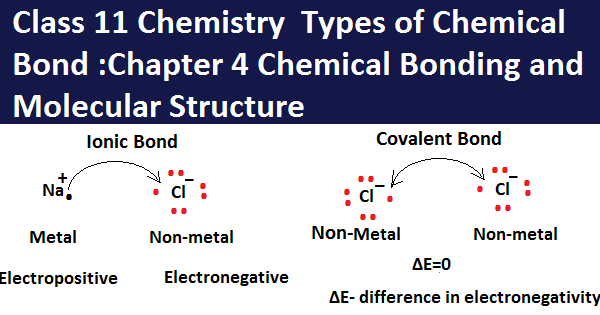
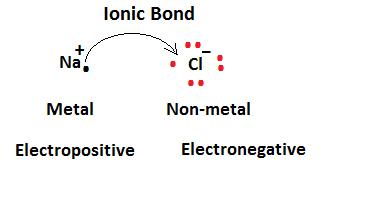
(i)Ionic Bond: Ionic bonds exist between two ions, in this both the ions are bounded by a force known as electrostatic force. The ionic bond is held between metal and nonmetallic atom in which the metallic atom donates the number of electrons forming cation and non-metallic atoms gains all the electrons donated by the metallic atom and forms anion.
In ionic compounds, one atom has a tendency of gaining electrons and another atom has a tendency to receive electrons. Ionic compounds are crystalline in nature, these compounds when dissolved in water dissociate into their constant ions and conduct electricity.
(ii) Covalent Bond: Covalent bond exist between the atoms which have the least difference in their electronegativity or almost the difference of zero. The covalent bond held between atoms of non-metals. These covalent compounds are insoluble in water and bad conductors of electricity.
Covalent compounds are formed by sharing of electrons, other examples of covalent compounds are diamonds, the formation of all the molecules, all the molecules of hydrocarbon if there is sharing of two electrons it forms a single covalent bond,if sharing is of 4 electrons it forms a double bond and if there is sharing of 6 electrons it forms a triple bond.
As an example formation of an oxygen molecule is an example of a double covalent bond, formation of a nitrogen molecule is an example of a triple covalent bond.
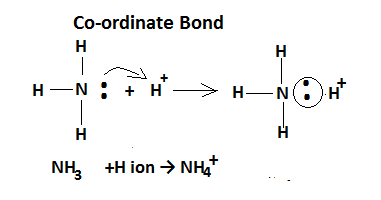
(iii)Co-ordinate Bond: This type of bond is held between a non-metallic molecule or ion and another non-metallic ion.Generally, the coordinate bond exists in the formations of polyatomic ions as example in the formation of an ammonium ion one molecule of ammonia donates its lone pair of electrons to the hydrogen ion.In the case of coordinate bonds electrons are shared from the same atoms,one atom coordinates with another atom in completing the octet , therefore it is called a coordinate bond.
(iv)Metallic Bond: Metalic bonds exist between the atoms of the same metals, there are free electrons in the metals which causes extensive bonding between the atoms.The metallic bond is held between the positively charged atoms of a metal, freeing electrons from the atom results the formation of a lattice of cation, the force of attraction between the cation is known as a metallic bond. The metallic bond exists in d -block elements like Cu, Fe,Mg, etc.
Intermolecular Chemical Bond: Chemical bond between molecules, intermolecular chemical bonds are week
(i)Vanderwal Force: The Vanderwal bond exists between the molecules of the same compound, this is the force of attraction between the atoms of two molecules in the lattice of a solid .liquid and gas. Atoms are polarised into two disparities positive end and negative end, one positive end of an atom attracts the negative end of the other atom which results in a net force of attraction between the molecules and it is that’s why all the molecules of the same matter held together.
The presence of free electrons makes the metals malleable, ductile, lustrous, and good conductors of electricity and heat.
(ii)Hydrogen Bond: A hydrogen bond takes place when it is bounded by a covalent bond with a highly electronegative atom.A hydrogen bond is between the molecules of hydrogen compounds formed with fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen. As an example in the molecule of HF, in the lattice of HF fluorine atom shares two electrons with the two hydrogen atoms of two molecules of HF .
The hydrogen atom attracts the shared electron towards it makes it slightly negative and the other end becomes slightly positive,so the negative end of the molecule attracts the positive end of another molecule,it is all about the hydrogen bond.
Circular Motion: Angular velocity and angular displacement
Projectile Motion Class 11 CBSE Physics Chapter 4 Motion in a Plane
Addition of Vectors: CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 -Motion in a Plane
Don’t forget to write a comment, subscribe us for the posts related to your study
Electronic Configuration of s,p and d orbitals
Atomic Radius Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 3 Periodicity in Properties
Why does a Rainbow look like a Bow?
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
Class 10 Maths Question Paper CBSE Half Yearly Exam 2022 With Solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution