How to solve NCERT-specific maths questions of Mensuration
Mensuration is the branch of mathematics in which we study physical quantities like area, perimeter, surface area, and volume of all geometrical figures. The questions of mensuration compulsorily are part of the maths textbook of every class and the questions of mensuration are also asked in every competitive exam so this post of Future Study Point is useful for everybody. Mensuration is classified into two parts (i) Two-dimensional geometrical figure (ii) Three-dimensional geometrical figure, here we will discuss few specific questions of mensuration for which students generally needed help from his tutor or teacher. These are the specific questions of mensuration which are asked in the CBSE board exam and in the competitive exam. We hope you will definitely get help from the way of solving the questions. Questions are explained through a step by step method by an expert of maths so that everybody could understand the way of solution.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
In this post, we have given 7 examples based on the Mensuration with solutions which are generally asked in various entrance exams. The solutions of these examples will let you know about the way of solution to the mensuration question. For the practice we also have created 8 questions which you can easily solve, if you face any problem then don’t hesitate to write in the comment box, you are free to communicate with us.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
How to solve NCERT specific maths questions of Mensuration
Example1.The length of a squire field is 25 m, how much area will be of the path of the width 3.5 m around it.
Ans. In this question, a squire field of the length 25 m is given

A path of the width 3.5 m is given around it given in the second figure
There are two squires one is ABCD which is circumscribed by another squire EFGH
Length of the square EFGH will be = 25 m + 2 × 3.5 = 25 +7 =32 m
Area of path = Area of squire EFGH – Area of squire ABCD
Area of path = 32 × 32 – 25 × 25
Area of path = 1024 – 625
Area of path = 399 sq.m
Therefore the area of bath = 399 sq.m
In the same way, you can solve all the following questions based on rectangles and circles.
Q1-The inside perimeter of a running track (shown in Fig. 20.24) is 400 m. The length of each of the straight portions is 90 m and the ends are semi-circles. If the track is everywhere 14 m wide, find the area of the track. Also, find the length of the outer running track.
Q2-Mrs. Kaushik has a square plot with the measurement as shown in the figure. She wants to construct a house in the middle of the plot. A garden is developed around the house. And the total cost of developing a garden around the house at the rate of Rs. 55 per m2.fig.link
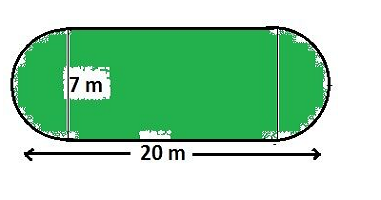
Q3.The shape of a garden is rectangular in the middle and semicircular at the ends as shown in the diagram. Find the area and the perimeter of this garden [Length of rectangle is 20 – (3.5 + 3.5) metres].
Q4. The diagram of the adjacent picture frame has outer dimensions = 24 cm × 28 cm and inner dimensions 16 cm × 20 cm. Find the area of each section of the frame, if the width of each section is the same.
Example.2- A flooring tile has the shape of a parallelogram whose base is 24 cm and the corresponding height is 10 cm. How many such tiles are required to cover a floor of area 1080 m2?
Ans- In this question, we are given the size of tiles which is in the shape of a parallelogram having the base of 24 cm and corresponding height 10 cm and the area of floor the tiles to be installed.
Area of parallelogram = Base × Altitude
Area of tile = 24 × 10 = 240 sq.cm
Let the number of tiles required to cover the floor area = n
n= (Area of the floor)/Area of tile
Because floor area is given in sq.m, therefore, converting it into sq.cm
1o80 m²
= 1080×100 ×100 = 10800000 cm²
n = (10800000)/240 = 45000
Therefore 45000 tiles are required to cover the floor
Solve the following similar questions
Q5.The floor of a building consists of 3000 tiles which are rhombus shaped end each of its diagonals is 45 cm and 30 cm in length. Find the total cost of polishing the floor, if the cost per m2 is Rs. 4.
Q6.What will be the labor charge for tiling a hall 72 m long and 18 m wide at the rate of Rs 12 per sq.m?
Example 3. Find the area of a rhombus whose side is 6 cm and whose altitude is 4 cm. if one of its diagonals is 8 cm long, find the length of the other diagonal.
Ans. Rhombus is a parallelogram have all sides are equal
Area of rhombus = (1/2) product of both diagonals = Side ×Corresponding altitude
Let one of the diagonal is d
(1/2) 8d = 6×4
d = (24/8)×2 = 6
Therefore another diagonal is of the length 6 m
Solve these questions based on rhombus
Q7.The perimeter of a rhombus is 420 meter and one of its diagonal has a length of 40 meters. Find the area of the rhombus.
Q8.The top surface of a raised platform is in the shape of a regular octagon as shown in the figure. Find the area of the octagonal surface.
Example4-Daniel is painting the walls and ceiling of a cuboidal hall with length, breadth, and height of 15 m, 10 m, and 7 m respectively. From each can of paint 100, m2 of the area is painted.
Ans. The area to painted is- four walls and ceiling, therefore determining the area of four wall and ceiling
Four walls area = 2h(l + b) and area of ceiling = lb
Area of both walls & ceiling = 2h(l + b) + lb
l=15 m, b = 10 m, h = 7 m
= 2 ×7(15 + 10) + 15 × 10
=14 × 25 + 150
= 350 + 150
= 500 sq.m
number of canes reqired to paint the area = area to be painted/capacity of cane
Number of canes required to paint the given area = 500/100 = 5
Therefore 5 canes are required to paint the given area
Example5-The lateral surface area of a hollow cylinder is 4224 cm2. It is cut along its height and formed a rectangular sheet of width 33 cm. Find the perimeter of rectangular sheet.
Ans. The lateral surface area of the hollow cylinder is given to us = 4224 sq.cm
The hollow cylinder is cut along its height and formed a rectangular sheet of the width(h) 33 cm and its length would become perimeter of circular ends as shown in the figure.

The lateral surface area of cylinder = 2πrh = lh
lh = 4224
l × 33 = 4224
l = 4224/33 = 128
Therefore the length of rectangular sheet = 128 cm
The perimeter of the rectangular sheet = 2(l + b) =2(l + h)
⇒2(l + h) = 2(128 + 33) = 2×161 = 322
Therefore the perimeter of the rectangular sheet is 322 cm
Example6-A road roller takes 750 complete revolutions to move once over to level a road. Find the area of the road if the diameter of a road roller is 84 cm and length is 1 m.
Ans. The road roller covers the area of road equal to its curved surface area in 1 revolution = 2πrh
r = 84/2 = 42 cm = 0.42 m
Curved Surface Area of road roller = 2πrh = 2×(22/7)×0.42 ×1 = 2.64
The roller takes 750 revolutions to level the road
∴ The area of road = Number of revolutions taken by the road roller×CSA of road roller750 × 2.64 = 1980
Therefore the area of road = 1980 sq.m
Example7-Water is pouring into a cuboidal reservoir at the rate of 60 liters per minute. If the volume of the reservoir is 108 m3, find the number of hours it will take to fill the tank.

Ans. The speed of water pouring into the reservoir = 60 liters/minute.
Converting 60 liters/minute into cubic.meter/minute
⇒ 1 cubic.meter = 1000 l
⇒60 l = 60/1000 = 0.06 cub.meter/minute
∴ The speed of the water in filling the tank = 0.06 cub.meter/minute
Volume of reservoir = 108 cub.meter
Time to be taken to fill the reservoir
=Volume of reservoir/speed of water pouring into it
=108/0.06 = 1800
Therefore the reservoir takes 1800 minutes (30 hours) to fill the tank.
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution



