Class X Science Important notes of Chapter 12- Magnetic effect of electric current-Second part
Here Class X Science Important notes of chapter 12- Magnetic effect of the electric current are created to help you in preparations of your forthcoming exams. . All notes of the class 10 science chapter 12-Magnetic effect of the electric current are prepared by 25 years experienced teacher.Here in future study point, you can study NCERT Solutions of science and maths from class 9 to 12, our articles on science and maths, sample papers, solutions of previous year question papers, our blogs for competitive exams and online jobs.
Download PDF-Class 10 Science Important notes of the chapter 12-Magnetic effect of electric current
PDF-Class 10 science NCERT Solutions of chapter 13-Magnetic effect of Electricity

You can also study
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
NCERT Solutions of all chapters of Maths for Class 10 from Chapters 1 to 15
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science : Chapter 1 to Chapter 15
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Maths : from chapter 1 to 15
Science Notes Class 10 CBSE
Functioning of Soda-Acid Fire Extinguisher
Important salts class 10 CBSE sceience notes
Reflection, Refraction, Dispersion, and Scattering
What is the difference between the soap and the detergent ?
Male and Female Reproductive System: Complete Anatomy for Grade 10 Students
The structure and anatomy of the Heart
Ionic and covalent compounds and the difference between them
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted.
Human Eye – Structure and functions
Myopia, Hypermetropia, and Presbyopia
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
Complete detail of electrical resistance and conductance
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
Science Notes Class 9 CBSE
Determining Valency, Net Charge and Molecular Formula
Structure and Function of Cell : Cell Biology
Archimedes Principle: Complete detail
Average Speed and Average velocity
The universal law of gravitational force
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat
Class 10 Science Important notes of chapter 12-Magnetic effect of electric current-II
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Q1. What is a solenoid? Show the magnetic field through a solenoid.
Ans. The solenoid is a winding of wire in the shape of a cylinder, it works just like a bar magnet one of its end connected with the negative terminal of the battery become north pole and other end connected with the positive terminal become a south pole of the solenoid. The direction of the magnetic field is followed by the right-hand thumb rule, If the direction of current in it is from right to left then the direction of the field is anticlockwise and if the direction of current is from left to right then field direction is clockwise. The magnetic field around a solenoid is shown bellow. The strength of the magnetic field around it is proportional to the amount of current flowing in it and the number of turns in the coil.
Latest Laptops and Desktops on very small EMI:no extra cost
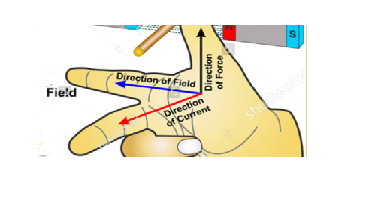
Q2. State Flaming’s left-hand rule.
Ans. If three fingers, middle finger, thumb and four fingers of the left hand are to be stretched perpendicular to one another in such a way that the middle finger shows the direction of the current, four-finger shows the direction of the magnetic field then thumb will show the direction of magnetic force.

Q3. State Flaming’s right-hand rule.
Ans. The right-hand fingers thumb, four-finger, and middle finger are to be stretched 90° to one another in such a way that four-finger shows the direction of the magnetic field, thumb shows the direction of motion of the conductor then middle finger will show the direction of induced current in the conductor.
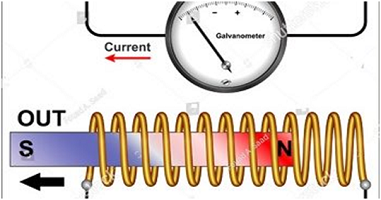
Q4.What is electromagnetic induction?
Ans. When a conductor moves in a magnetic field or magnetic field around it varies a voltage is produced across the ends of the conductor known as electromagnetic induction and the kind of current passed through it is known as induced current.
As an example, if in a coil we insert a magnet directing its north pole into the coil then the indicator of galvanometer deflected left side, it is because of a voltage produced across the conductor due to the change in the magnetic field.
When we enter the magnet directing its south pole inside it then the indicator of the galvanometer deflects the right-hand side, it is because of the direction of current changes across the coil.
Q5.Draw a label diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and working. What is the function of a split ring in an electric motor?
Ans.
The basic principle of an electrical motor is based on the property of magnets that opposite poles attract each other and similar poles repel.
In the first figure, a couple of magnetic force between N-S and S – N tends to rotate the suspended magnet at the middle of a showcase magnet. On the same case, a coil between two poles N and S of two different magnets also arranged to be rotated .
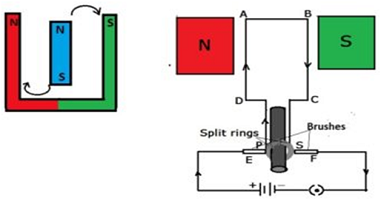
Principle- The electric motor is based on the principle of electromagnetic, the rule is, if a charge moves or current is flowing through a conductor in a magnetic field then a magnetic force is exerted on the charge or conductor. The direction of the force on the conductor is given by the right-hand rule of Flaming which is already discussed in question number (3).
Working- When motor is switched on , the current moves from D to A perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field from left to right then a downward force is applied on AD which tends to move AD in the downward direction and when current moves B to C an upward force is applied on BC which tend to move BC in the upward direction, a couple of forces in AC and BC rotate the coil between N and S pole of both magnet.
Role of the split ring– The split rings are connected to the brushes which are used to pass current from the circuit to the armature(coil) , the split ring changes the direction of electric current and maintains the direction of current in one way only that’s why these split rings are known commutator (means communicator) . It works like this after half rotation position of AD is replaced by BC and the direction of current reversed, the split rings S and P also change their positions in place of each other but brushes E and F remains on their position, so the split ring S come in contact of the brush E and the direction of current is maintained in a unidirectional way or in other words the current flows in the same direction as before and armature of the motor carried to rotate in the same direction.
Link for the study of chapter 12- Magnetic effect of the electric current(I part)-LINK
You can compensate us
Paytm number 9891436286
The money collected by us will be used for the education of poor students who leaves their study because of a lack of money.
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution



