Atomic Radius Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 3 Periodicity in Properties
Atomic Radius is one of the properties of the elements which changes periodically from left to right in a period and from top to bottom in a group in the periodic table of the elements. The electrons are added from left to right and from top to bottom then why does the atomic radius decrease from left to right and increase downwards in a group? Before we discuss it let’s understand about atomic radii of the elements. Atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost shell (valance cell))of the atom but it is difficult to determine the precise value of the radius of the atom because the electron behaves like a wave so the electron cloud around the nucleus has not a sharp boundary due to varying position of electrons,it is that’s why its position is defined by four quantum number.
It is not possible to isolate a single atom for determining the radius of the atom.
Quantum Numbers and Orbitals Class 11 Chemistry CBSE
Shapes of s,p and d Orbitals Class 11 Chemistry CBSE
The alternative discovered by scientists in determining atomic radius is by the state of bonds but these atomic radii also change as per the state of the bond between the atoms and concluded to the point that there are three types of atomic radius, these radii depend upon the elements are metals or non-metals.
Tupes of Atomic radius:
(i)Covalent radius
(ii)Van der walls radius
(iii)Metalic radius
Ionic radius(special case of metalic radius)
In the case of non-metals atomic radius refers to either a covalent radius or wander wals radius.
The atomic radius is measured by x-ray or another spectroscopic method.
Covalent radius:
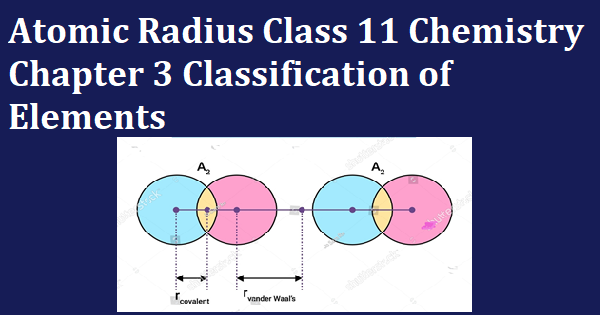
It is half of the distance between the nuclei of two covalently bonded atoms.
Covalent bonds are formed as a result of the overlapping of the orbitals of two atoms.
It is generally used for non-metals.
Let the radius of the covelent bond is rc
rc = (Bond length)/2
Metalic radius:
Metalic radius is half of the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent metallic atoms
In a metallic bond, there is no overlapping of atoms, therefore, the metallic radius is always larger than the covalent radius.
Metalic radius is measured by x-ray or another spectroscopic method
Metalic radius ∞ 1/(Metalic bond strength)
If metallic bond strength is more then the packing efficiency of the metal is more
Metalic radius = d/2
Van der walls radius: Van der wal radius is half of the distance between nuclei of two non-bonded neighboring atoms of two adjacent molecules.
Rwanderwaal= distance between two neighboring atoms of two adjacent molecule/2
Van der waal radius is frequently used as inert gas radius because inert gas usually do not form a chemical compound, therefore their atomic radii are usually expressed as wan der Waal radii, inert gas radii or covalent radii.
Let there is a diatomic non-metal A then wan der Waal radius is given as follows
Comparison of different types of radii:
Wan der waal radius >Metalic radius >Covalent radius
Trends in Atomic radius through the Periodic Table:
(i)In a Period: In a period atomic radius(atomic size) generally decreases from left to right across a periodic table .It is because within the period outer shell electrons are in the same valence shell and the effective nuclear charge increases as the atomic number increases resulting in the increased attraction of the electrons to the nucleus.
As an example the elements of second period with their atomic numbers are Li(3),Be(4),B(5),C(6), N(7),O(8) and F(9)
Their electronic configurations are
1s22s1,1s22s2,1s22s22p,1s22s22p2,1s22s22p3,1s22s22p4 and 1s22s22p5
It can be observed that number of electrons i are being added on the second shell in case of every element but the nuclear charge is increasing ,therefore the force of attraction towards the nucleus is increasing which cause the size of atom decreases from left to right in a periodic table.
(ii)In a Group: In a group, atomic radius(atomic size) generally increases downwards in the periodic table. It is because within the group the number of shells increases as the principal quantum number(n) increases with the increase of atomic number resulting in the valence shell being farther from the nucleus.
As an example, the elements of the first group are Li,Na,K,Rb, Cs and Fr
Their electronic configurations end at ns1
2s1,3s1,4s1, 5s1and 6s1
It can be observed that the number of shells are increasing downwards,therefore the size of the atom increases downwards in a group.
You can compensate us
Paytm number 9891436286
The money collected by us will be used for the education of poor students who leaves their study because of a lack of money.
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
Class 10 Maths Question Paper CBSE Half Yearly Exam 2022 With Solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution