Class 11Physics Chapter 4 Circular Motion in a Plane
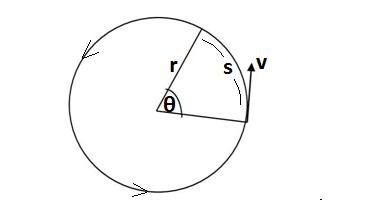
Examples of circular motion are the rotation of the earth around its own axis and the motion of the moon around the earth. there are two types of displacement in a circular motion, one is linear displacement and angular displacement .linear displacement is the length of the arc covered by an object is s and the radius of the circle is r then angular displacement is s/r radian, linear displacement divided by time results linear velocity and angular displacement divided by time results angular velocity.
Class 11Physics Chapter 4 Circular Motion in a Plane
Let the angular displacement of a rotating object is θ and linear displacement is s
Angular displacement = Arc/Radius
θ = s/r
s =rθ, is the relationship between linear and angular displacement
Linear velocity =Linear displacement/Time
Let there is Δs change in linear displacement, change in angular displacement is Δθ in time Δt, then average velocity and average angular velocity are given by
Average linear velocity =Change in linear displacement/Change in time and Average angular displacement =Change in angular displacement/Change in time
vav = Δs/Δt and wav = Δθ/Δt
If Δt is infinitesimally small then corresponding linear displacement and angular displacement are ds and dθ then instantaneous linear velocity and instantaneous angular velocity is evaluated as following
vins = ds/dt and wins = dθ/dt
Angular velocity is an axial vector, so the direction of angular velocity is in outward of the plane. If the object is moving clockwise then the direction of angular velocity is otward of the plane and if the object is moving anticlockwise then the direction of angular velocity is inward of the plane.
The relationship between angular velocity and linear velocity:
The equations are known to us
v = Δs/Δt …..(i) w = Δθ/Δt…….(ii)
Dividing equation (i) by equation (ii)
v/w = Δs/ Δθ
Putting the value of
s =rθ
v/ω= Δ(rθ)/ Δθ
v/ω = r(Δθ)/ Δθ[ r is constant)
v = rω
Angular velocity of an object which is moving in a straight line:
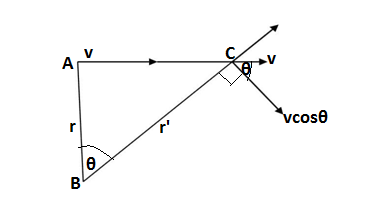
Let there is a point B wherefrom we are going to observe the angular velocity of an object at A which is moving at the velocity of v in a straight line.
ω = v/r,here v and r should be perpendicular to each other
Now, let us consider the angular velocity at C, at point C the linear velocity remains the same as it is supposed that the object is moving with a uniform velocity v but its angular velocity changes with the change in the value of θ(i.e angular displacement)
For evaluating the value of angular velocity we have to consider the component of the velocity which is directed perpendicular to its distance from B(i.e r’) which is vcosθ
Therefore in this case the angular velocity will be
ω = vcosθ/r
Angular velocity of a moving object in a straight line with respect to another moving object:
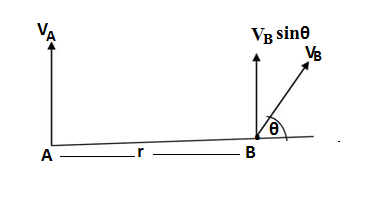
Let the velocity of an object at A is vA
and the velocity of another object which is at a distance of AB and moving with a velocity of vB by an angle θ with the distance AB
Angular velocity of the object B with respect to A = ωBA
First of all let’s calculate the component of the linear velocity vB which is perpendicular to the distance AB
The vertical component of vB is =vB sinθ
The relative velocity of the object B with respect to A = vBA = vB -vA
Forces and Newton’s First Laws of motion:Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 CBSE
Addition of Vectors: CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 -Motion in a Plane
Don’t forget to write a comment, subscribe us for the posts related to your study
Electronic Configuration of s,p and d orbitals
Atomic Radius Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 3 Periodicity in Properties
Why does a Rainbow look like a Bow?
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
Class 10 Maths Question Paper CBSE Half Yearly Exam 2022 With Solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution