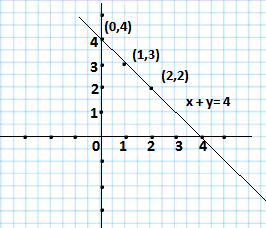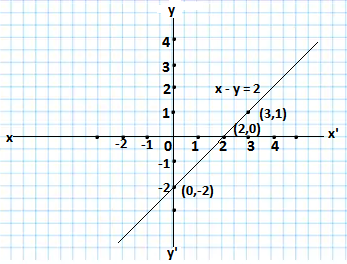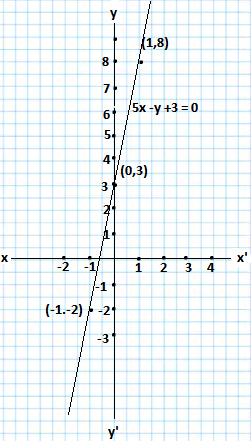NCERT Solutions of class 9 maths exercise 4.3-Linear equations in two variables
NCERT Solutions of exercise 4.3 are the solutions of unsolved questions of class 9 maths NCERT textbook prescribed by CBSE for 9 class students. All questions are solved by the maths expert by a step by step method. Exercise 4.3 is good for the preparation of exams because every year one or two questions of 3 to 5 marks are compulsorily asked from this exercise.
Exercise 4.1 & 4.2 -Linear Equations in Two Variables
Class 9-Sample papers and question papers
Solutions of important question papers of last year’s question papers
Solutions of specific questions
How to write linear equation in two variable
Technics of achieving hundred percent marks in Maths
Maths assignments for class 9 and 10
9 class maths assignment for SA-1
Addition, subtraction,multiplication and division of polynomial
NCERT Solutions of class 9 maths exercise 4.3 of chapter 4- Linear equations in two variables
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Q1. Draw the graph of each of the following linear equations in two variables.
(i) x + y =4 (ii) x – y = 2 (iii) y = 3x (iv) 3 = 2x + y
Ans.(i) We are given the equation x + y =4
For x = 0, y= 4, for x = 1, y= 3, for x =2, y= 2
So, we have the following solutions of the equation
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y | 4 | 3 | 2 |
Drawing the graph of the equations as follows.
(ii) The given equation is x – y = 2
For x =0, y= -2,for x = 2, y = 0,for x = 3, y=1
The solutions of the given equation is shown as follows
| x | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| y | -2 | 0 | 1 |
Drawing the graph of the given equation as follows.
(iv) We are given the equation 3 = 2x + y
When x = 0, y = 3, x =2, y= -1, x =3, y= -3
The table of solutions of the equation is given below.
| x | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| y | 3 | -1 | -3 |
Q2. Give the equations of two lines passing through (2,14), How many more such lines are there, and why?
Ans. The given coordinates of the point are =(2,14)
Observing the coordinates of the point we find that the ratio between x-coordinate and the y coordinate is 1: 7, so we have
y- 7x = 0
We also observe that the difference between both coordinates is 2-14 = -12
So,x – y = -12
x -y + 12 = 0
Both of these equation satisfies the coordinates (2,14)
Hence the required two-equation passes through (2,14) are y- 7x = 0 and x -y + 12 = 0
From one point infinite lines can be drawn, so through the point (2,14), there are such of infinite lines pass out.
Q3. If the point (3,4) lies on the graph of the equation 3y = ax +7, find the value of a.
Ans. We are given that the point (3,4) lies on the graph of the equation 3y = ax +7,so the coordinates of the given point will satisfy the equation.
Putting x = 3 and y = 4 in the equation 3y = ax +7
3 × 4 = a× 3 + 7
3a = 12 – 7
3a = 5
Therefore the value of a is 5/3.
Q4. The taxi fare in a city is as follows: for the first kilometer, the fare is Rs 8 and for the subsequent distance it is Rs 5 per kilometer. Taking the distance covered as x km and total fare as Rs y . Write the linear equation for this information, and draw its graph.
Ans. The distance covered is = x km
The fare for the first 1 kilometer is = Rs 8
After the taxi covered 1 km the rest of the distance is = x -1
The rate of fare for the rest of the distance is = Rs 5/km
Fare for the distance (x -1) km = Rs 5( x- 1)
The total fare is given = y
So, the linear equation as per the question is given by
y = 8 + 5(x – 1)
y = 8 + 5x -5
5x -y +3 = 0
So, the required linear equation is 5x -y +3 = 0
Solving the linear equation
for x = 0, we get y = 3, when x =1, y = 8, when x =-1, y = 2
The solutions of the given equation are shown as follows
| x | 0 | 1 | -1 |
| y | 3 | 8 | -2 |
Drawing the graph of the given equation as follows.
Q5. From the choices given below, choose the equation whose graphs are given in the given figure.
For the first figure
(i) y = x
(ii)x + y=0
(iii) y = 2x
(iv) 2 + 3y = 7x
For the second figure
(i) y = x+ 2
(ii) y= x -2
(iii)y = -x + 2
(iv)x + 2y = 6
Ans. In the first figure, the graph of the equation is passing through (0,0), (-1.1) and (1.-1)
The equation x + y=0 is satisfied by the coordinates (0,0), (-1.1) and (1.-1), so for the first fig. the answer is (ii)
In the second figure, the graph is passing through the points (-1,3), (0,2), and (2,0)
These coordinates satisfy the equation y = -x + 2, so for the second figure, the answer is (iii).
Q6. If the work done by a body an application of a constant force is directly proportional to the distance traveled by the body, express this in the form of an equation in two variables and draw the graph of the same by taking the constant force as 5 units. Also read from the graph the work done when the distance traveled by the body is
(i) 2 units (ii) 0 units
Ans. Let the work done is y ,the constant force is k and the distance travelled is x
So, we have
Work done = force × displacement (i.e distance travelled in the same direction ,x)
y = kx
k, constant force = 5 units
The equation become
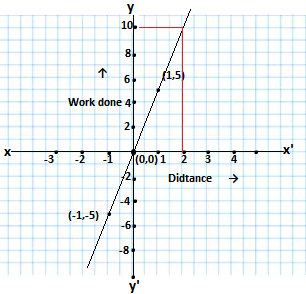
y = 5x
The solutions of the given equation y = 5x, are given as follows
When x = 0, y = 0,for x = 1, y= 5, for x= -1, y = -5
The table of solutions of the equation is as follows
| x | 0 | 1 | -1 |
| y | 0 | 5 | -5 |
Drawing the graph of the equation
(i) Observing the graph, the corresponding value of work done when the distance, x = 2 units is = 10 units
(ii) When distance is 0, the corres[ponding value of work done is = 0 units.
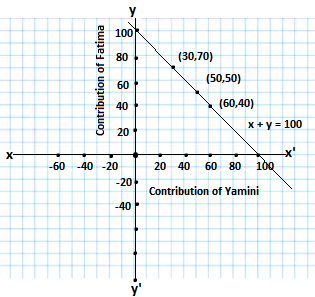
Q7. Yamini and Fatima , two students of class ix of a school, together contributed Rs 100 towards the Prime Minister’s relief fund to help the earthquake victims. Write a linear equation that satisfies this data .(You may take their contributions as Rs x and Rs y). Draw the graph of the same.
Ans.Let the Yamini contributed Rs x and Fatima contributed Rs y towards Prime Minister’s relief fund
Both of them contributed total sum of Rs 100
So, x + y = 100
Solving the equation for different values of x,we get different values of y
When x = 50, y = 50, when x = 30, y = 70, when x =60, y = 40
The solutions of the table is shown below
| x | 50 | 30 | 60 |
| y | 50 | 70 | 40 |
Drawing the graph of the equation
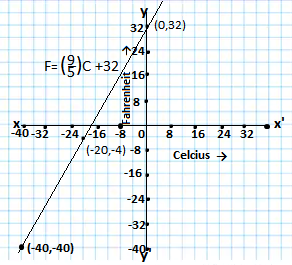
Q8. In countries like the USA and Canada, the temperature is measured in Faherignhite, whereas in countries like India it is measured in celsius. Here is a linear equation that converts Fahreinhite to celsius:
(i) Draw the graph of the linear equation above using Celcius for the x-axis and Faherenhite for the y-axis.
(ii) If the temperature is 30°C, what is the temperature in Fahrenheit.
(iii) If the temperature is 95°F, what is the temperature in Celcius.
(iv) If the temperature is 0°C , what is the temperature in Fahrenheit and if the temperature in 0°F, what is the temperature in Celcius.
(v) Is there a temperature that is numerically the same in both Fahrenheit and Celcius? If yes, find it.
Ans. (i) The given equation is
Solving the equation by putting different values of C for getting different values of F
When C = 0, F = 32, When C=-20, F= =-4, When C = -40,F =-40
| C | 0 | -20 | -40 |
| F | 32 | -4 | -40 |
Drawing the graph as follows
(ii) We have the equation
When C = 30°C, the temperature in Fahrenheit is calculated as follows
F = 54 + 32 = 86
Hence in Fahrenheit, the temperature is 86°F
(ii) If the temperature in Fahrenheit is 95°F, then the temperature in Celcius is calculated as follows.
The given equation is
Therefore the temperature in Celsius is 35°C
(iv) If the temperature in Celcius = 0°C, then value in Fahrenhit is calculated as follows
The given equation is
F = 32
When the temperature in Fahrenheit is =0°F, then the temperature in Celcius is calculated as follows.
Hence,the temperature in Celcius is =-17.77°C
So,when C = 0, F= 32 and when F =0, C= -17.77
(v) The given equation is
Putting F =C
Hence,at -40°C, both Fahrenhit and Celcius are equal.
Study science notes
Archimedes Principle: Complete detail
Average Speed and Average velocity
The second law of motion
The universal law of gravitational force
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
NCERT Solutions of all chapters of Maths for Class 10 from Chapters 1 to 15
Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
Class 11 Physics NCERT Solutions
Science and Maths NCERT solutions for Class 9 ,10 and 11 classes
Previous year maths question paper of class 11
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution