Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam is created here by an expert of science in order to help class 10 science students to boost their preparation for class 10 science question paper in CBSE Term 2 Exam.
The feature of the Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 2 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22 are the following.
(i)All questions are compulsory.
( ii) The question paper has three sections and 15 questions.
(iii) Section–A has 7 questions of 2 marks each; Section–B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section–C has 2 case-based questions of 4 marks each.
(iv) Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
Solutions of class 10 last year’s Science question papers
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Latest sample paper of science 2020
Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 2 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22 with Solution
Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 1 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22 with Solution
Class 10 science Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board 2020-21
Class 10 Biology Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board 2020-21
Class 10 Chemistry Practical Based Questions for CBSE 2020-21 Board Exam
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions for CBSE Board 2020-21
Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
You can download PDF-Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
PDF-Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
SECTION A
Q1.An element M has atomic number 12
(a) Write its electronic configuration (b) Write its group number
Ans.Atomic number of M =12
Since Atomic number = no. of electrons
M12= 2,8,2
(b)No of orbitals= 3 and balance electrons =2
Therefore group no. is 2 and the number of periods is 3
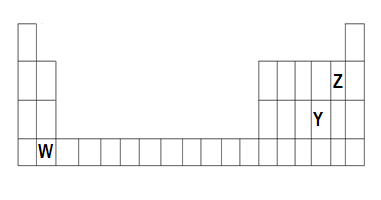
Q2.The diagram below shows part of the periodic table.
(a) Which elements would react together to form covalent compounds?
(b) Between the two elements W and Z, which will have a bigger atomic radius? Why?
Ans. (a) Covalent bonds are formed by the elements which couldn’t form ions, Y and Z elements lie in the group 16 and 18,
therefore both Y and Z are non-metals, both have the tendency to receive electrons, therefore, they can’t form ions instead they form Covalent bonds when reacting together.
(b)Between the two elements W and Z, Z will have a bigger atomic radius since atomic size decreases from left to right in the periodic table because of increasing positive charges.
Q3.How are covalent compounds different from ionic compounds? List their two characteristics properties.
Ans. Covalent compounds are formed when two elements share the electrons, the elements in a covalent compound are bonded by a covalent bond of the type of single, double, or triple bond depending upon the no. of electrons shared while ionic compounds are formed due to the formation of cation(+ ion) and anion(- ion), the force of attraction between two opposite ions creates an ionic bond between the elements.
Characteristic properties: Covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity and their melting points is lower.
Ionic compounds are good conductors of electricity and their melting points are higher.
Q4.In-circuit five resistance of 50 ohm,20 ohms,15 ohm, and 20 ohm and 10 ohms are connected in series with a 6 V battery. Find total resistance and total current in the circuit.
Ans. Five resistance of 5 ohm,20 ohms,15 ohm, and 20 ohm and 10 ohms are connected in series
The total current is equivalent resistance(Rt) of 5 resistors
Rt= (5 +20+ 15+20+10)Ω =70Ω
Let total current in the circuit is I,then total current is
I = V/Rs= =6V/70Ω =3/35 A
Q5.Mustard was growing in two fields-A and B. While field A produced green-colored seeds, field B produced yellow coloured seeds.It was observed that in field A, the offspring showed only the parental trait for consecutive generations, whereas in field B, the majority of the offspring showed a variation in the progeny. What are the probable reasons for these?
Ans. The offspring of green coloured seeds produce the seeds that have parental traits for consecutive generations is the result of sexual reproduction as a result of self-pollination between the similar flowers while offspring of yellow seeds produced in field B showed a variation in the progeny because of the cross-pollination between the dissimilar flowers.
OR
If we cross purebred tall (dominant) pea plant with purebred dwarf (recessive) pea plant we will get pea plant of the F1 generation. If we now self cross the plant of the F1 generation, then we obtain pea plants of the F2 generation.
(a)What do the plants of the F1 generation look like?
(b)State the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in the F2 generation.
Ans.(a)If we cross purebred tall (dominant) pea plant(TT) with purebred dwarf (recessive) pea plant (tt)we will get pea plant of the F1 generation, according to the law of inheritance (monohybrid cross), After crossing (TT) and (tt), the progeny in first-generation are Tt, Tt, Tt, Tt which are heterozygous tall plants in which tallness is dominated and dwarfness is recessive
(b)After crossing two plants of first-generation (Tt and Tt), plants in second-generation are produced TT, Tt,Tt, tt
In second-generation plants TT -homozygous tall, Tt and Tt-Hetrogygous tall, and tt-homozygous dwarf
Hence the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in the second generation is 3: 1
Q6.For the current-carrying solenoid as shown below.
(a)Explain where magnetic field strength will be maximum and minimum and why?
(b)How will you recognize the south pole and north pole in the solenoid?
Ans. (a)Magnetic field lines originate from the north poles and merge in the south pole. Magnetic field strength is maximum at the poles because no. of magnetic field lines per unit area at the poles are more as compared to the rest of space around the solenoid and magnetic field strength is minimum at the middle because magnetic field lines per unit area are least at the middle.
(b) The end of the solenoid connected to the positive terminal of the battery is the south pole and the other end of the solenoid connected to the negative terminal of the battery forms the north pole.
OR
(a) What is the principle of an electric motor?
(b) What is the function of brushes and split rings?
Ans.(a) The principle of the electric motor is based on the Flaming’s left-hand rule, the Flaming’s left-hand rule states that if we stretch our left hand in such a way that index finger, middle finger, and thumb are in the right angles to one another and index finger shows the direction of the magnetic field, middle finger shows the direction of current then thumb will show the direction of the force.
In the electric motor when a current is allowed to flow in a rectangular coil under the impact of a magnetic field then a force is produced which is perpendicular to the direction of the current and magnetic field that spins the coil.
(b) The brushes allow the flow of electric current from stationary wires of power supply and the moving coil and since AC current reverses its direction after a half cycle so the role of split ring is to reverse the direction of electric current or it maintains the uni-direction of the current which enables coil of the motor to move in one direction only.
Q7.What is biological magnification? Will the levels for this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem?
OR
What is meant by food chain? The number of trophic levels in the food chain is limited? Give reasons to justify the statement.
Click the link and study you will get answers of both questions Food chain and food web in an ecosystem
SECTION -B
Q8.From the following elements:
4Be ; 9F ; 19K ; 20Ca
(i)Select the elements having one electron in the outermost shell.
(ii) Two elements of the same group.
(iii)Write the formula and mention the nature of the compound formed by the union of 19K and element X (2,8,7).
Ans.(i) The electronic configuration of the given elements are given as
4Be = 2,2
9F = 2,7
19K =2,8,8,1
20Ca =2,8,8,2
Therefore the element having one electron in the outermost shell is 19K
(b) Generally balance electrons are related to the group no
Group no of the given elements are
4Be →valance e’s =2 implies that group no is 2
9F →valance e’s =7 implies that group no is 10 +7=17 (add 10 to the no. of balance electrons in case of non-metals)
19K →valace e’s =1 implies that group no is 1
20Ca →balance e’s =2 implies that group no is 2
Therefore group no of 4Be and 20Ca are the same
(c)The compound formed by 19K and element X (2,8,7) is decided by their valance electrons
19K has 1 valance electron so it tends to donate its one electron, thus it forms K+ion
X (2,8,7) has 7 valance electrons it tends to receive one electron, thus it forms X–ion
The valency of K is +1 and the valency of X is -1, therefore formula of the compound formed by K and X is KX and the nature of this compound is an ionic compound.
Q9.(a) How many isomers are possible for the compound with the molecular formula C4H10? Draw the electron dot structure of the branched-chain isomer.
(b) How will you prove that C4H10 and C5H12 are homologous?
Ans. The molecular formula of the given compound is C4H10 states that it is butane
The possible isomers of butane are 2
Where second one(isobutane) is the branched-chain isomer
(b) The given compounds C4H10 and C5H12 are homologous because both have the same formula CnH2n+2 and the same properties.
OR
Give a reason why carbon neither forms C4+ and C4- ions but forms covalent compounds which are bad conductors of electricity and have low melting and boiling points.
Ans. The carbon atom has 4 valence electrons so either it can gain 4 electrons or donate 4 electrons to form C4+ and C4- ions, if it gains 4 electrons then a number of (6+4 =10) electrons is a burden for 6 protons to bind them towards the nucleus, therefore it can’t form C4- ion . If a C atom donates 4 electrons, but to free 4 electrons excess energy is required due to the strong force of attraction towards the nucleus created by 6 protons, therefore the C atom can’t form C4- ion.
It is the insufficiency of the carbon atom to form ions, therefore it shares the electrons with other atoms during a chemical reaction and thus forms a covalent bond. Since all valence electrons are shared in the formation of covalent bonds therefore there are no free electrons to conduct electricity, so such types of compounds are bad conductors of electricity. In the molecule of these compounds, each atom is bonded with a strong covalent force that leads to weak molecular force between two molecules which results in them having low melting and boiling points.
Q10.Two pea plants -one with round yellow seeds (RRYY) and another with wrinkled green (rryy) seeds produce F1 progeny that has round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are self-pollinated, which new combination of characters is expected in F2 progeny? How many seeds with these new combinations of characters will be produced when a total of 160 seeds are produced in the F2 generation? Explain with reason.
Ans. Two pea plants – one with round yellow seeds (RRYY) and another with wrinkled green (rryy)
Seeds produce in F1 that has round, yellow (RrYy) seeds
The gametes transfer from F1 to F2 are (Rr) and (Yy )which can be combined as (RY),(Ry),(rY),(ry)
The alleles (RY),(Ry),(rY),(ry) further can be arranged by random selection giving out the type of plants in the F2 generation
inkled green is 9:3: 3:1
Since a total of 160 seeds are produced in the F2 generation
The no. of round yellow seeds = (9/16)×160 =90
The no. of round green seeds = (3/16)×160 =30
The no. of wrinkled yellow seeds = (3/16)×160 =30
The no. of wrinkled green seeds = (1/16)×160 =10
Q11.Two lamps, one rated 60 W at 220 V and the other 40 W at 220 V are connected in parallel to the electric supply at 220 V.
(a) Draw a circuit diagram to show the connections.
(b) Calculate the current drawn from the electric supply.
(c) Calculate the total energy consumed by the two lamps together when they operate for one hour.
Ans.(a)
(b) Current drawn into the bulbs = Power/Voltage
Since both bulbs are connected in parallel to the electric supply of 220 V, therefore the voltage across them will be the same.
Current drawn into the bulb of 40 W = 40/220 =2/11 A
Current drawn into the bulb of 60 W = 60/220 =3/11 A
Total current drawn into the circuit = (2/11 +3/11)A=5/11 A
(c) Total energy consumed by the two lamps together = Heat energy(H) dissipated by the bulbs
H = Power × Time = (40+60)W×1 h=100 Wh
1 kWh =1000 Wh
H = 100/1000 =0.1 kWh
Q12.In the below circuit, if the current reading in the ammeter A is 2A, what would be the value of R1 ?
Ans. 5 Ω ,10Ω and R1 are combined in parallel
Their equivalent resistance is
1/Rp =1/5 +1/10 +1/R1
1/Rp = (2R1+R1+10)/10R1
Rp = 10R1 / (3R1+10)
6Ω,6Ω are combined in series
There equivalent resistance is
Rs = 6 +6 =12Ω
Net resistence of the circuit is
Rnet =Rp +Rs =12 +10R1 / (3R1+10)
V = IRnet
Rnet = V/I =30/2 =15Ω
12 +10R1 / (3R1+10) = 15
10R1 / (3R1+10)=3
9R1+30 = 10R1
R1= 30Ω
OR
A wire of given material having length L and area of cross-section A has a resistance of 4 ohms. What would be the resistance of another wire of the same material having length L/2 and area of cross-section is 2A.
Ans. Let the resistance of another wire is R’
The length of the wire is L and its area of cross-section is A
The relation between L(length), A(area of cross-section), and R (resistance) of a conductor is given as
Where ρ is the resistivity of the material,R =4Ω
If the length of another wire of the same material is half of the length of the previous wire(L/2) and the area of cross-section is twice(2A)
On dividing equation (i) by equation (ii) ,we get
4 = 4/R’
R’ = 1
Hence the resistance of another wire is 1 Ω
Q13.Gas A, found in the upper layers of the atmosphere, is a deadly poison but is essential for all living beings.The amount of this gas started declining sharply in the 1980s.
a.Identify Gas A . How is it formed at higher levels of the atmosphere?
b.Why is it essential for all living beings? State the cause for the depletion of this gas.
Ans. Click here for answers of this question Ozone Layer and How it is Getting deplteted.
SECTION -C
This section has 02 case-based questions(14 and 15). Each case is followed by 03 sub-questions(a,b, and c).Parts a and b are compulsory. However, an internal choice has been provided in part c.
Q14.Ansari has observed colorful flowers in the garden and wants to know how a flower changes into fruit. He has observed their pollination. He has observed different parts of flowers. In gymnosperms, the ovule is not contained in a carpel but exposed on the surface of a dedicated support organ. Pollination is considered a very important process in angiosperms. Pollen grain has two layers intine and extine in which many changes occur after fertilization.
(a)What is self and cross-pollination?
Ans. When pollens are transferred from anther to the stigma of the same flower or genetically similar flower then it is known as self-pollination.
When pollens are transferred from anther of a flower to the stigma of another flower or genetically different flower then it is known as cross-pollination.
(b)Draw a labeled diagram showing germination of pollination on the stigma of a flower.
(c)Which part of the flower will give rise to seed and fruit.
Ans. Male gamete(pollens) reaches from anther to stigma then further transported through style to the ovary where male gametes meet eggs. Both male gamete (pollen)and female gamete(egg) fused together and form the zygote, zygote transforms into embryo and embryo changes into seeds, the ovary develops into the fruit.
OR
(c) What is double fertilization?
Ans. Double fertilization occurs generally in flowering plants when a male gamete fertilizes an egg and union of both fused to another sperm, in double fertilization one egg and sperm fused together form seeds and fusion of union of both with the secondary nucleus of another sperm resulting formation of fruit.
Q15.Substance through which charges cannot pass is called insulators. Glass, pure water, and all gases are insulators. Insulators are called dielectrics. In insulators, the electrons are strongly bound to their atoms and cannot get themselves freed. Thus, free electrons are absent in insulators. Insulators can easily be charged by friction. This is due to the reason that when an electric charge is given to an insulator, it is unable to move freely and remains localized. But this does not mean that conductors can’t be charged by rubbing it with silk if it is held in a handle of glass or amber.
(a) Calculate the current in a wire if a 1500 C charge is passed through it in for 5 minutes.
Ans. The relation between charge(Q) and current(i) is
i = Q/t ,where t is time
Q = 1500 C, t = 5 minutes = 5×60 = 300 seconds
i = 1500/300 = 5
Hence current in the given wire is 5 A
(b)(i) Write practical application of the heating effect of current.
Ans. The household appliances like iron, heater, geyser, electric toaster, electric oven, etc are operated due to the application of the heating effect of current. The heating element of these appliances is made of material that has high resistivity and a high melting point.
An electric fuse is used to protect the electric appliances, the excess flow of current causes to heat the fuse wire which results to burn it, and the circuit is broken, The fuse wire is made of material that has high resistivity and a low melting point.
The filament of incandescent bulbs is made of material that has material of high resistivity and a high melting point, in this device non-reactive gases nitrogen and argon gases are flushed into it, the filament of the bulb is heated due to the flow of the current and emits light
(ii)Name the material that you would advise to use in the heater element of the electric heating device and why?
Ans. The material used in the heater element of the electric heating device should be an alloy like nichrome which have high resistivity and a high melting point.
(c)Define 1 ampere.
Ans. The relationship between electric current, charge, and time is Q= it, where Q is a charge, i is current and t is time
Q = it
Q=1 C ,t =1 s then i=1C/1s =1 A
Therefore 1 A current is defined as the flow of 1 C charge in 1 second.
OR
State ohm’s law
Ans.
Potential difference (V)is directly proportional to the electric current (i)
V ∝ i
V =iR
Where R is the constant of proportionality known as the resistance of the circuit
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
50 important science questions for cbse 10 class
Chemical properties of acid and base
Chemistry viva voce questions & answers
Chemistry practical based questions
Solutions of previous year’s science & maths question papers
Solutions of class 10 Science question paper 2019 CBSE
Solutions of class 10 CBSE maths question paper 2020
CBSE Class 10 science question paper 2020 SET -3 solutions
Download e-book of Science NCERT 634 questions with solutions for Polytechnic and NDA entrance exams