Class 10 Biology Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board
Here, all answers to Viva Voce questions of class 10 biology are presented by future study points for the purpose of motivating you to enhance your knowledge and interest in biology subject. The study of these Viva Voce questions of class 10 biology will help you to boost up your preparation for the CBSE board exam of 2020-21. All Viva Voce questions of biology of class 10 are answered by a subject expert as per the CBSE norms. The set of questions and answers are also useful for the preparation of all kinds of competitive entrance exams also.
All answers to Viva Voce questions of class 10 biology are created here will help class 10 students as well as the candidates who are going to appear in competitive entrance exams. These Viva Voce questions are taken from the CBSE Science manual books ,the questions and anwers mentioned here are as per the CBSE norms.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
Q1.What is the function of guard cells in stomata?
Ans. The guard cells regulate/control the opening and closing of stomata.
Q2.Why are stomata absent in roots.
Ans. As a little gas exchange takes place in roots hence stomata are not present in them.
Q3.Each stoma is surrounded by two bean-shaped cells. What are they called?
Ans. They are called guard cells.
Q4.Which surface of dicot leaves more stomata are present?
Ans.On the lower surface of leaves i.e lower epidermis.
Q5.What is transpiration?
Ans. The loss of water in the form of vapours from the surface of leaves is called transpiration.
Q6. How will one identify monocot leave and a dicote leave on the basis of stomata?
Ans. Guard on the monocot leaves are dumb-bell shaped while in dicot leaves they are kidney-shaped or bean-shaped.
Q7.Which side of leaves should be observed for stomata in dicot plants?
Ans. Stomata is present in both sides of the dicot leaf.
Q8.What are the function of the stomatal apparatus?
Ans. The function of the stomata are:
(a) For the exchange of gases during respiration and photosynthesis.
(b) During transpiration for loss of water.
Q9. Do the guard cells have rigid or elastic walls? Justify your answers.
Ans. Guard cells have thicker cell walls on inner side than the outer side. This adds to their flexibility while opening and closing.
Q10.Define venation.
Ans. The pattern of veins in a leaf lamina is called venation. Some plants monocots have parallel venation and others (dicots) have network type venation(reticulate).
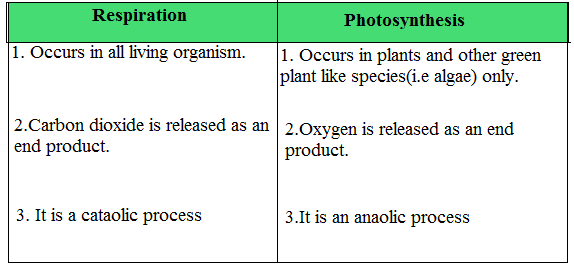
Q11. State the difference between photosynthesis and respiration.
Ans.
Q12. What do you mean by a catabolic process?
Ans. Catabolism means the metabolic activities which involve breakdown of complex substances like glucose in cells is broken simpler substances(H2O & CO2).
Q13.Define breathing.
Ans. The physical process of inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide is called breathing.
Q14.Define fermentation.
Ans.It is a type of anaerobic respiration. It also releases CO2 as a by-product.
Best Amazon deals
Q15. Why we use germinating seeds but not green leaves of a plant to demonstrate respiration.
Ans. Germinating seeds are under rapid growth hence they actively respire. On the other hand, green leaves of a plant will undergo photosynthesis also along with respiration. Thus it will utilize CO2 produced during respiration, hence the presence of CO2 may not be detected properly.
Q16. What is the role of KOH in this experiment?
Ans.KOH absorbs the CO2 produced thus creating a partial vacuum in the flask.
Q17.Why germinating seeds are moistened so that they don’t dry up and continue respiration with the help of moisture.
Ans. The seeds are moistened so that they don’t dry up and continue respiration with the help of moisture.
Q18.What are raw materials for respiration?
Ans. Sugars and oxygen.
Q19.Write the chemical reaction introduced in respiration.
Ans
Q20. What is the full form of ATP.
Ans. Adenosine Triphosphate, it is an energy-rich molecule.
Q21. What is asexual reproduction?
Ans. It is a mode of reproduction in which a single organism produces new organisms without the formation of ay special cell(gamete). A single parent produces two or more individuals.
Q22.Define fission and type of fissions.
Ans. A mode of reproduction when an organism divides into two or more off sprigs. The parent organism splits into two or more off sprigs. The parent organism splits into two or more parts. Fission is of two types.
(a) Binary fission: Organism divides into two daughter cells.
(b) Multiple fission: Organism divides into two or more than two individuals.
Q23.Name an organism which divides by multiple fission,
Ans. Plasmodium (Malaria parasite)
Q24.How many fissions occurs in Amoeba?
Ans. A mature cell of amoeba undergoes karyokinesis(i.e division of nucleus first followed by cytokinesis (i.e division of the cytoplasm) resulting in the formation of two daughter cells. The parent amoeba cell loses its identity in such division.
Latest electronic items,mobiles,laptops and desktops at easy instalments
Q25.What is vegetative propagation?
Ans. Growing of plants from vegetative parts of it like leaf, root, or stem is known as vegetative propagation. It is an asexual mode of reproduction.
Q26. Is budding in yeast different from hydra? Justify your answer.
Ans. In yeast, budding occurs in the form of a protuberance on the parent yeast cell. It may separate or may not separate and can further develop into several daughter buds. In hydra, the bud separates due to repeated mitotic cell division and is a multicellular single organism itself.
Q27.Which type of cell division involved in binary fission?
Ans. Mitosis, as the number of chromosomes, remains the same.
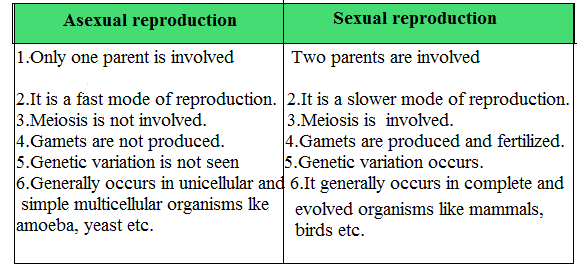
Q28. Mention the points of differences between sexual ad asexual reproduction.
Ans.
Important Science Notes for Class 9 and 10 grade
Class 10 CBSE Science Notes
Class 10 Biology Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board 2020-21
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Chemistry Practical Based Questions and Answers
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
Chemical properties of Acids and Bases-A note for grade 10 students
What is pH value and its importance in everyday life.
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted.
Myopia, Hypermetropia and Presbyopia
Human eye structure and its function
Electrical resistance and conductance
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
What is a potential difference across an electric field ?
Myopia, Hypermetropia and Presbyopia
Difference between soaps and detergents
Why do the star twinkle but planets don’t
Light reflection, refraction, scattering, and dispersion
Extraction of metals as per the activity series
Ionic and covalent compounds and the difference between them
Food chain and food web in an ecosystem
Class 9 CBSE Science Notes
Three Laws of Motion: Class 9 CBSE
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat -Class 9 CBSE notes
What is an atom,molecule and atomicity of a substance?
How to determine Valency,net charge of an ion and Molecular formula of a substance.
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
The Complete Detail of Archimedes Principal
Average Speed and Average Velocity: Differences
How to evaluate recoil velocity of gun
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?
Molar mass,molecular mass and mole concept
What is second law of of motion ?
What is universal law of gravitational force
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |