What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Physical properties of metals:Metals can be easily identified by their physical properties,metals are generally hard and lustrous substances, some of the metals can be beaten into thin sheets. This property of metals is known as malleability.The metals can be drawn into wire,such a property is known as ductility of metals.Metals are used for manufacturing vessels for cooking due to their properties of high melting point and high conductivity of heat.Metallic wires are used for electric wiring and coated with polyvinylchloride(PVC) a rubber like material because of their property of conductance of electricity.Metals are used to make musical instruments because of their property of being sonorous.
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
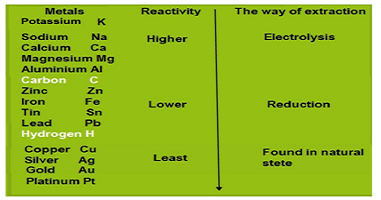
Metals are regrouped on the basis of their reactivity, metals that are at the top of the series are (K, Na, Ca, Mg, and Al) , these are so reactive that are never found in nature as free elements. The metals in the middle of the reactivity series (Zn, Fe, Pb, etc) are moderately reactive. The metals at the bottom of the reactivity series are least reactive. They are often found in a free state. For example, gold, silver, platinum, and copper are found in a free state, copper and silver are also found in the earth’s crust in the form of their oxide or sulfide ores.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
You can also study
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Chemistry Practical Based Questions and Answers
What is the atom, molecule, and atomicity of a substance?
How to determine Valency,net charge of an ion and Molecular formula of a substance.
What is an atom,molecule and atomicity of a substance?
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
What is pH value and its importance in everyday life.
Chemical properties of Acid and Bases-A note for grade 10 students
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Difference between soaps and detergents
Class 10 chapter 2 science notes on salts
Extraction of metals as per the activity series
Ionic and covalent compounds and the difference between them
Trends in the property of element from left to right and up to down in the modern periodic table.
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Chemical Properties of Metals
Reaction with oxygen: Almost all metals reacts with oxygen to form metal oxides.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal oxide
Examples: When copper and aluminium are heated to air,it combines with oxygen to form copper(I)oxide(black in colour) and aluminium oxide(white in colour).
2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
Sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals they combine with oxygen and get fire, it is that’s why they are kept inside the kerosene that keeps them away from oxygen.
4Na + O2 → 2Na2O
4K + O2 → 2K2O
Most of the metalic oxides are insoluble in water but some of them like Na2O and K2O dissolves in water and forms alkalis as follows.
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq)
K2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq)
Oxides of metals are basic in nature but oxides of a few of the metals Al, Zn, Sn,Pb, Cu,Be show the properties of acids as well as base, such type of oxides which behaves like acid and base known as amphoteric oxides. Aluminum oxides react with acid and base in the following manner, which means it neutralizes both acid and base-forming salts and water.
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 2H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO3 + H2O
Aluminum oxides reacting with hydrochloric acid form aluminum chloride and reacting with sodium hydroxide forms sodium aluminate.
The reaction of metals with water: Metal reacts with water and produces metal oxide and hydrogen gas, metal oxides that are dissolved in water to further form a metal oxide and a metal hydroxide.
Metal + Water → Metal oxide + Hydrogen
Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide
Metals like pottasium and sodium reacts with water violently with cold water,the reaction releases heat in such an extent that evolved hydrogen gas catch fire.
2K(s) + H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat energy
2Na(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat energy
The reaction of calcium with water is less violent with cold water. The heat evolved is not sufficient for the hydrogen to catch fire.
Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2 + heat energy
Calcium starts floating because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the metal.
Magnesium does not react with cold water. It reacts with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen. It also starts floating due to the bubbles of hydrogen gas sticking to its surface.
Metals like aluminum, iron and zinc do not react either with cold or hot water. But they react with steam to form a metal oxide and hydrogen.
2Al(s) + 3H2O(g) → Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
Metals such as lead, copper, silver and gold do not react with water at all.
Please follow us on pintrest
The reaction of metal with acids: Metals react with acids to give a salt and hydrogen gas.
Metals + Dilute acid → Salt + Hydrogen
Examples
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Al + HCl → AlCl3 + H2
Magnesium and aluminum react with hydrochloric acid gives magnesium chloride and aluminum chloride respectively,all metals react with HCl give hydrogen gas and their corresponding chlorides.
Hydrogen gas is not evolved when a metal reacts with nitric acid. It is because HNO3 is a strong oxidizing agent. It oxidizes the H2 produced to water and itself gets reduced to any of the nitrogen oxides (N2O, NO, NO2), but magnesium(Mg) and manganese(Mn) react with very dilute HNO3 to evolve H2 gas.
Example: Al +6HNO3 → Al(NO3)3 + 3NO2 + 3H2O
3Cu + 8HNO3 → 3Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO + 4H2O
Aluminum and copper react with nitric acid produces aluminum nitrate and copper nitrate with oxides of nitrogen and water.
The reaction of metals with the solutions of other salts: All metals are not equally reactive.The comparison in the reactivity of the metals can be identified through the displacement reaction. When a more reactive metal reacts with the salt solution of less reactive metal, then more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal and substitutes it to form its own salt as follows.
Metal A + Salt solution of metal B → Salts solution of A + Metal B
In the above reaction metal A displaces metal B from its salt forming the salt solution of A indicates that metal A lies at higher lebel in the reactivity series compared to B.
As an example
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
Here the highly reactive iron displaces lower reactive Cu forming ferrous sulphate.
The reactivity series
The reactivity series is on the basis of the activity of the metal also known as activity series.
Metals that are at the top of the series (K, Na, Ca, Mg, and Al) are extracted from their ore by electrolysis,The metals in the middle of the reactivity series (Zn, Fe, Pb, etc) are extracted from their ore by reduction and gold, silver, platinum, and copper are found in a free state.
Selection of subjects or a coarse : A turning point of life
Important Science Notes for Class 9 and 10 grade
Class 10 CBSE Science Notes
Class 10 Biology Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board 2020-21
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted.
Myopia, Hypermetropia and Presbyopia
Human eye structure and its function
Electrical resistance and conductance
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
What is a potential difference across an electric field ?
Why do the star twinkle but planets don’t
Light reflection, refraction, scattering, and dispersion
Food chain and food web in an ecosystem
Class 9 CBSE Science Notes
Three Laws of Motion: Class 9 CBSE
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat -Class 9 CBSE notes
What is an atom,molecule and atomicity of a substance?
How to determine Valency,net charge of an ion and Molecular formula of a substance.
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
The Complete Detail of Archimedes Principal
Average Speed and Average Velocity: Differences
How to evaluate recoil velocity of gun
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?
Molar mass,molecular mass and mole concept
What is second law of of motion ?
What is universal law of gravitational force
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper and Question Papers for Term-1 and Term 2 2021-22 CBSE Board
Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper Term-1 2021-22 CBSE Board
Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 2 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22 with Solution
Solutions of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard Examination (First) 2021 -22 Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Sample paper of Science 2020
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE