The Complete Detail of Archimedes Principal
Archimedes Principle with Complete detail
Archimedes Principle-Archimedes was a great physicist and mathematician of ancient Greek, It is Archemidies who first discovered the area of the sphere he also contributed in the field of optics also, here we are going to discuss his one of the greatest discovery of the hydrostatic principle that is known as Archimedes Principle.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
You can also study related topics
Three Laws of Motion: Class 9 CBSE
Average Speed and Average Velocity: Differences
How to evaluate recoil velocity of gun
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?
What is second law of of motion ?
What is universal law of gravitational force
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
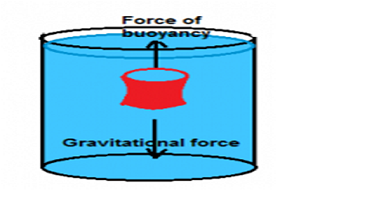
Have you observed weightlessness of a jug when you pressurize it into a water-filled bucket, This weightlessness is actually caused by an upward thrust exerted by the liquid known as the force of buoyancy. You also would have observed that few of the objects submerges partially, completely and few of them floats on the surface of the water. A small needle made of iron sinks while a large ship made of iron floats. All your such doubts will be clear now, actually, the fluids exerted an upward force on the object which is partially or completely submerged into it known as the force of buoyancy.
Apparent weight(Weight in water) = Actual weight of the object – Force of buoyancy
Force of buoyancy = Actual weight of the object – Apparent weight (weight in water)
The upward force or buoyant force exerted by the liquid on the object depends upon the density of the object and liquid.
Laws of floating.
- If the density of the liquid is greater than the density of the object then the objects float on the surface of the liquid
- If the density of the liquid is lesser than the density of the object then the object is immersed into the liquid.
- If the density of the liquid is equal to the density of the object then the object is partially immersed.
Archimedes Principle.
Archimedes discovered that any submerged objects into a liquid feels a loss of weight (Actual weight of the object – Apparent weight ) which he finds equal to the weight of displaced liquid by the object.
If an object is partially or completely immersed into the liquid then the amount of the buoyant force exerted by the liquid on the object is equal to the weight of the displaced liquid by the object.
The calculation of the buoyant force.
Let the mass of the object is = m, gravitational acceleration = g, the density of liquid = ρ
Mass of the displaced liquid = density of liquid × Volume of the displaced liquid
m = ρv……….(i)
Waight of the displaced liquid = Mass × Gravitational Acceleration
W = mg……(ii)
Substituting m = ρv in (ii)
W = ρVg
This is the upward thrust experienced by an immersed object into the liquid
∴Buoyant force = ρ × V × g
Application of Archimedes principle.
Boats and Ships– Boats and Ships are designed in such a way that the weight of displaced water is more than the weight of Boat or Ship, the upward thrust or buoyant force more than their weight makes them float on the surface of the water.
Submarine. It is engineered in such a way when water is flushed into its tanks its weight becomes more than the weight of displaced water or buoyant force that makes it sinks and goes down into the depth of the ocean and when water flushed outward which makes the weight of displaced water or buoyant force more than the weight of submarine, it lifts up towards the surface of the ocean.
Hot balloon. The weight of the balloon due to hot air is less than the air displaced by the balloon, thus the upward thrust is more than the weight of the balloon so balloon rises up into the sky when the temperature of the air inside the balloon is let down, the weight of the air inside it decreases and thus upward thrust becomes less than the weight of displaced air by the balloon and so it goes down towards the earth surface.
Hydrometer. This is the device used to calculate the relative density of the liquid, its working principle is based on the Archimedes principle, it contains lead shots which floats in a vertical column in which the liquid to be tested is poured down, it is calibrated for measuring the relative density if the liquid to be tested has lesser density then lead shot sinks up to a mark that represents the relative density of the liquid.
Q1. Suppose that an ice cube floats in a glass of water filled to the brim. As the ice melts, will the glass overflow?
Ans. The density of ice is less than the density of water when it melts the space between its particles becomes less so when changes into water, its volume decreases so, the glass will not overflow.
Q2.Why do you float more easily in the ocean than in freshwater?
Ans. It is due to the high concentration of dissolved salt, the density of ocean water is more than the density of fresh water, so the upward thrust i.e ρVg is more compared with freshwater, therefore we float more easily in the ocean water than in freshwater.
Q3.Suppose you have two balloons of the same weight, and they both contain the same amount of helium, one is rigid and the other is free to expand. When released, which balloon will rise higher.
Ans. The upward thrust( ρVg ) on the balloon which is free to expand will be more because its volume is more than the volume of the balloon which is rigid means unable to expand, therefore the balloon free to expand will rise higher.
Purchase your favourite mobile,laptops or Desktops in affordable EMI
Q4. Does the buoyant force on a diving bell deep beneath the ocean surface have the same value as when the diving bell is just beneath the surface? explain?
Ans. The pressure of water increases as per the depth and pressure is inversely proportional to the volume of the gas inside the diving bell, therefore the upward thrust(ρVg ) on a diving bell deep beneath the ocean will decrease because of the decrease in the volume of the air inside the diving bell as compared to when the diving bell is just beneath the surface.
Q5. A barge containing a tall pile of sand approaches a low bridge and can not pass under it. Should sand be added to the barge or removed in order to allow it to pass? Explain.
Ans. For lowering the height of a tall pile of sand so that the barge could pass under a bridge, if we add more sand up to a certain height since the density of sand is more than the density of water the barge will sink up to more depth compared to the added height of the sand if we decrease the height of sand the barge will be lifted up to more height so it can’t pass under the bridge, therefore, we have to add the sand allowing the barge to pass through under the bridge.
Q6. Block of wood with dimensions 0.12 by 0.34 by 0.43 cubic meters floats along a river with the broadest face facing down. The wood is submerged to a height of 0.053 meters. What is the mass of the piece of wood?
Ans. The broadest face of the wooden block is =0.34m × 0.43 m, its height 0.12 m vertical, submerged height = 0.053 m, the density of water = 1000 kg/cubic meter.
The volume of displaced water by the block of wood is, V= Area of base × submerged height = 0.34 × 0.43× 0.053=0. 0077486 cubic meter
Since the wood is floating on the surface of the water
Therefore, The weight of wooden block = weight of the displaced water(buoyant force)
mg = ρVg
m = ρV =1000 × 0. 0077486= 7.7486≈ 7.75 kg
Therefore the mass of the wooden block is = 7.75 kg
Q7.You plunge a basketball beneath the surface of a swimming pool until half the volume of the basketball is submerged. If the basketball has a radius of 12 centimeters, what is the buoyancy force on the ball due to the water?
Ans. The density of water, ρ = 1000 kg per cubic meter, radius of basketball =12 cm = 0.12 m,g =9.8 m/s²
The volume of basketball =
The volume of the submerged part of basketball =
Therefore the volume of displaced water by basketball, V = 0.0036 cubic meter
The force of buoyancy = ρVg = 1000 × 0.0036 × 9.8 = 35.28 N
Therefore force buoyancy exerted by the water on basketball is = 35.28 N
Important Science Notes for Class 9 and 10 grade
Class 10 CBSE Science Notes
Human reproductive systems of Male & Family
Modes of reproduction used by single organisms-Asexual reproductions
The structure and anatomy of the Heart
Anatomy of the Human brain-Class 10 CBSE
NEET Sylabus and its preparation
Myopia, Hypermetropia and Presbyopia
Human eye structure and its function
Electrical resistance and conductance
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
What is a potential difference across an electric field ?
Why do the star twinkle but planets don’t
Light reflection, refraction, scattering, and dispersion
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Chemistry Practical Based Questions and Answers
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
Chemical properties of Acids and Bases-A note for grade 10 students
What is pH value and its importance in everyday life.
Difference between soaps and detergents
Extraction of metals as per the activity series
Ionic and covalent compounds and the difference between them
Class 9 CBSE Science Notes
Three Laws of Motion: Class 9 CBSE
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat -Class 9 CBSE notes
What is an atom,molecule and atomicity of a substance?
How to determine Valency,net charge of an ion and Molecular formula of a substance.
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
The Complete Detail of Archimedes Principal
Average Speed and Average Velocity: Differences
How to evaluate recoil velocity of gun
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?
Molar mass,molecular mass and mole concept
What is second law of of motion ?
What is universal law of gravitational force
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper and Question Papers for Term-1 and Term 2 2021-22 CBSE Board
Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper Term-1 2021-22 CBSE Board
Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 2 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22 with Solution
Solutions of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard Examination (First) 2021 -22 Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Sample paper of Science 2020
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution







Very quickly this site will be famous among all blogging viewers, due
to it’s fastidious articles
Here is my webpage … Buy CBD