Why do the star twinkle?
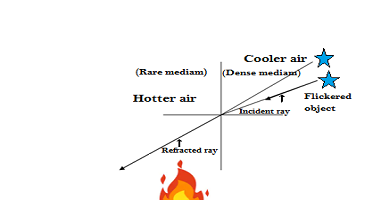
The star appears as they are twinkling because of physical phenomena known as atmospheric refraction. Refraction is bending of a light ray when it passes from one medium to another medium. The process of the light ray deviates from its own way when it travels from one medium to another medium is known as refraction. To understand this you would have to go through your experience, have you seen the things across a fire? You would have observed the things appears to the eye flickering from their places it’s reseasoning is that when light ray falls on the things across the fire, the reflected rays pass from cooler air(one medium) to hotter air(another medium) in turn of this light ray deviates from its own path and then reaches to our eyes, due to the change in temperature of the air around the fire caused by the flame of fire changes the density of air, that causes positions of the image of the things changes continuously and the things appear to flicker or twinkle from their places.
The twinkling of the star is almost the same phenomenon as described earlier due to the atmospheric refraction. The stars are too far away from the earth, they look like small light points. The light from them has to pass a very long path. As we know the space between stars and the earth is a vacuum, the light travels on the straightway until it reaches the atmosphere of the earth, as soon as the light ray enters the atmosphere of the earth, it starts to refract, and then as a result of continuing refraction of the light through the different layers of the atmosphere reaches to our eyes (the continue refraction of light ray occurs due to different atmospheric layers ). After refraction of the light through the atmosphere light ray incident on our eyes, the path of this incident ray varies due to the changing atmospheric conditions, thus we see the changing virtual images of the star.
The temperature of these atmospheric layers varies due to variations in atmospheric conditions resulting in the change in the path of refracted ray incidents on our eyes thus giving way to changing virtual positions of the star that is why stars appear as they are twinkling.
What is the difference between virtual and real images?,
Light Refraction, Reflection, Dispersion And Scattering
Image formation by Convex and Concave Mirrors,
Image formation by Convex and Concave Lenses,
Image formation by Convex and Concave Mirrors,
Difference between Convex and Concave lenses,
Human Eye – Structure and functions ,
Myopia, Hypermetropia, and Presbyopia,
Why do planets not twinkle?
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Planets are much closer because they are part of our solar system. Even they don’t have their own light they appear brighter than the stars because they are much nearer. The star looks like pinpoints and the light ray from there has a longer path so their rays are highly refracted as compared to the incoming rays from the planets, the planets look like a disc so the light rays from them fall to our eyes as a bunch of rays , this bunch of rays doesn’t refract that much as the ray of the star so their image appears to our eyes stable therefore the planets don’t twinkle.
Class X Science Important notes of the lesson 13,Magnetic effect of electric current-II
Buy Class 10 physics and chemistry notes-e-book at the price of Rs 30
Class 10 Physics Important Notes
What is the difference between virtual and real images?,
Image formation by Convex and Concave Mirrors,
Difference between Convex and Concave lenses,
Why does the Sun appear reddish in the evening and morning: Complete Detail
Reflection, Refraction, Dispersion, and Scattering
Image formation by Convex and Concave Lenses,
Human Eye – Structure and functions
Myopia, Hypermetropia, and Presbyopia
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
What is a potential difference across an electric field ?
Complete detail of electrical resistance and conductance
Class X Science Important notes of chapter 12-Magnetic effect of electric current-I
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions for CBSE Board 2020-21
Buy Class 10 physics and chemistry notes-e-book at the price of Rs 50
Class 9 Physics Important Notes
What is the difference between Distance and Displacement
Difference between velocity and speed
Average Speed and Average velocity
Momentum: Definitions,units,formula and Uses in real life:Class 9 CBSE
The universal law of gravitational force
What is the difference between mass and weight
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
Archimedes Principle: Complete detail
What is the difference between Work,Energy and Power: Class 9 CBSE
CBSE IX Class Science Sample Papers
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution