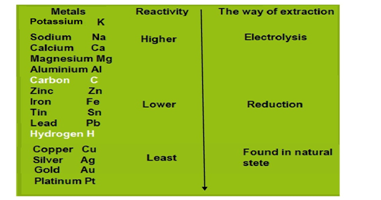
Extraction of metals as per the activity series
Metals are extracted as per their level in the activity series. Some of the metals are found in the earth’s crust in free states and some of them are found in the form of their compound known as ore. The metals are differentiated on the basis of their reactivity known as activity series. The metals at the bottom of the activity series are the least reactive found in a free state for example gold, silver, platinum, and copper are found in the free state. The metals in the middle of the activity series are moderately reactive as example zinc, iron, lead, etc. These metals are found in the earth”s crust in the form of their oxides, carbonates, and sulfides The metals at the top of the activity series are so reactive that they never found in nature as free elements as for example potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, and aluminum.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
You can also study
Physical and Chemical Properties of Metals
Class 10 Science Chapter 3-Metals and Non-Metals NCERT solutions
Chemical properties of acid and base
Chemistry viva voce questions & answers
Chemistry practical based questions
Trends in the property of element from left to right and up to down in the modern periodic table.
What is pH value and its importance in everyday life.
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat
What is an atom,molecule and atomicity of a substance?
How to determine Valency,net charge of an ion and Molecular formula of a substance.
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted
Molar mass,molecular mass and mole concept
What is the difference between the soap and the detergent ?
Tips to get success in competitive exams
Conclusively, the metals are classified into three groups on the basis of reactivity.(i) Metals of low reactivity (ii) Metals of medium reactivity (iii) Metals of high reactivity. Different techniques are to be used for obtaining the metals falling in each category.
Extraction of metals low in the activity series
The oxides of these metals can be reduced to metals by heating alone. For example, cinnabar (HgS) is an ore of mercury. When it is heated in air, it is first converted into mercuric oxide (HgO). Mercuric oxide is then reduced to mercury on further heating.
2HgS (s) + 3O2(g) →2HgO(s) + 2SO2(g)
2HgO(s) →2Hg(l) + O2((g)
Similarly, copper which is found as Cu2S in nature can be obtained from its ore by just heating in air.
2CuS(s) + 3O2g) → 2CuO(s) + 2SO2(g)
2CuO + Cu2S →6Cu(s) + SO2(g)
Extraction of metals in the middle of the activity series
The metals in the middle of the activity series such as Fe, Zn, Pb, Cu, etc, are moderately reactive. These are usually available in the earth’s crust as sulfides or carbonates. Since it is easier to extract metal from their oxides by the method of reduction, so the sulfides and carbonates of metals must be converted to their metal oxides. Sulfide ores of metals are converted into oxides by heating strongly in presence of excess air, this process is known as roasting.
Carbonate ores are converted into oxides of metal by heating strongly in limited air. This process is known as calculation.
NEET Sylabus and its preparation
As example zinc is available in the earth as zinc sulfide and zinc carbonate, so ZnO is derived from these ores by the method of roasting and calcination as follows.
Roasting
2ZnS(s) + 3O2(g) →2ZnO(s) +2SO2(g)
Calcination
ZnCO3(s) → ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
Zinc oxide is then heated with carbon and thus reduced to Zinc.
ZnO(s) + C(s) →Zn(s) + CO(g)
Oxides of the metals can also be reduced to the metal by using the displacement reaction. In this way the metal of higher activity series displaces the required metal from its oxide.
As an example when magnesium oxide is heated with aluminum powder, it gives magnese.
3MnO(s) + 4Al(s) →3Mn(l) + 2Al2O3(s) +Heat
These displacement reactions are highly exothermic. The amount of heat is so large that metal is produced in the molten state, such reaction is also known as thermit reaction.
Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(l) – Al2O3(s) + Heat
This reaction is also used to join railway tracks and cracked machine parts.
Please follow us on Pinterest
Extraction of metals in the top of the activity series
The metals high up in the reactivity series are very reactive, they can’t be obtained from their compound by heating with carbon. Carbon is unable to reduce the oxides of Na K Mg and Ca, this is because these metals have more affinity for oxygen than carbon. These metals are extracted by the electrolysis of their molten chlorides. The metal is deposited at the cathode (-ve charged electrode) and chlorine is liberated at the anode (+ve charged electrode). The reactions are
Na(+) → e + Na
2Cl( – ) + 2e →Cl2
Class 10 Chemistry Important Notes
How to Balance the Chemical Reaction :Class 10 Chapter 1 NCERT
Important salts class 10 CBSE sceience notes
Why do calcium and magnesium float on the surface of the water?
Functioning of Soda-Acid Fire Extinguisher
Class 9 Chemistry Important Notes
Evaporation, Vapourization, and Latent heat
How does the water kept in an earthen pot become cold during summer?
What are the factors affecting evaporation?,
What is the difference between solution, colloid, and suspension?
What is the difference between the element and the compound?
Determining Valency, Net Charge and Molecular Formula
Molar mass,molecular mass and mole concept
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution