Average Speed and Average Velocity
Average speed and average velocity-The The speed is defined as the distance per unit time and average speed is defined as total distance covered in per unit of total time or the average rate of covering the total distance. The relationship between total distance, time and average speed is, the total distance is the product of total time taken and average speed. The average speed is the total distance covered per unit time and the average velocity is total displacement covered in per unit time is known as average velocity. The average velocity and average speed both are very important in Dynamics or Kinematics in the calculation of net energy. Before we study in detail what is average speed and average velocity, we are needed to study first what are distance and displacement.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Distance. The total distance covered by an object during its journey is known as distance. The distance is a scalar quantity since it is represented by a magnitude only. The S.I unit of distance is meter.
You can also study related topics
Three Laws of Motion: Class 9 CBSE
How to evaluate recoil velocity of gun
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?
What is second law of of motion ?
What is universal law of gravitational force
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
Displacement. The shortest distance between the initial and final position of an object during its journey is known as displacement. Displacement is the vector quantity since it represented by direction and magnitude. The S.I unit of displacement is meter.
Laptops on very small EMI
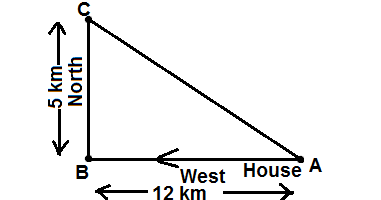
Example. Mohan went 12 km west from his house and then turned 5 km towards the north, show the displacement and the distance covered by him.
The distance covered covered by Mohan is = 12 + 5 =17 km
The displacement is = shortest distance = AC
Triangle ΔABC is the right triangle in which ∠B is the right angle
The displacement covered by Mohan = 13 km
When anything changes its position with respect to time then we say that the thing is in motion. According to the state of motions, it is of two kinds (i) Uniform Motion (ii) Non-Uniform Motion.
(i) Uniform Motion
- A moving car on a busy road.
- A Boy running in the field
(ii) Non-Uniform Motion.
- Moving fan
- Moon around the earth
Distance. The distance is the total distance covered by an object during its travel in a given time.
Displacement. The shortest distance covered by an object during the travel, in other words, the minimum distance from the initial point and final point during the journey of an object.
Average Speed. Per unit of the total distance covered in per unit of the total time is known as average speed.
Average Velocity. Per unit of the total displacement covered in per unit, time is known as average velocity.
Example. Rohit traveled a distance of 24 km through a bicycle in 1 hour and then turned right and traveled 7 km in 10 minutes, find the average velocity and average speed of the bicycle he is cycling.
Solution.
The total distance covered is = 24 + 7 = 31 km
Total time taken = 1 hour + 10 minutes
Therefore average speed is = 26.57 km/h
Total displacement = shortest distance in journey = BC
Total displacement = 25 km
Total time is taken = 7/6 Hr
Hence the average velocity of the bicycle is 21.43 km/h
Science and Maths NCERT solution for Class 9 to 12 class
Example. Ramaswami Lingham went to his school with an average velocity of 6 km/h and returned to his home at an average speed of 8 km/h, find his average speed in his journey?
Solution. Let the distance from his home to school is = x km
His speed from home to school = 6 km/h
Time is taken by him from home to school = x/6
Distance from school to home = x km
His speed from school to home = 8 km/h
Time is taken by him from school to home = x/8
Total time taken in total journey = x/6 + x/8 = 7x/24
∴ The total distance he covered = x + x = 2x km
Therefore the average speed of Ramswami Lingam is 6.86 km/h.
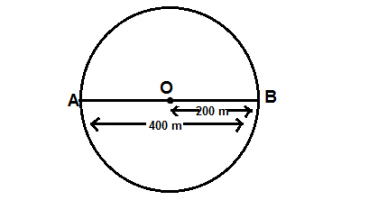
Example. Shyam makes a round of a circular ground in 5 minutes if the radius of the ground is 350 m, find how much distance, displacement, he will cover in 12.5 minutes?
Solution. Distance covered by Shyam in one round of the ground = circumference of the ground = 2πr
Where r is the radius of the ground which is given to us = 350 m
Distance covered in one round = 2 × (22/7) × 350 = 2200 m
Time is taken to cover one round = 5 minutes
Speed = 440 meter/min
Time is given = 12.5 min.
Distance = Speed × Time = 440 × 12.5 = 5500 meter = 5.5 km
In 5 minutes Shyam covers → 1 round
In 1 minute he will cover → 1/5 round
In 12.5 minutes he will cover → 12.5 × 1/5 = 2.5 round
Suppose Shyam starts to move from A then after 2.5 round his position will be at B
The displacement = AB = Diameter of the ground = 400 meter
Important Science Notes for Class 9 and 10 grade
Class 10 CBSE Science Notes
Human reproductive systems of Male & Family
Modes of reproduction used by single organisms-Asexual reproductions
The structure and anatomy of the Heart
Anatomy of the Human brain-Class 10 CBSE
NEET Sylabus and its preparation
Myopia, Hypermetropia and Presbyopia
Human eye structure and its function
Electrical resistance and conductance
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
What is a potential difference across an electric field ?
Why do the star twinkle but planets don’t
Light reflection, refraction, scattering, and dispersion
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Chemistry Practical Based Questions and Answers
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
Chemical properties of Acids and Bases-A note for grade 10 students
What is pH value and its importance in everyday life.
Difference between soaps and detergents
Extraction of metals as per the activity series
Ionic and covalent compounds and the difference between them
Class 9 CBSE Science Notes
Three Laws of Motion: Class 9 CBSE
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat -Class 9 CBSE notes
What is an atom,molecule and atomicity of a substance?
How to determine Valency,net charge of an ion and Molecular formula of a substance.
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
The Complete Detail of Archimedes Principal
Average Speed and Average Velocity: Differences
How to evaluate recoil velocity of gun
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?
Molar mass,molecular mass and mole concept
What is second law of of motion ?
What is universal law of gravitational force
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper and Question Papers for Term-1 and Term 2 2021-22 CBSE Board
Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper Term-1 2021-22 CBSE Board
Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 2 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22 with Solution
Solutions of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard Examination (First) 2021 -22 Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Sample paper of Science 2020
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution