Difference between the homologous and analogous structure of organs
Difference between the homologous and analogous structure of organs
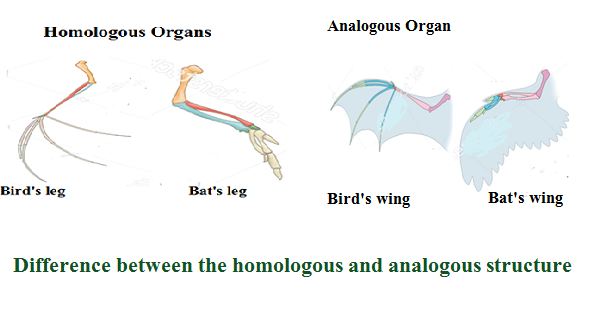
The structures which have the same anatomy, morphology, embryology, and genetics but have different functions are called homologous structures. Structures of organs that look externally similar but don’t have the same function are known as homologous structures. Analogous structures are the structures that perform the same function but these structures are found in the organisms that have different looks, out of these clues scientists conclude that these organisms had different ancestors.
We can work out the evolutionary relationships of the species we see around us. We can do this by identifying hierarchies of characteristics between species. Similarities among organisms allow us to group them and then study the groups. The characteristics of the organisms mark a very basic difference in body design, because of the specialization of cell types and tissues. The more characteristics two species have in common, the more closely they are related, if it is so then more recently they would have a common ancestor.
Structure and Function of Cell : Cell Biology
Human digestive system structure and function
The structure and anatomy of the Heart
NEET Sylabus and its preparation
Modes of reproduction used by single organisms-Asexual reproductions
Anatomy of the Human brain-Class 10 CBSE
Difference between the homologous and analogous structure of organs
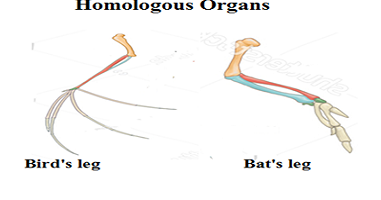
Homologous structures: Homologous is the Greek word, homo means same, and logos mean relation that means originated from the same ancestor. In the descendants, this structure may or may not have the same function. The homologous structures evolved as a result of adaptation to various environments.
The structures which have the same anatomy, morphology, embryology, and genetics but have different functions are called homologous structures. Structures of organs that look externally similar but don’t have the same function are known as homologous structures.
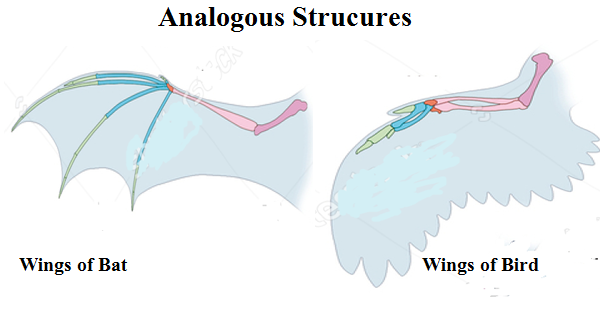
Analogous structures: Analogous is the word that came out from the word analogy which means two different things are adapted to the environment for doing the same thing. Analogous structures are the structures that perform the same function but these structures are found in the organisms that have different looks, out of these clues scientists conclude that these organisms had different ancestors.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Examples of the Homologous structures: The animals with four legs and birds (two legs and two wings), these organisms are tetrapods (animals with four limbs). Four limbs in birds and bats show the example of homologous structures that tell us that birds and bats inherited four limbs from a common ancestor.
Examples of the analogous structures: The wings of the bat and wings of birds are an example of analogous organs since the wings of bat are the cover of the skin stretched between bones of the fingers and arms while birds’ wings consist of features that are extended all along the arms,it shows that bat and the birds got their wings from different ancestors.
Science Notes
Why does the Sun appears reddish in the evening and morning: Complete Detail
What is the difference between virtual and real images?
Image formation by Convex and Concave Lenses
Image formation by Convex and Concave Mirrors
Difference between Convex and Concave lenses
What are the factors affecting evaporation?
How does the water kept in an earthen pot become cold during summer ?
Functioning of Soda-Acid Fire Extinguisher
Structure and Function of Cell : Cell Biology
Archimedes Principle: Complete detail
Average Speed and Average velocity
The universal law of gravitational force
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat
Important salts class 10 CBSE sceience notes
Reflection, Refraction, Dispersion, and Scattering
Determining Valency, Net Charge and Molecular Formula
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted.
Human Eye – Structure and functions
Myopia, Hypermetropia, and Presbyopia
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
Complete detail of electrical resistance and conductance
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board 2020-21
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Important maths notes
Tricks – How to write linear equations
Tricks- How to solve question from algebraic equations
Three ways of solving quadratic equation
Solutions- Specific questions of mensuration
Finding the roots of the polynomial by Complete square method
Technics – Achieving 100% marks in Maths
You can compensate us
Paytm number 9891436286
The money collected by us will be used for the education of poor students who leaves their study because of a lack of money.
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper and Question Papers for Term-1 and Term 2 2021-22 CBSE Board
Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper Term-1 2021-22 CBSE Board
Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 2 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22 with Solution
Solutions of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard Examination (First) 2021 -22 Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Sample paper of Science 2020
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution