Modes of reproduction used by single organisms-Asexual reproductions
When Birth of new generation occures due to the involvement of single parent,then such a reproduction is known as asexual mode of reproduction where new individual is delivered by a solitary parent. The new individual delivered are hereditarily and physically is indistinguishable from one another, i.e., they are identical to their parent.
Asexual reproduction is seen in both multicellular and unicellular life forms. The asexual reproduction doesn’t include any sort of gamete combination and there won’t be any adjustment in the quantity of chromosomes by the same token. Reproduced organism acquires similar genes as the parent, aside from certain situations where there is an opportunity of rare mutation to occur.
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
You can also study
Human digestive system structure and function
Human reproductive systems of Male & Family
Modes of reproduction used by single organisms-Asexual reproductions
The structure and anatomy of the Heart
Anatomy of the Human brain-Class 10 CBSE
NEET Sylabus and its preparation
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
Fission
For unicellular organisms, cell division, or fission., leads to the creation of new individuals. Many different patterns of fission have been observed. Many bacteria and protozoa(amoeba,euglena, paramecium etc) simply split into two equal halves during cell division, it is known as binary fission. Splitted cells are known as daughter cells, these daughter cells are identical to each other and to their parent cell. In organisms such as Amoeba, etc the splitting of the two cells during division can take place in any plane but the division of euglena takes place longitudinally.

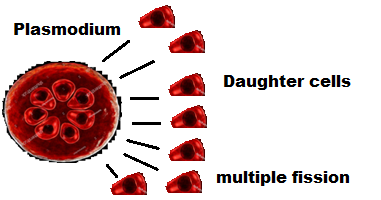
Some of the single-celled organisms, such as the malaria parasite, plasmodium , divide into numerous of daughter cells simultaneously, it is known as multiple fission,each of splitted daughter cells are identical to each other and to their parent cell. Multiple fission also occurs in other single-cell organisms like sporozoans and algae
Fragmentation:
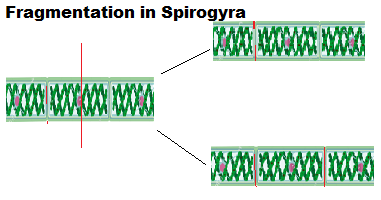
In this mode of asexual reproduction parental body divided into two or more fragments,later each fragment develops into a new individual.In multi-cellular organisms with relatively simple body organization, simple reproductive methods can still work. Spyro Gyra, for example simply breaks up into smaller pieces upon maturation. These pieces or fragments grow into new individuals. The fragmentation of the organism is not possible in other multicellular organisms because they are not simply a random collection of cells. In other multicellular organism has specialized cells organized as tissues, and tissues are organized into organs,so cell by cell division in them is not possible and thus, need to use more complex ways of reproduction.
Regeneration:
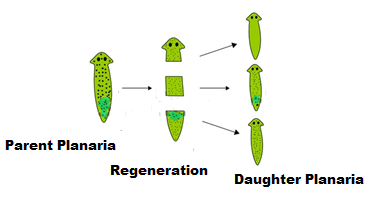
Some of the organism have speialised cells,which can differentiate and grow into new organism,such of the organisms designed in such a way that they are capable to grow new individuals from their body parts, as an example the animal with simple body design Hydra and Planaria can be cut into any number of pieces, and each piece grow into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration. Regeneration in the organism is carried out by specialized cells. These cells proliferated and make a large number of cells. From this mass of cells, different cells undergo changes to become various cell types and tissues. These changes take place in an organized sequence referred to as development.
Budding:
Some of the organism uses regenerative cells and for this buds developed in their body. Each buds develops into a new organism,it is known as budding. In hydra, a bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site.These buds develops into tiny individual and when fully mature.detach from the parental body and become new individuals.

Vegetative Propagation:
Plants can be reproduced under appropriate conditions through their vegetative parts such as roots, stems, leaves, and buds. This property of vegetative propagation is used in methods such as layering or grafting to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses, and grapes for increasing the rate of productivity in agriculture since plants used in vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits faster than those produced from seeds. Such methods are useful in the propagation of plants such as banana, orange, rose, and jasmine that has lost the capacity to produce seeds.

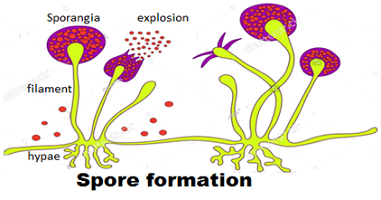
Spore Formation:
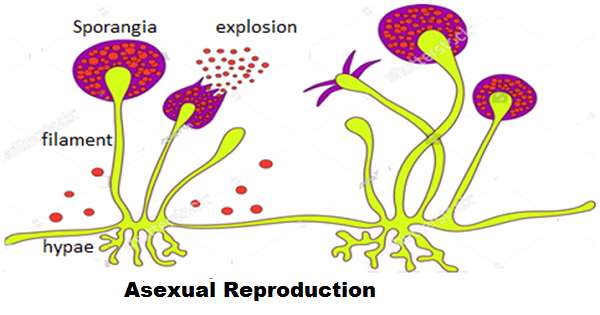
In many multi-cellular organisms, specific reproductive parts are created known as sporangia,it is a tiny blob on a stick structure developed in some of plants, fungi, bacteria, and algae. The sporangia contain reproductive cells known as spores. Spores are covered by thick walls that protect them until they come into contact with another moist surface, the interaction of moist and sporangia leads the sporangia blasted and spores spread in the air, and again when these spores come in contact to a moist surface these can begin to grow into a new individual.
Important Science Notes for Class 9 and Class 10 grade
Class 10 CBSE Science Notes
Class 10 Biology Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board 2020-21
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions and Answers
Class 10 Chemistry Practical Based Questions and Answers
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
Chemical properties of Acids and Bases-A note for grade 10 students
What is pH value and its importance in everyday life.
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted.
Myopia, Hypermetropia and Presbyopia
Human eye structure and its function
Electrical resistance and conductance
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
What is a potential difference across an electric field ?
Difference between soaps and detergents
Why do the star twinkle but planets don’t
Light reflection, refraction, scattering, and dispersion
Extraction of metals as per the activity series
Ionic and covalent compounds and the difference between them
Food chain and food web in an ecosystem
Class 9 CBSE Science Notes
Three Laws of Motion: Class 9 CBSE
Evoporation,Vapourization and Latent heat -Class 9 CBSE notes
What is an atom,molecule and atomicity of a substance?
How to determine Valency,net charge of an ion and Molecular formula of a substance.
Thrust and Pressure : Difference
The Complete Detail of Archimedes Principal
Average Speed and Average Velocity: Differences
How to evaluate recoil velocity of gun
If energy is conserved then why do we need to save it for future generations?
Molar mass,molecular mass and mole concept
What is second law of of motion ?
What is universal law of gravitational force
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
CBSE Class 9-Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 9-Sample paper of science
CBSE Class 9-Unsolved question paper of science 2019
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper and Question Papers for Term-1 and Term 2 2021-22 CBSE Board
Solution of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard 2021-22:Term 2 CBSE Board Exam
Solutions of Class 10 Science Sample Paper Term-1 2021-22 CBSE Board
Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 2 CBSE Board Exam 2021-22 with Solution
Solutions of Class 10 Science Question Paper Preboard Examination (First) 2021 -22 Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 – Question paper of science 2020 with solutions
CBSE class 10 -Sample paper of Science 2020
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE



