Structure and functions of each part of the eye
The human eye is the most sensitive and incredible sense organ among all sense organs because with its help we become able to see beautiful and wonderful colors of the world. We can identify the objects around us to some extent by touch, smell, and sound. It is, however, impossible to detect colors while closing the eyes. The structure of the human eye is almost spherical in shape with a diameter of 2.3 cm. The human eye is just like a camera, its lens system also projects the images on a screen called the retina just like a camera. Here in this post, we have presented a post-human eye-structure and functions of each part which will help you answer each question related to the structure and functions of the human eye.

Structure and functions of each part of the eye
The human eye is made of three chambers, the first chamber is between cornea and iris which is filled with aqueous humor, the second chamber is between iris and crystalline lens and the third chamber is between the crystalline lens and retina which is filled with vitreous humor. Its two main lenses are the cornea and crystalline lens which refracts light rays and focus to the retina where the inverted image is formed, at the exit of the eye the optic nerve gets the signal of the inverted image, this signal transported to the brain than brain deciphers this inverted image to erected image. At the end of the post ‘Human Eye – Structure and functions of each part’ please don’t forget to write your comment that how did you like our this post “Human eye-Structure and function of each part”.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science from chapter 1 to 16
You can also study related topics
Myopia, Hypermetropia and Presbyopia
Why do the star twinkle but planets don’t
Light reflection, refraction, scattering, and dispersion
Human Eye, Structure & Functions
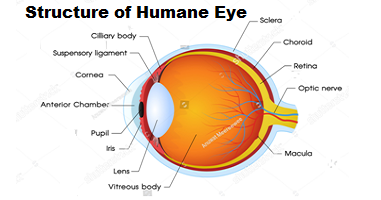
Cornea.
In the structure of the eye, the cornea has a very important role. the cornea is a 5 layered transparent vascular tissue made of collagens and cells, it is the outermost lens of the eye and bulged in shape, light rays, first of all, fall on it and then refracted into the eye. The 65 to 75 % of the total refraction of the light takes place through it.
Aqueous humor.
Aqueous humor is a transparent fluid between cornea and iris and between iris and lens, it is composed of water vitamins, sugars, proteins, and other nutrients. The role of aqueous humor is to nourish the cornea and lense because both of them does not contain blood vessel. The aqueous humor maintains the intraocular pressure of the eye and protects the eye from dust, pollen grains, wind, and microbes.
Iris.
The colored part of the eye is known as iris, it is located between the cornea and crystalline lens. Iris is made of the dark muscular diaphragm made of connective tissue and muscle covered with pigments responsible for the color of the eye, it surrounds the pupil. Iris controls the size of the pupil.
Pupil
The pupil is actually the aperture of the eye, It is an opening at the center of the iris and circular in shape, the function of pupil is to allow light to enter the eye so it can be focused on the retina. It appears black color because the light focused on the retina is completely absorbed by the retina and is not reflected back.
Christine lens
The Christine lens is basically is an eye lens that is transparent and located behind the iris. It is not having blood vessels so it is nourished by aqueous humor that exists between iris and lens. One-third of the total net refraction of light through the eye is taken place by the Christine lens. it is made of small flexible smooth muscles called ciliary muscles, these muscles change the shape of the lens. When we see nearby objects, these muscles constrict and radius of curvature of the lens decreases so that images could be focused on the retina and when we see the far objects these muscles dilate and radius of curvature of lens increases so that images could be focused on the retina, this action of eye is known as accommodation of eye.
Vitreous humor
Vitreous humour is a jelly-like transparent fluid that contains 99% water and it’s 1% is sugar, vitamins, proteins, hyaluronic acids, and collagens. This fluid pressurizes the retina to remain in its place and gives the spherical shape to the eye.
Retina
The retina is located at the back end of the eye, it is made of photosensitive cells called photoreceptors, photoreceptors are of two kinds cones and rods. The rods show us images in dim light or when it is dark, cons show us light during the day time or when light is intense, we see colors of the images because of cons.

Optic nerve.
The images formed in the retina is inverted, the signal of the image is conducted through the optic nerve to the visual cortex of the brain, the image is decoded by the brain and then we see the inverted image as an erected image.
Important Science Notes for Class 9 and 10 grade
Click for online shopping
Future Study Point.Deal: Cloths, Laptops, Computers, Mobiles, Shoes etc
Class 10 Physics Important Notes
What is the difference between virtual and real images?,
Image formation by Convex and Concave Mirrors,
Difference between Convex and Concave lenses,
Why does the Sun appear reddish in the evening and morning: Complete Detail
Reflection, Refraction, Dispersion, and Scattering
Image formation by Convex and Concave Lenses,
Human Eye – Structure and functions
Myopia, Hypermetropia, and Presbyopia
Electric Current and Heating effect of Electric Current
What is a potential difference across an electric field ?
Complete detail of electrical resistance and conductance
Class X Science Important notes of chapter 12-Magnetic effect of electric current-I
Class 10 Physics Viva Voce Questions for CBSE Board 2020-21
Class 10 Chemistry Important Notes
How to Balance the Chemical Reaction :Class 10 Chapter 1 NCERT
Important salts class 10 CBSE sceience notes
Why do calcium and magnesium float on the surface of the water?
Functioning of Soda-Acid Fire Extinguisher
What are Corrosion and Rancidity ?
Chemical properties of Acid and Bases-A note for grade 10 students
What is pH value and its importance in everyday life.
Type of Chemical Reactions with Complete detail
What are the physical and chemical properties of metals?
Extraction of metals as per the activity series
Trends in the property of element from left to right and up to down in the modern periodic table.
Ionic and covalent compounds and the difference between them
What is the difference between the soap and the detergent ?
Class 10 chemistry Viva Voce Questions and Answers for CBSE Board 2020-21
Class 10 Important Biology Notes
What is the importance of hormones?
Male and Female Reproductive System: Complete Anatomy for Grade 10 Students
The structure and anatomy of the Heart
Human digestive system structure and function
What is the difference between the homologous and analogous structure of organs
Modes of reproduction used by single organisms-Asexual reproductions
Anatomy of the Human brain-Class 10 CBSE
Ozone Layer and How it is Getting depleted.
Food chain and food web in an ecosystem
English Grammer
Antonyms and Synonyms Lists for The Preparation of CUET and other Entrance Exams
Download: Antonyms and Synonyms List
Direct and Indirect Narration rules Tenses wise and Sentences wise
Active Voice to Passive Voice Rules
Learn Tenses in English and translate Hindi sentences into English language
Download PDF-Learn Tenses in English and translate Hindi sentences into the English language
Download: PDFActive Voice to Passive Voice rules, tenses wise and sentences wise
You can compensate us by donating any amount of money for our survival
Our Paytm NO 9891436286
NCERT Solutions of Science and Maths for Class 9,10,11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for class 9 maths
NCERT Solutions for class 9 science
NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Half yearly question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10 -Question paper of maths 2020 with solutions
CBSE Class 10-Question paper of maths 2019 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
NCERT Solutions for class 11 maths
| Chapter 1-Sets | Chapter 9-Sequences and Series |
| Chapter 2- Relations and functions | Chapter 10- Straight Lines |
| Chapter 3- Trigonometry | Chapter 11-Conic Sections |
| Chapter 4-Principle of mathematical induction | Chapter 12-Introduction to three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 5-Complex numbers | Chapter 13- Limits and Derivatives |
| Chapter 6- Linear Inequalities | Chapter 14-Mathematical Reasoning |
| Chapter 7- Permutations and Combinations | Chapter 15- Statistics |
| Chapter 8- Binomial Theorem | Chapter 16- Probability |
CBSE Class 11-Question paper of maths 2015
CBSE Class 11 – Second unit test of maths 2021 with solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
chapter 3-Motion in a Straight Line
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
Chapter 1-Some basic concepts of chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
NCERT solutions for class 12 maths
| Chapter 1-Relations and Functions | Chapter 9-Differential Equations |
| Chapter 2-Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Chapter 10-Vector Algebra |
| Chapter 3-Matrices | Chapter 11 – Three Dimensional Geometry |
| Chapter 4-Determinants | Chapter 12-Linear Programming |
| Chapter 5- Continuity and Differentiability | Chapter 13-Probability |
| Chapter 6- Application of Derivation | CBSE Class 12- Question paper of maths 2021 with solutions |
| Chapter 7- Integrals | |
| Chapter 8-Application of Integrals |
Class 12 Solutions of Maths Latest Sample Paper Published by CBSE for 2021-22 Term 2
Class 12 Maths Important Questions-Application of Integrals
Solutions of Class 12 Maths Question Paper of Preboard -2 Exam Term-2 CBSE Board 2021-22
Solutions of class 12 maths question paper 2021 preboard exam CBSE Solution



